异常诊断
最后更新时间:2025-07-09 14:51:24
异常诊断功能为用户的数据库实例提供实时的性能监控、健康巡检、故障诊断,让用户既可以直观地感知数据库实例实时的运行状况,也可以定位实时出现的性能异常。
整体概览
查看诊断信息
1. 登录 DBbrain 控制台。
2. 在左侧导航栏,选择诊断优化。
3. 在上方选择对应的数据库类型和实例 ID,选择异常诊断页签。
4. 在页面右侧选择查看实时或历史诊断信息。

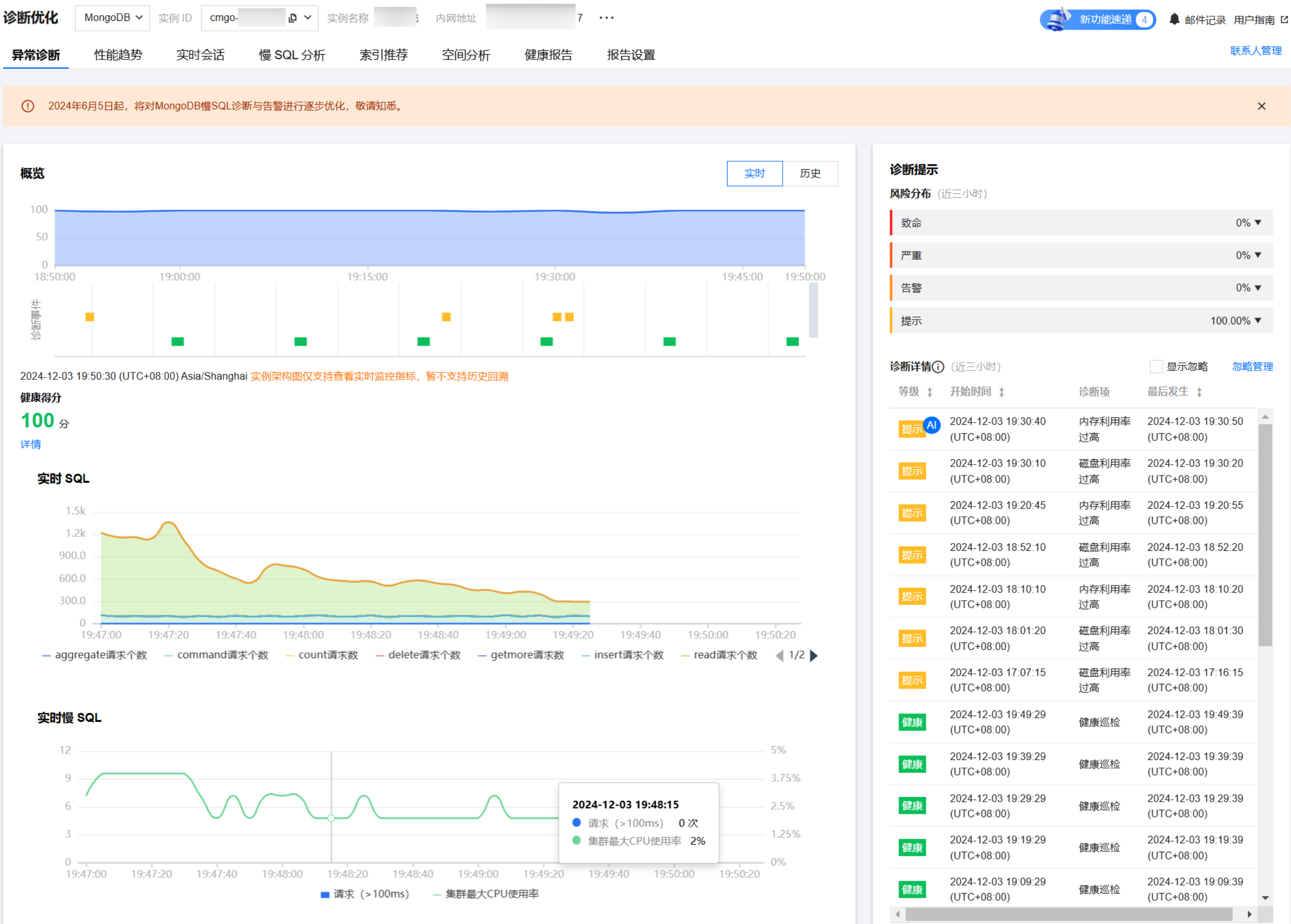
5. 查看时间轴范围内的健康得分趋势图、诊断的异常事件和实例架构图。
查看健康得分趋势图
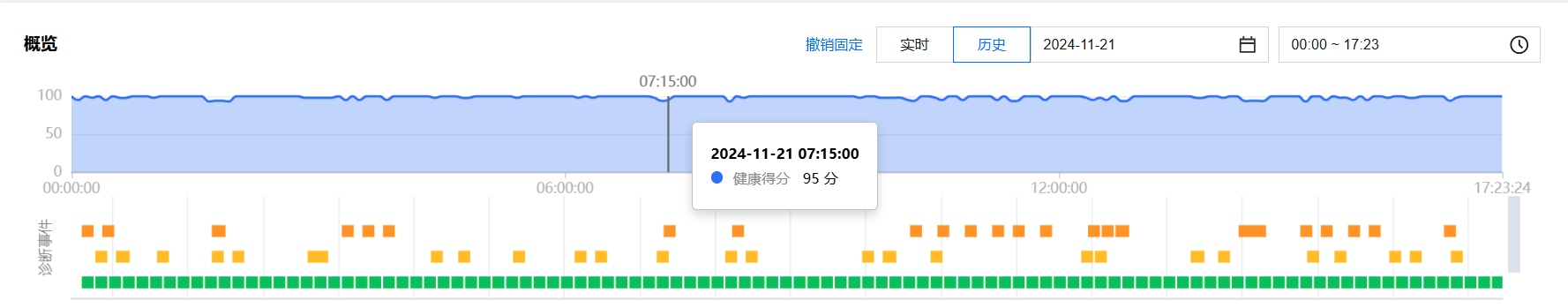
单击趋势图中的任意时间点,显示该时间点的健康得分。

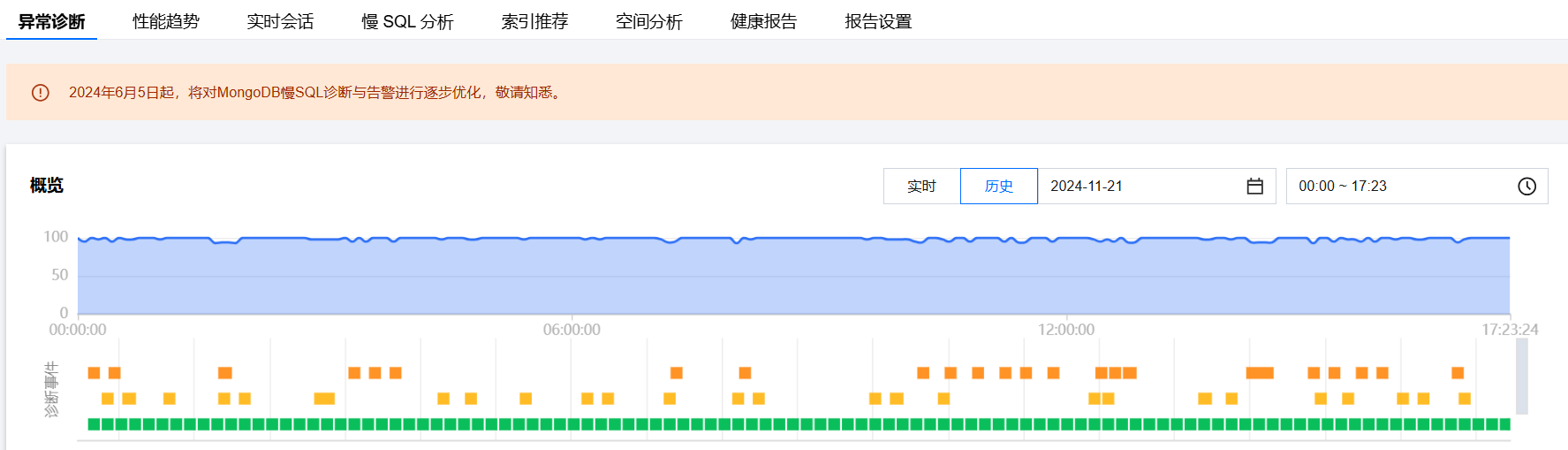
查看诊断事件条形图
将鼠标悬停在诊断事件时间轴上,上下滚动鼠标滑轮,可放大/缩小时间轴范围。


查看健康得分、副本集实例架构图或分片实例的实时 SQL 趋势图和实时慢 SQL 趋势图
说明:
MongoDB 副本集实例:展示健康得分和实例架构图实时数据信息。
MongoDB 分片实例:展示健康得分、实时 SQL 趋势图和实时慢 SQL 趋势图。
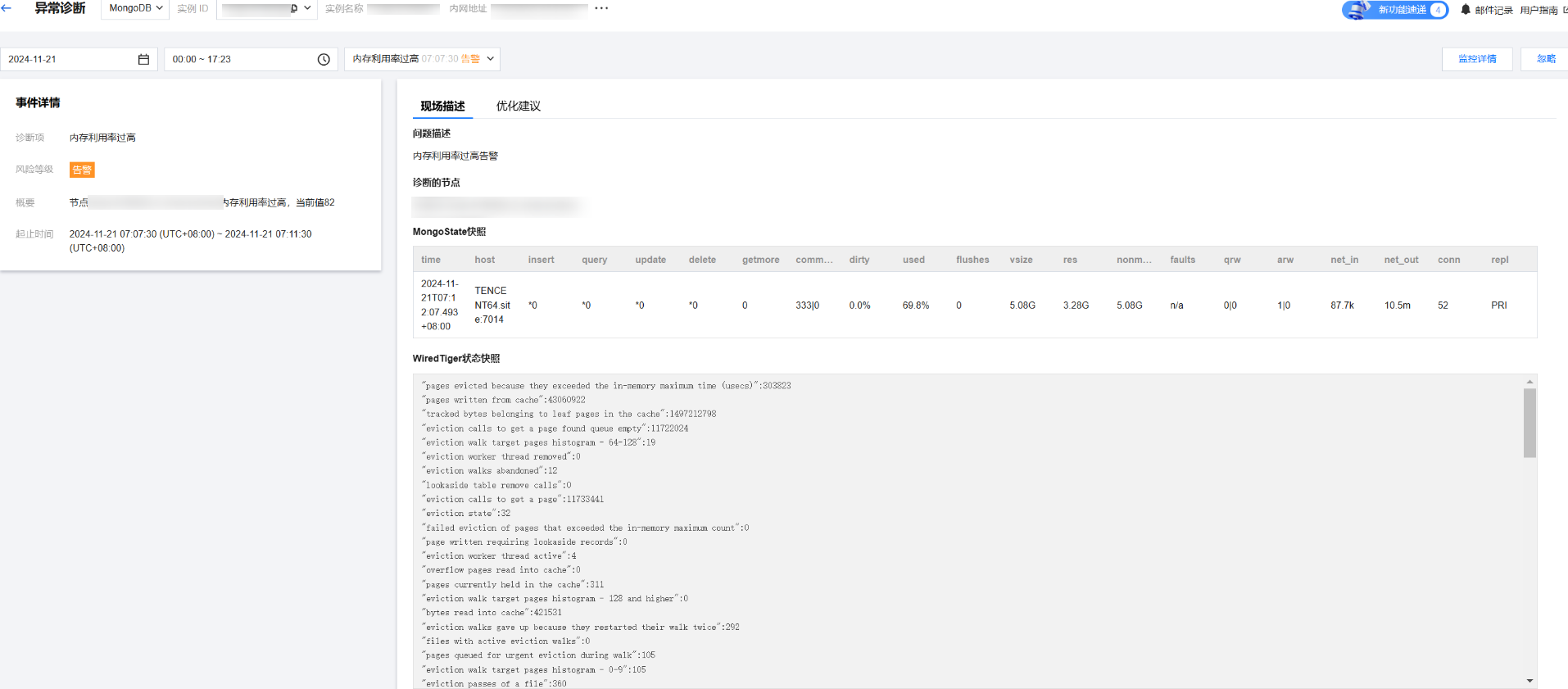
健康得分
展示实时的健康得分。在健康得分下单击详情,可跳转至健康报告页面,查看健康得分、得分详情和健康报告。
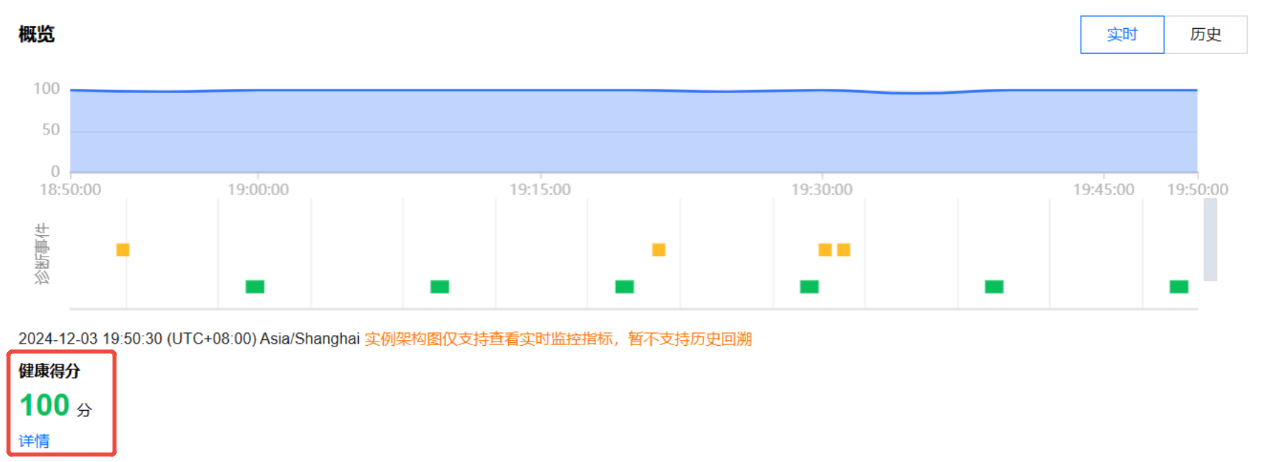

副本集实例架构图
实例的 Proxy 和节点架构、发生告警的节点位置,将鼠标悬浮在对应节点上,鼠标悬停至对应节点或 Proxy 上,可显示对应的指标均值。
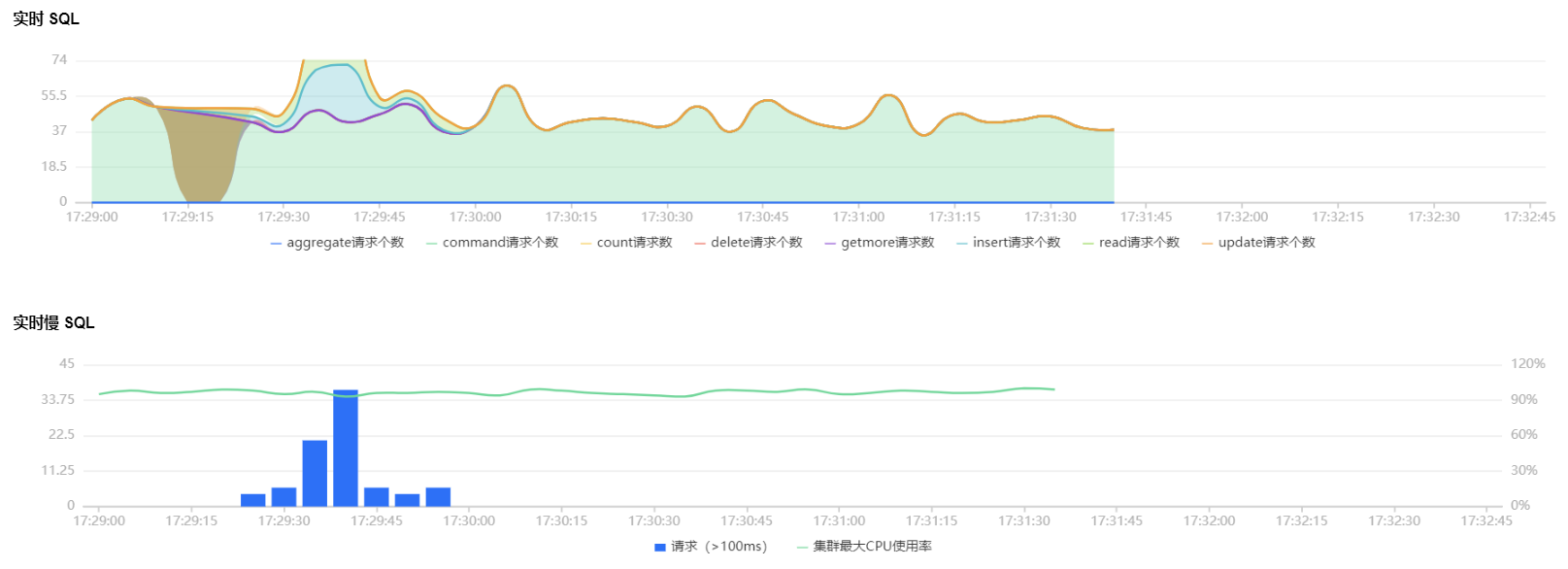
分片实例的实时 SQL 趋势图和实时慢 SQL 趋势图
实时 SQL 趋势图:展示 aggregate、command、count、delete、getmore、insert、read、update 请求个数。
实时慢 SQL 趋势图:展示100ms 以上的请求次数和集群最大 CPU 使用率。
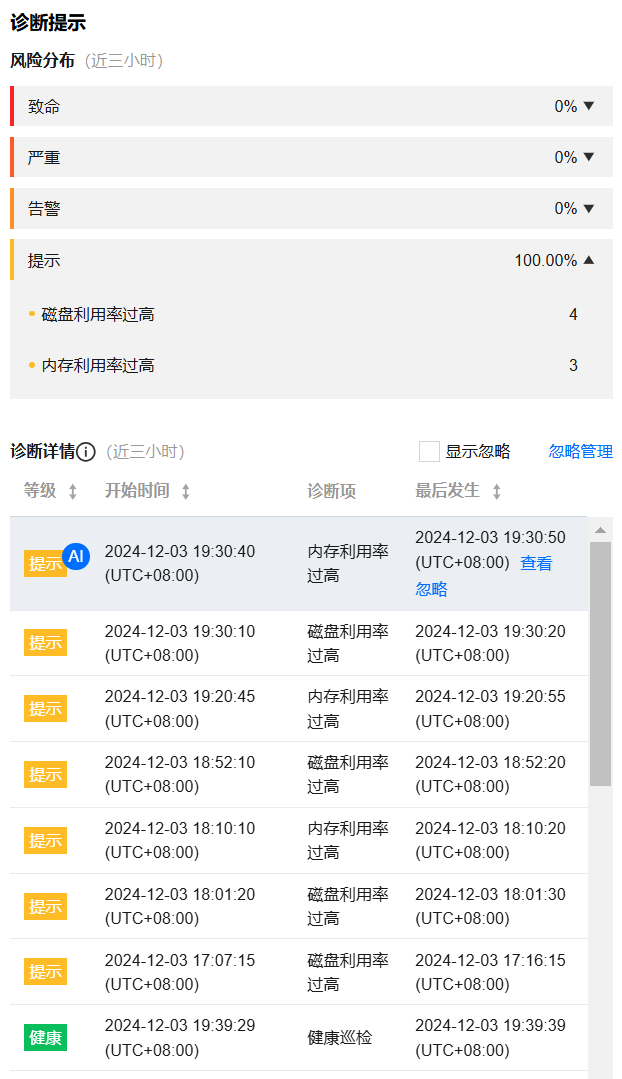
查看诊断提示
诊断事件显示等级分为健康、提示、告警、严重、致命。DBbrain 会定期(每10分钟)的对实例进行健康巡检。
1. 登录 DBbrain 控制台。
2. 在左侧导航栏,选择诊断优化。
3. 在上方选择对应的实例 ID,选择异常诊断页签。
4. 在页面右侧选择查看实时或历史诊断信息。
实时:选择实时,展示近三小时的风险分布和诊断详情。
历史:选择历史,展示已选时间段的风险分布和诊断详情。
5. 查看已选时间范围的诊断提示。

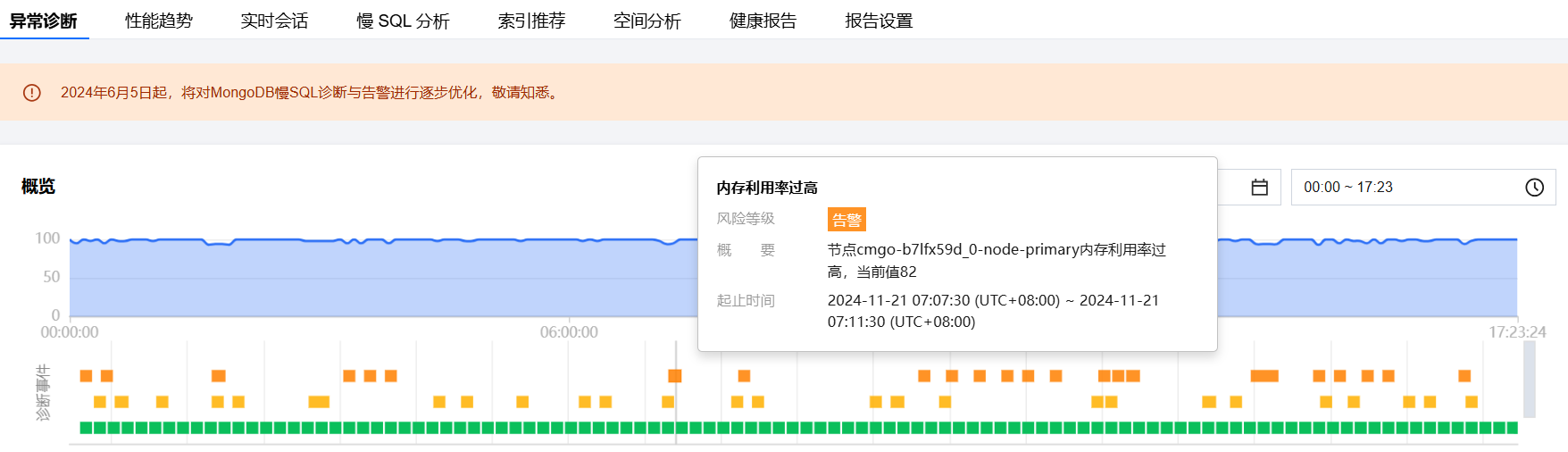
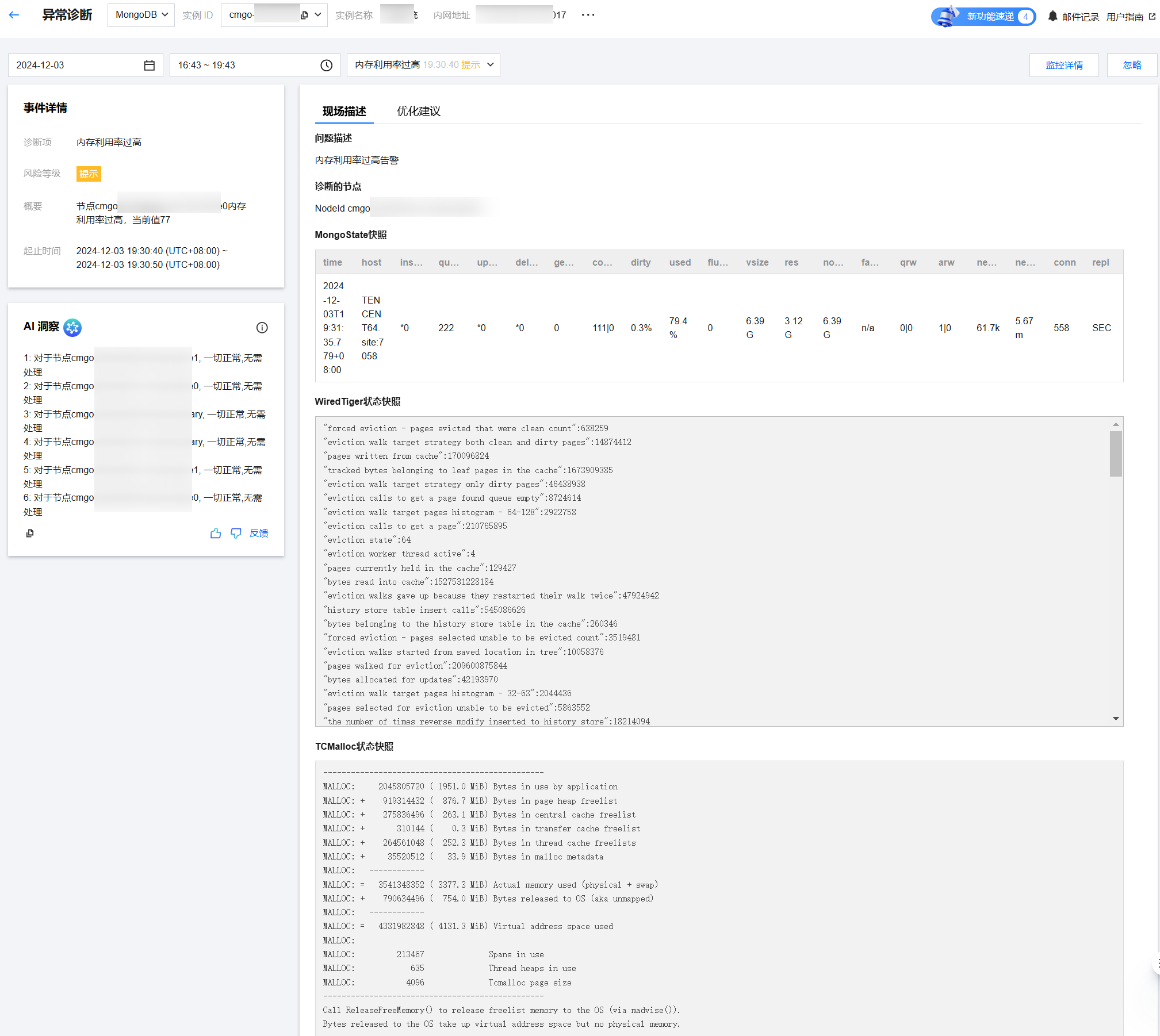
查看诊断事件详情
在诊断详情中,单击具体的事件告警所在行,或者鼠标悬停至事件告警上,单击查看,进入事件详情页面,查看事件详情。
事件详情主要包括事件详情、现场描述、智能分析、优化建议等信息。诊断类型不同展示的事件详情不同,请以实际展示为准。
事件详情:包括诊断项、起止时间、风险等级、概要等信息。
AI 洞察:展示各节点的洞察结果。
现场描述:异常事件(或健康巡检事件)的外在表现现象的快照和性能趋势等信息。
优化建议:给出异常诊断事件的优化建议。
忽略/取消忽略告警
在诊断详情中,鼠标悬停至事件告警上,单击忽略,可选择忽略本条、忽略此类型,单击确定。同时支持在事件详情页忽略告警。
说明:
该功能仅针对诊断项为非“健康巡检”的异常告警。
忽略本条:仅忽略本条告警。
忽略此类型:忽略后,由相同根因产生的异常告警也将被忽略。
已被忽略的诊断事件,将会被置为灰色。若需取消忽略,也可单击取消忽略。
诊断项详细说明
诊断项为智能诊断的项目,其类别包括性能、可用性、可靠性、可维护性四类,每个诊断项仅属于一个类别。
诊断项名称 | 诊断项类别 | 说明 | 风险等级划分 |
节点连通性检查 | 可用性 | 数据库连接异常,无法连接数据库实例 | 致命 |
读等待队列高 | 性能 | 在进行读操作时,等待访问数据库的请求数量较多 | 提示:读等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 1分钟 告警:读等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 10分钟 严重:读等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 30分钟 致命:读等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 60分钟 |
写等待队列过高 | 性能 | 在进行写操作时,等待访问数据库的请求数量较多 | 提示:写等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 1分钟 告警:写等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 10分钟 严重:写等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 30分钟 致命:写等待队列 ≥ 64,且持续时间 ≥ 60分钟 |
连接过多 | 可用性 | 数据库连接数过多 | 提示:70%>连接数利用率 ≥ 60% 告警:80%>连接数利用率 ≥ 70% 严重:90%>连接数利用率 ≥ 80% 致命:连接数利用率 ≥ 90% |
主从延迟 | 可维护性 | 主从节点数据同步延迟过大 | 提示:10分钟>主从延迟 ≥ 1分钟 告警:30分钟>主从延迟 ≥ 10分钟 严重:60分钟>主从延迟 ≥ 30分钟 致命:主从延迟 ≥ 60分钟 |
Oplog 保存时间 | 可维护性 | Oplog 保存时间过长 | 提示:480分钟>Oplog保存时间 ≥ 120分钟 告警:120分钟>Oplog保存时间 ≥ 60分钟 严重:60分钟>Oplog保存时间 ≥ 30分钟 致命:Oplog保存时间<30分钟 |
缓存使用高 | 性能 | 数据库的内存缓存使用率较高 | 提示:WT 缓存使用率超过95%,且持续时间1分钟 告警:WT 缓存使用率超过95%,且持续时间5分钟 严重:WT 缓存使用率超过95%,且持续时间10分钟 致命:WT 缓存使用率超过95%,且持续时间30分钟 |
脏缓存过高 | 性能 | 内存中存在大量未写入磁盘的数据 | 提示:Cache Dirty 超过20%,且持续时间1分钟 告警:Cache Dirty 超过20%,且持续时间5分钟 严重:Cache Dirty 超过20%,且持续时间10分钟 致命:Cache Dirty 超过20%,且持续时间30分钟 |
入流量过高 | 性能 | 数据库接收到的请求或数据流量超过了其处理能力 | 提示:1000MB>节点入流量 ≥ 800MB 告警:1200MB>节点入流量 ≥ 1000MB 严重:1500MB>节点入流量 ≥ 1200MB 致命:节点入流量 ≥ 1500MB |
节点出流量过高 | 性能 | 某个节点(如主节点或从节点)向外部发送的数据流量过大 | 提示:1000MB>节点出流量 ≥ 800MB 告警:1200MB>节点出流量 ≥ 1000MB 严重:1500MB>节点出流量 ≥ 1200MB 致命:节点出流量 ≥ 1500MB |
磁盘利用率过高 | 可用性 | 数据库实例的磁盘使用率接近或达到其最大容量 | 提示:80%>磁盘利用率 ≥ 60% 告警:90%>磁盘利用率 ≥ 80% 严重:95%>磁盘利用率 ≥ 90% 致命:磁盘利用率 ≥ 95% |
内存利用率过高 | 可用性 | 数据库实例的内存使用率接近或达到其最大容量 | 提示:80%>内存利用率 ≥ 70% 告警:90%>内存利用率 ≥ 80% 严重:95%>内存利用率 ≥ 90% 致命:内存利用率 ≥ 95% |
CPU 利用率过高 | 可用性 | 数据库实例的 CPU 使用率接近或达到其最大容量 | 提示:80%>CPU 利用率 ≥ 60% 告警:90%>CPU 利用率 ≥ 80% 严重:95%>CPU 利用率 ≥ 90% 致命:CPU 利用率 ≥ 95% |
节点内存超限 | 可用性 | 某个 MongoDB 实例或节点的内存使用量超过了其配置的限制 | 致命 |
慢查询 | 性能 | 执行时间较长的查询,这些查询可能会影响数据库的性能和响应时间 | 提示:发生慢 SQL,且 CPU 利用率 ≤ 40% 告警:发生慢 SQL,且40%<CPU 利用率 ≤ 60% 严重:发生慢 SQL,且60%<CPU 利用率 ≤80% 致命:发生慢 SQL,且 CPU 利用率 > 80% |
实时活跃会话过高 | 可用性 | 同时连接到数据库的会话数量超过了系统的承载能力 | 提示:100000>活跃会话 ≥ 2000 告警:400000>活跃会话 ≥ 100000 严重:900000>活跃会话 ≥ 400000 致命:活跃会话 ≥ 900000 |
节点 pageheap 内存过高 | 可用性 | 使用的内存量超过了预期 | 通知 |
文档反馈

