开通数据库审计
最后更新时间:2025-10-21 14:30:00
TDSQL MySQL 版具备数据库审计能力,记录对数据库的访问及 SQL 语句执行情况,帮助企业进行风险控制,提高数据安全等级。
开通 SQL 审计服务
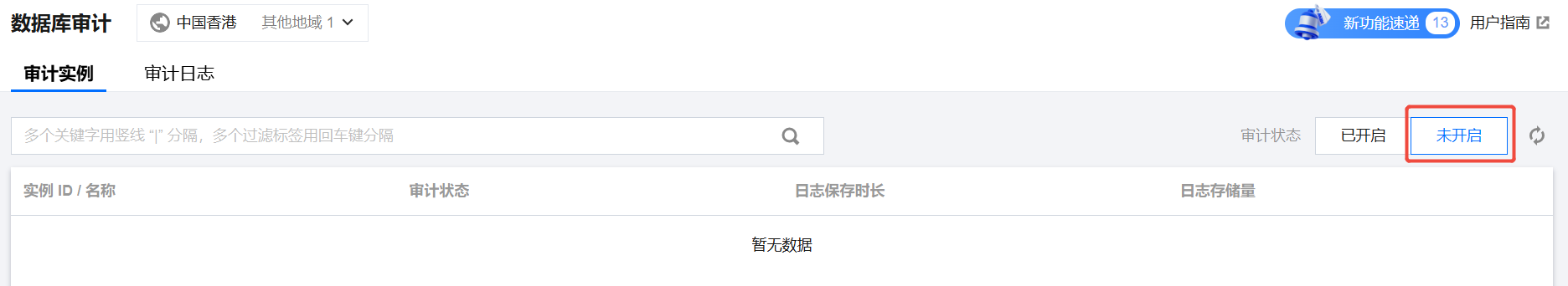
1. 登录 TDSQL MySQL 版控制台,在左侧导航选择数据库审计页,在上方选择地域后,在审计实例页,单击未开启过滤未开启审计的实例。
说明:
或在审计日志页的审计实例处,直接搜索未开通的实例进行开通。
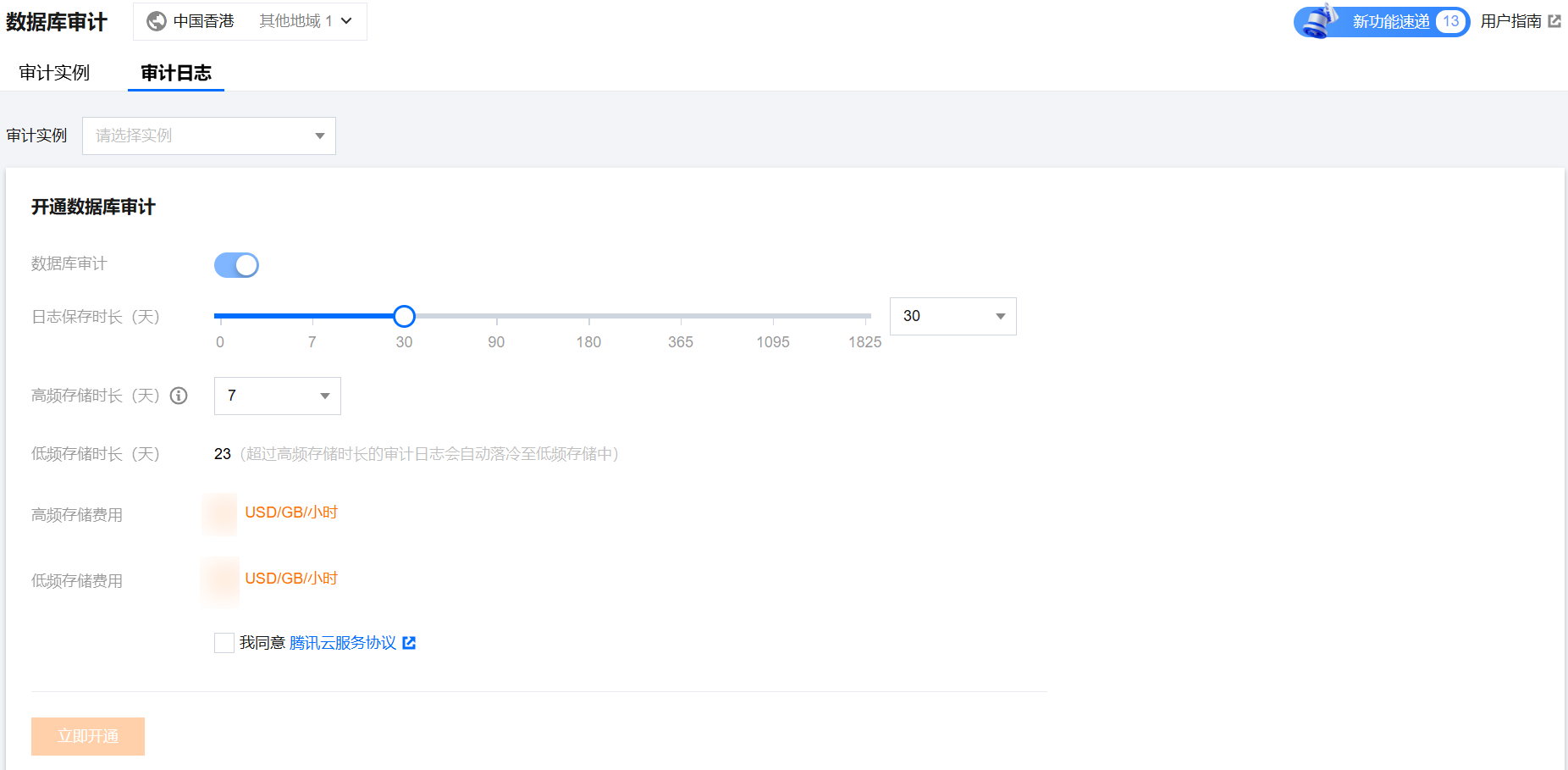
2. 在审计实例页,单击需要开通审计的实例 ID 进入开通页面,勾选同意协议,单击立即开通。
说明:
审计日志保存时长支持选择7天、30天、3个月、6个月、1年、3年、5年。开通完后也可在控制台修改保存时长,请参见 修改日志保存时长。
为保证满足安全合规性对 SQL 日志保留时长的要求,建议用户选择180天及以上的保存时长。
查看审计日志
文档反馈

