- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Practical Tutorial
- Message Queue Model
- Message Topic Model
- Migration Description
- Solutions and Cases
- API Documentation
- SDK
- Service Level Agreement
- Glossary
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Practical Tutorial
- Message Queue Model
- Message Topic Model
- Migration Description
- Solutions and Cases
- API Documentation
- SDK
- Service Level Agreement
- Glossary
The close collaboration between leading third-party mobile finance payment solution providers such as SwiftPass and WeChat Pay promotes the use of WeChat Pay among brick-and-mortar stores in various industries, which helps reduce the need of cash payments and improve the payment efficiency. The main architecture of the payment system is as follows:
When a user submits a payment request at a convenience store (such as 7-Eleven) to WeChat Pay, WeChat Pay will return an ACK after confirming the request.
After the returned ACK is confirmed, WeChat Pay will deliver a successful order payment message to SwiftPass, describing the account information, time, amount, and device information of that transaction.
SwiftPass writes the message details to CMQ for temporary storage. The successful order payment message will be used as an important credential for settlement between SwiftPass and the merchant (i.e., the convenience store); therefore, it must be reliably delivered with guaranteed arrival.
The order payment message in CMQ will be returned to the server of the merchant (i.e., the convenience store), which can be async since it does not need to be in real time. Specifically, it will be written to a queue, pulled by an HTTP proxy, and then sent to the merchant after being fetched out.
Before CMQ is connected, if SwiftPass fails to notify the merchant, it will initiate a new request to WeChat Pay which then will deliver the same order payment message to SwiftPass. After CMQ is connected, from WeChat's perspective, the success rate of SwiftPass' system is greatly improved, and its rating (reliability and credibility) in WeChat system will be increased.
Finally, all order payment messages will be continuously delivered by another topic to the risk management, campaign management, and promotion campaign systems. For example, the risk management system will continuously analyze the order payment conditions in each message delivered by the topic. If the transaction amount of merchant A soars in a short period of time (suspiciously fake orders), the callback API will be used to prohibit subsequent transactions for merchant A.
Please see the following figure: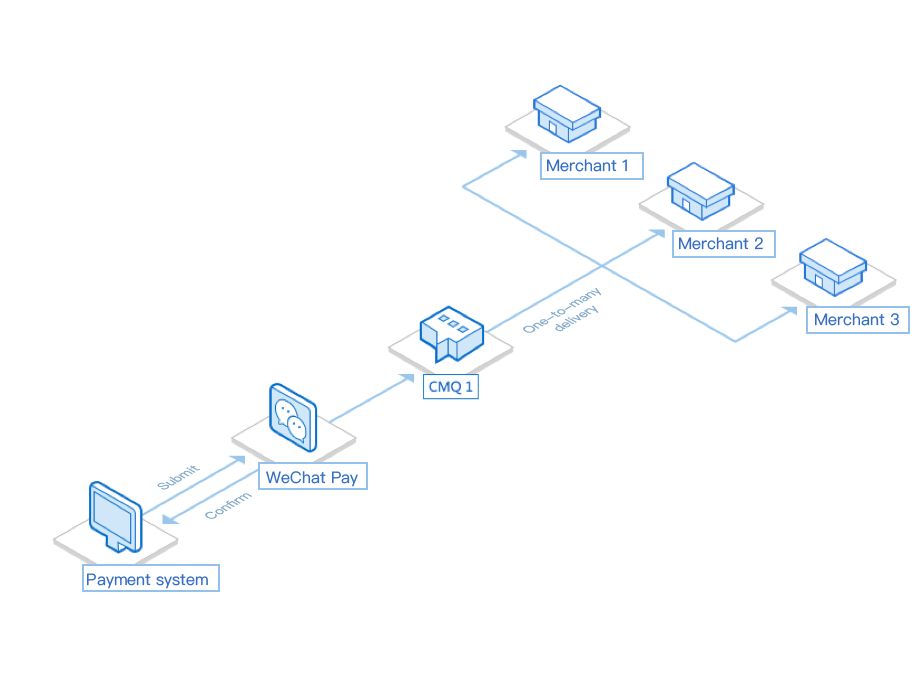

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?