このページは現在英語のみで、表示されている言語を準備しています。
关闭
TDSQL-C for MySQL
- Service Agreement
- TDSQL- C ポリシー
ドキュメントTDSQL-C for MySQL
Enabling Audit Service
最終更新日:2024-12-18 16:20:31
Enabling Audit Service
最終更新日: 2024-12-18 16:20:31
TDSQL-C for MySQL provides database audit capabilities to help you record accesses to databases and executions of SQL statements, so you can manage risks and improve the database security. This document describes how to enable the audit service in the console.
Prerequisite
Directions
1. Log in to the TDSQL-C for MySQL console.
2. On the left sidebar, click Database Audit.
3. After selecting a region at the top, click on Audit Status on the Audit Instance page, and select the Disabled option to filter instances that have not enabled audit.
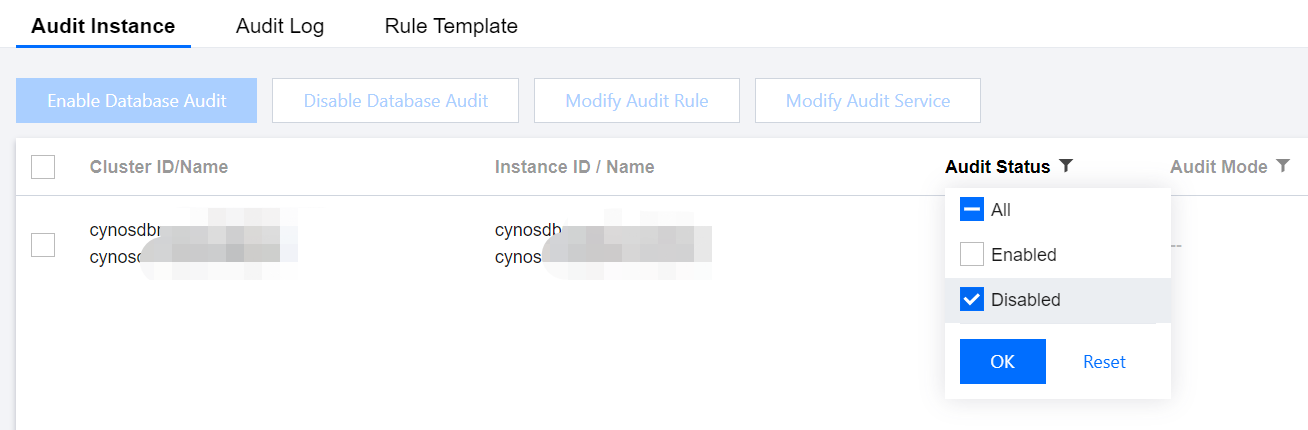
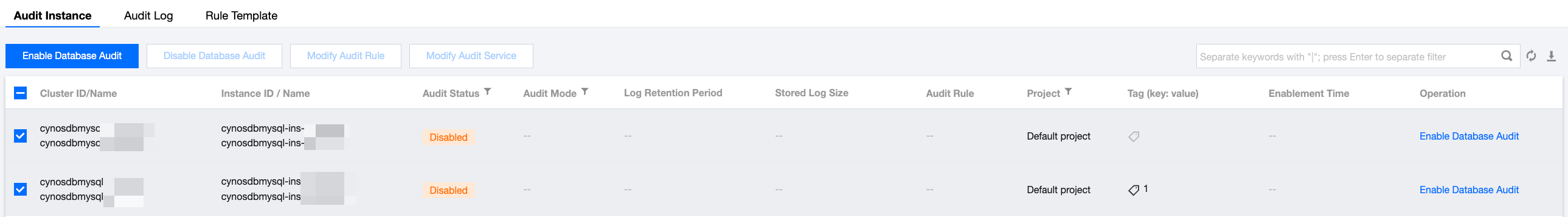
4. Find the target instance in the audit instance list, or search for it by resource attribute in the search box, and click Enable Database Audit in the Operation column.
Note:
You can batch enable the audit service for multiple target instances by selecting them in the audit instance list and clicking Enable Database Audit above the list.
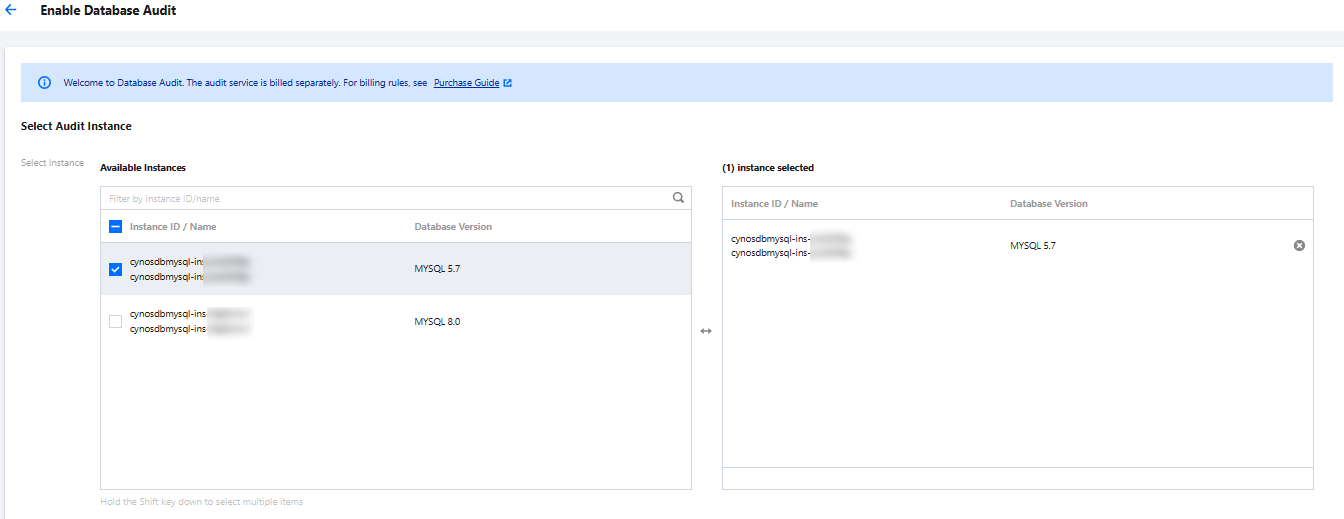
5. On the Enable Database Audit page, configure Select Audit Instance, Audit Rule Settings, Configure Audit, read and indicate your consent to the Tencent Cloud Terms of Service, and click OK.
5.1 Audit instance selection
In the Select Audit Instance section, all instances selected in Step 4 are selected by default. You can select other or more target instances in this window or search for target instances by instance ID/name in the search box. Then, set the audit rule.
5.2 Audit Rule Settings
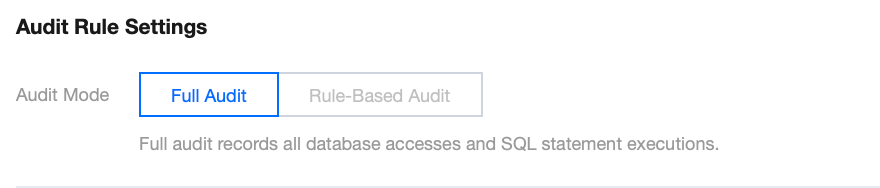
In the Audit Rule Settings section, select Full Audit or Rule-Based Audit. Their differences are as detailed below:
Parameter | Description |
Full Audit | Full audit records all database accesses and SQL statement executions. |
Rule-Based Audit | Rule-based audit records the access to the database and the execution of SQL statements based on the customized audit rules. |
When the audit mode is set to Full Audit, you can perform the following operations.
Select an existing rule template or create a rule template. For more information, see Create Rule Template.
Note:
You can apply up to five rule templates, with an OR relationship between different rule templates.
The rule template is designed for instances of Full Audit mode. It is used only for risk level and alarm policy settings of the audit logs that match the rule content in the template. Audit logs that do not match the rule content are still retained.
When the audit mode is set to Rule-Based Audit, you may select an existing rule template from the rule template or create a rule template. If an existing rule template from the rule template is chosen, you can directly proceed to the audit service settings. If there is no suitable rule templates in the rule template, you can refresh after creating a rule template, and then select the created one. For more information, please refer to create rule template.
Note:
You may apply up to five rule templates, with the relationship between different rule templates being "or".
The rule template is designed for instances of Rule-Based Audit mode. It is used for log retainment and risk level and alarm policy settings of the audit logs that match the template rule content. Audit logs that do not match the rule content are no longer retained.
5.3
Audit service settings
In the Configure audit section, set the audit log retention period as well as frequent and infrequent access storage periods, read and indicate your content to the Tencent Cloud Terms of Service, and click OK. 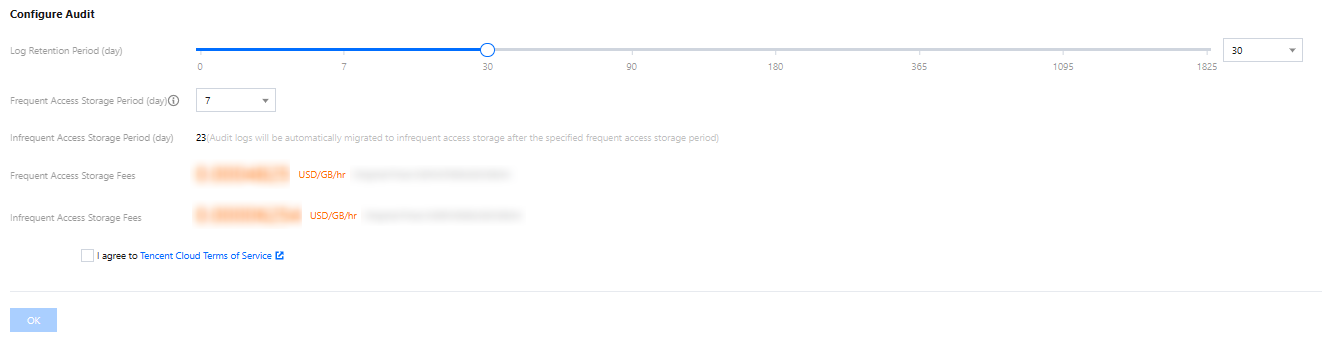
Parameter | Description |
Log Retention Period | The audit log retention period in days, which can be 7, 30, 90, 180, 365, 1,095, or 1,825 days. |
Frequent Access Storage Period | Frequent access storage has the best query performance as it uses ultra high-performance storage media. Audit data is initially stored in frequent access storage for the time period specified here, after which it is automatically migrated to infrequent access storage. These two storage types only differ in performance but both support auditing. For example, if the log retention period is set to 30 days, and frequent access storage period is set to 7 days, then the infrequent access storage period will be 23 days by default. |