Cost Performance
Last updated: 2024-07-22 12:50:55
TXRocks has a performance comparable to that of InnoDB; however, its LSM tree structure reduces wastes caused by InnoDB half-full pages and fragments, saving more storage space and delivering an ultra high cost performance.
Background
TXRocks is used in TencentDB products as an important supplement to InnoDB. With a similar performance, it is further optimized and improved to save more storage space. Below is the comparison between the two engines in terms of space usage and performance.
TXRocks Uses Less Space than InnoDB
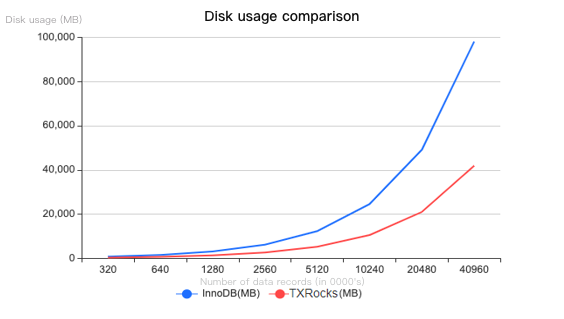
Test scenario: Both storage engines use the default configuration and the default table structure of sysbench. Each table contains 800,000 records, and the total number of tables gradually increases from 4 to 512.
The space usage of TXRocks and InnoDB under the specified test conditions is as shown above. The disk usage is displayed on the Y axis.
As shown in the test data, the greater the data volume, the slower the increase of disk usage by TXRocks, and the higher the storage space utilization of TXRocks (it uses only 42.71% of the space used by InnoDB in the best case). For data records with highly repetitive prefixes, TXRocks has a higher compression rate and storage cost performance.
TXRocks and InnoDB Have a Similar Performance
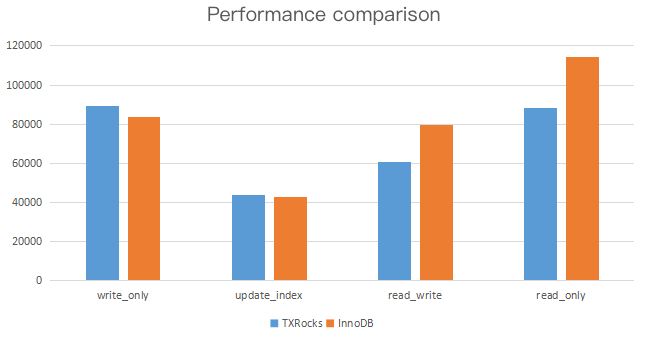
Test scenario: An 8-core 32 GB MEM instance and six tables containing five million rows of data each are used for testing. Each test case is performed after cold instance restart and runs for 1,200 seconds.
The performance comparison between TXRocks and InnoDB under the specified test conditions is as shown above. You can see that TXRocks and InnoDB have a similar performance.
Key parameters in the sysbench command:
sysbench --table-size=5000000 --tables=6 --threads=32 --time=1200
Summary
TXRocks is a TencentDB for MySQL storage engine that has a performance comparable to that of InnoDB but uses less space. It not only guarantees the business performance, but also reduces the storage costs. For more information, see Overview.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

