Use Cases of Custom Commands
Last updated: 2024-11-05 10:22:22
Through VIP encapsulation, Memory Edition (Cluster Architecture) delivers a user experience in cluster mode comparable to the standalone edition, making it much easier for use in different scenarios. However, in Ops scenarios, each node in the cluster needs to be accessed frequently to locate exceptions. In this case, the custom command feature can add a node ID parameter to the parameter list of the original command in the format of
COMMAND arg1 arg2 ... [node ID] in order to easily get the information of the specified node. The node ID can be obtained from the Node Management page in the TencentDB for Redis® console or through the cluster nodes command.Version Description
On proxy agent versions prior to v5.5.0, the node ID is required for the execution of custom commands, but it is unnecessary on v5.5.0 and later.
INFO
This command returns the information and statistics of a server.
Custom command format
info [section] [node ID]
Here, optional parameters can be used to select a specific part of the information:
server: The general information of a Redis server.clients: The information of connected clients.memory: The information of memory usage.persistence: The information of RDB and AOF.stats: The general statistics.replication: The information of master/replica replication.cpu: The information of CPU usage.commandstats: The statistics of Redis commands.cluster: The information of a Redis cluster.keyspace: statistics of databaseOptional parameters can also take the following values:
all: Returns all the information.default: Returns the default information.Sample code
The following example runs the
INFO command with section being server: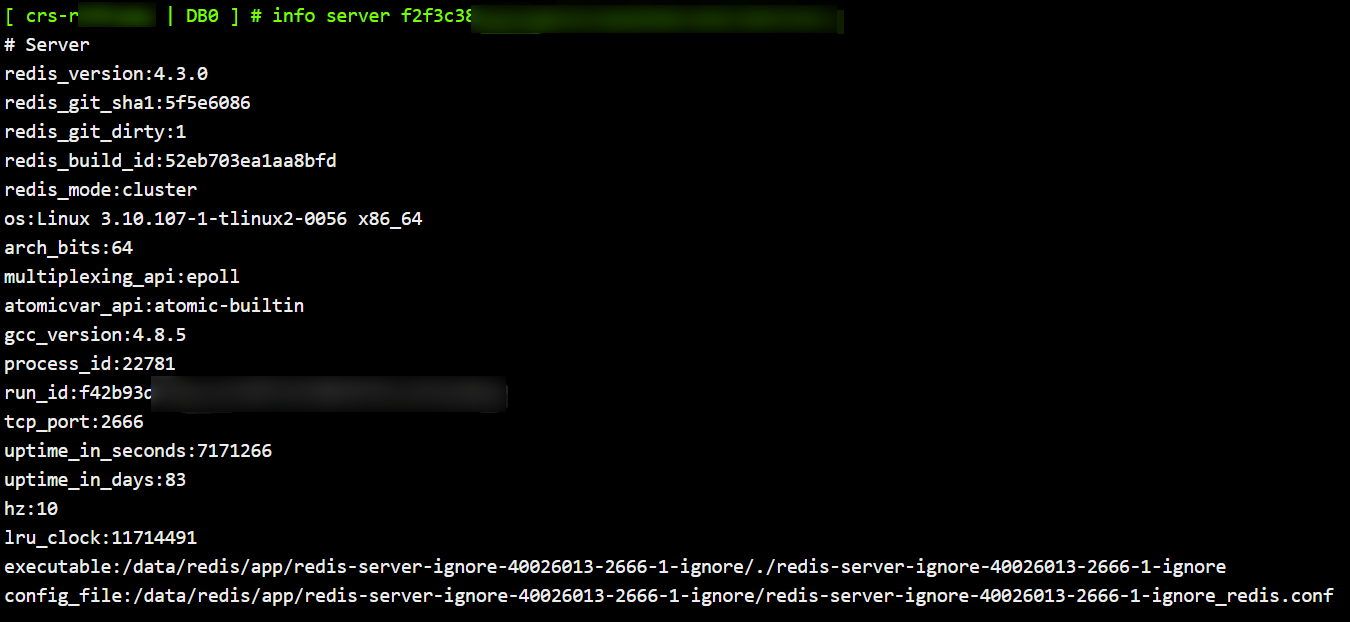
SLOWLOG
This command reads slow logs. It uses
SLOWLOG GET to return the entries in slow logs. You can specify to return only the last N entries and pass other parameters to this command, such as SLOWLOG GET 10.Custom command format
slowlog get [Redis node ID]slowlog get [slow log quantity][Redis node ID]
Sample code
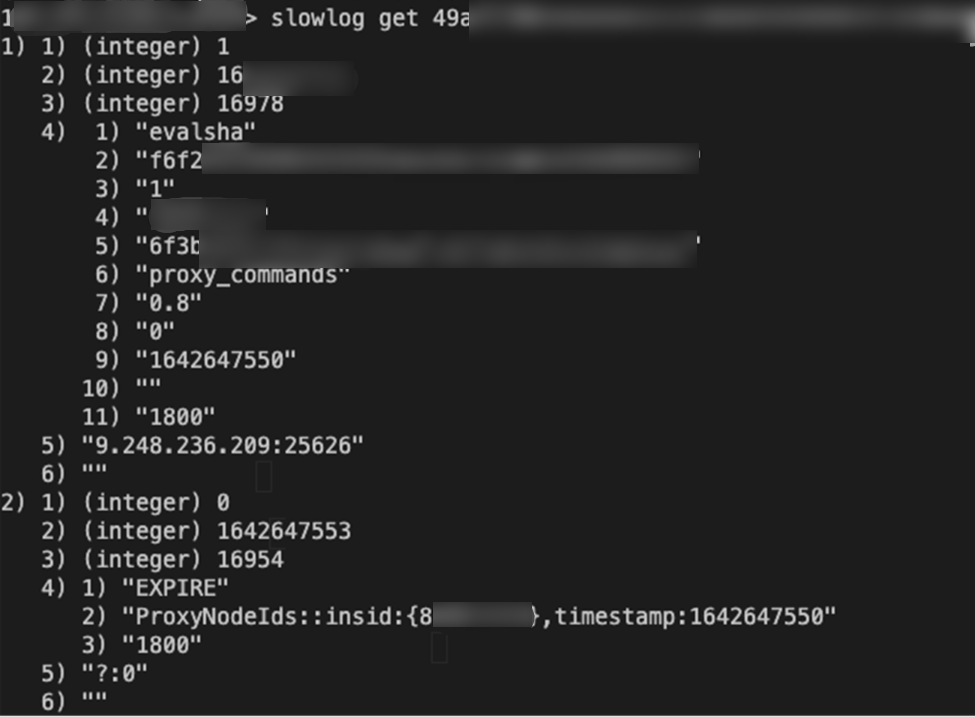
FLUSHDB
This command deletes all keys of the currently selected database. It will never fail.
Custom command format
flushdb [Redis node ID]
Sample code
cd-crs-rhxxxay.sql.tencentcdb.com:24894> flushdb f2f3c387b9fab0e67af02039845c60278b13bed0OK
PING
This command is often used to test whether the connection still exists or to measure the latency.
Custom command format
ping [message] [node ID]
Sample code
[ crs-rh**** | DB0 ] # PING "PONG" f2f3c3************************PONG[ crs-rh**** | DB0 ] # PING "hello world"hello world
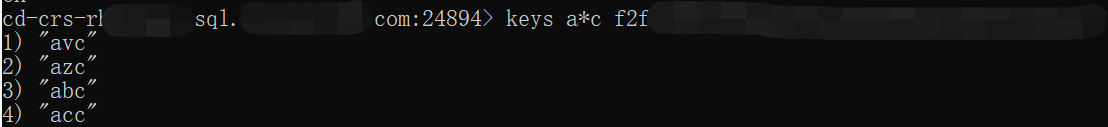
KEYS
This command queries all the matched keys.
Custom command format
keys [pattern] [Redis node ID]
Sample code
keys a* f2f3c3*************************
SCAN
Custom command format
scan cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] [Redis node ID]
Sample code
[ crs-******** | DB0 ] # scan 0 f2f3c3*************************1) "2"
IMonitor
Note:
The iMonitor command requires the Redis proxy version of 5.6.0 or later.
Native Redis does not support the iMonitor command, and redis-cli cannot recognize this command. To execute this command, you should use the telnet tool.
The command needs to be executed on the proxy node, and the parameter is the ID of the Redis shard node.
imonitor [Redis node ID]
Use Cases
imonitor 3dba154c67925520ef1a1e2c41d8cc22d7f4****+OK+1680504260.729707 [0 127.0.0.1:6379] "auth" ******+1680504260.730070 [0 127.0.0.1:6379] "info" "commandstats"+1680504262.243004 [0 127.0.0.1:6379] "AUTH" ******
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

