Automatic Read/Write Separation Overview
Last updated: 2024-07-22 15:20:14
This document describes the automatic read/write separation feature of the database proxy service in TencentDB for MySQL and its strengths and routing rules.
Automatic Read/Write Separation
Automatic Read/Write Separation
Currently, businesses of many users in the production environment have problems such as more reads and less writes and unpredictable business loads. In application scenarios with a large number of read requests, a single instance may not be able to withstand the pressure of read requests, which even may affect the businesses. To implement the auto scaling of read capabilities and mitigate the pressure on the database, you can create one or multiple read-only instances and use them to sustain high numbers of database reads. However, this solution requires that businesses can be transformed to support read/write separation, and the code robustness determines the quality of business read/write separation, which imposes high technical requirements and has low flexibility and scalability.
Therefore, after creating a read-only instance, you can purchase a database proxy, configure access address policy, and configure the database proxy address in your application so as to automatically forward write requests to the source instance and read requests to the read-only instance. In addition, this method provides natural solutions to other business challenges as detailed below:
Scenarios where the load is unpredictable or fluctuates irregularly with obvious peaks and troughs
In internet business scenarios, business load and access pressure are often unpredictable and unstable, and there will be frequent great fluctuations. If the business uses a large number of non-persistent connections to access the database, it is easy to generate many new connections. In other words, the number of connections between the database and the application is likely to fluctuate as the business access pressure changes frequently, and this is often difficult to predict.
Connection management for the dedicated database proxy allows you to efficiently reuse database connections to appropriately scale applications that handle unpredictable workloads. First, this feature allows multiple application connections to share the same database connection to effectively use database resources. Second, it allows you to adjust the number of open database connections to maintain predictable database performance. Finally, it allows you to delete unusable application requests to guarantee the overall application performance and availability.
Scenarios where the application is frequently connected to and disconnected from the database
Applications built based on technologies such as serverless, PHP, or Ruby on Rails may frequently open and close database connections to process application requests.
The dedicated database proxy can help you maintain a database connection pool to prevent unnecessary pressure on data computing and the memory used to establish new connections.
Scenarios where the database access connection is idle for a long time and is not released
SaaS applications and traditional ecommerce applications may make database connections idle to minimize the response time for user reconnection. You can use the dedicated database proxy to retain idle connections and establish database connections as needed instead of excessively increasing the threshold or providing database services with higher specifications to support most idle connections.
Scenarios where you want to improve the smoothness and stability of database PaaS service failover
With the dedicated database proxy, you can build applications that can tolerate active and passive database failures in an imperceptible manner with no need to write complex failure processing code. The dedicated database proxy will automatically route read traffic to new database instances while retaining the application connections.
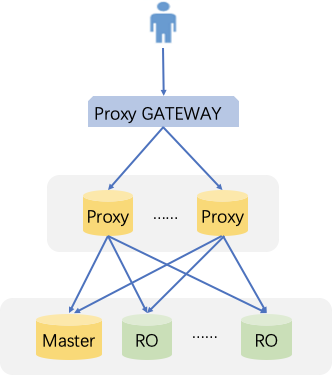
Advantages
Read/write requests are automatically separated with a unified access address.
Native linkage support improves the performance and reduces the maintenance costs.
You can flexibly set weights and thresholds.
Failover is supported, so that even if the database proxy fails, requests can access the source database normally.
When a source instance is switched, or its configuration is changed, or a read-only instance is added/removed, the database proxy can dynamically hot reload the configuration without causing network disconnections or restarts.
Read/Write Separation Routing Rules
Sending to the source instance
DDL statements such as
CREATE, ALTER, DROP, and RENAME.DML statements such as
INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.SELECT FOR UPDATE statement.Statements related to temp tables.
Certain system function calls (such as
last_insert_id()) and all custom function calls.Statements related to
LOCK.Statements after transaction is enabled (including
set autocommit=0).Stored procedures.
Multiple statements concatenated by ";".
KILL (SQL statement, not command).All queries and changes of user variables.
Sending to the read-only instance
Non-transactional read (
SELECT) statements.Sending to all instances
show processlist statement.All changes of system variables (
SET command).USE command.Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

