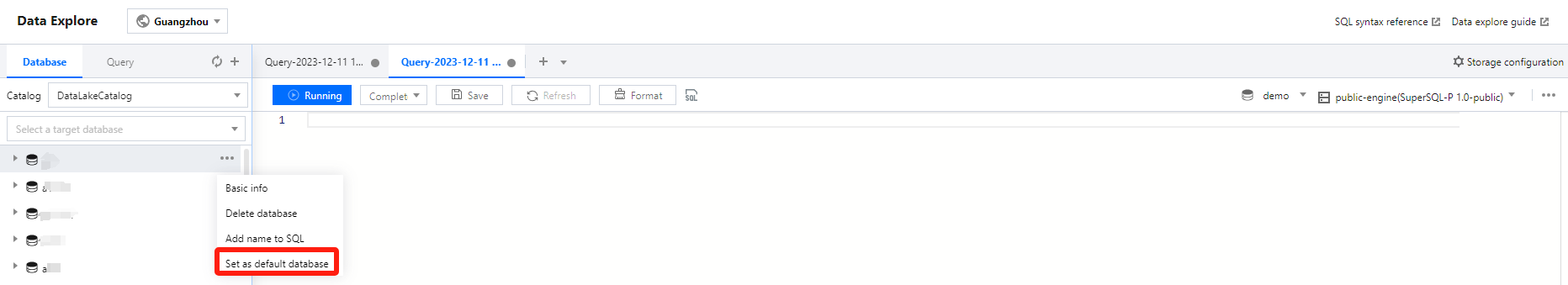
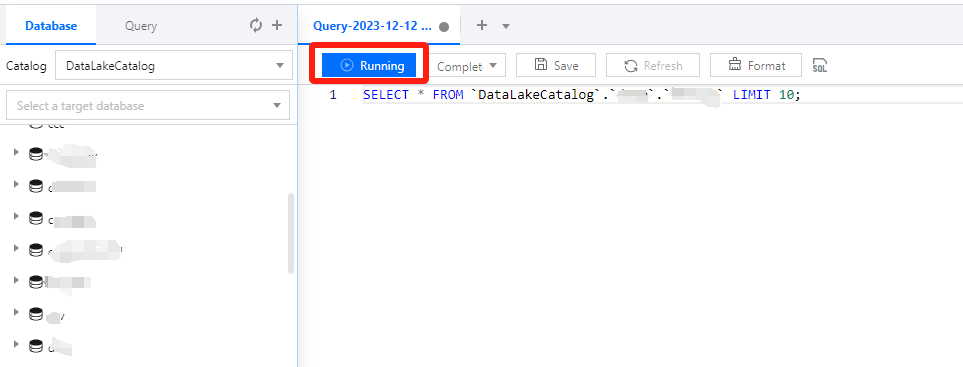
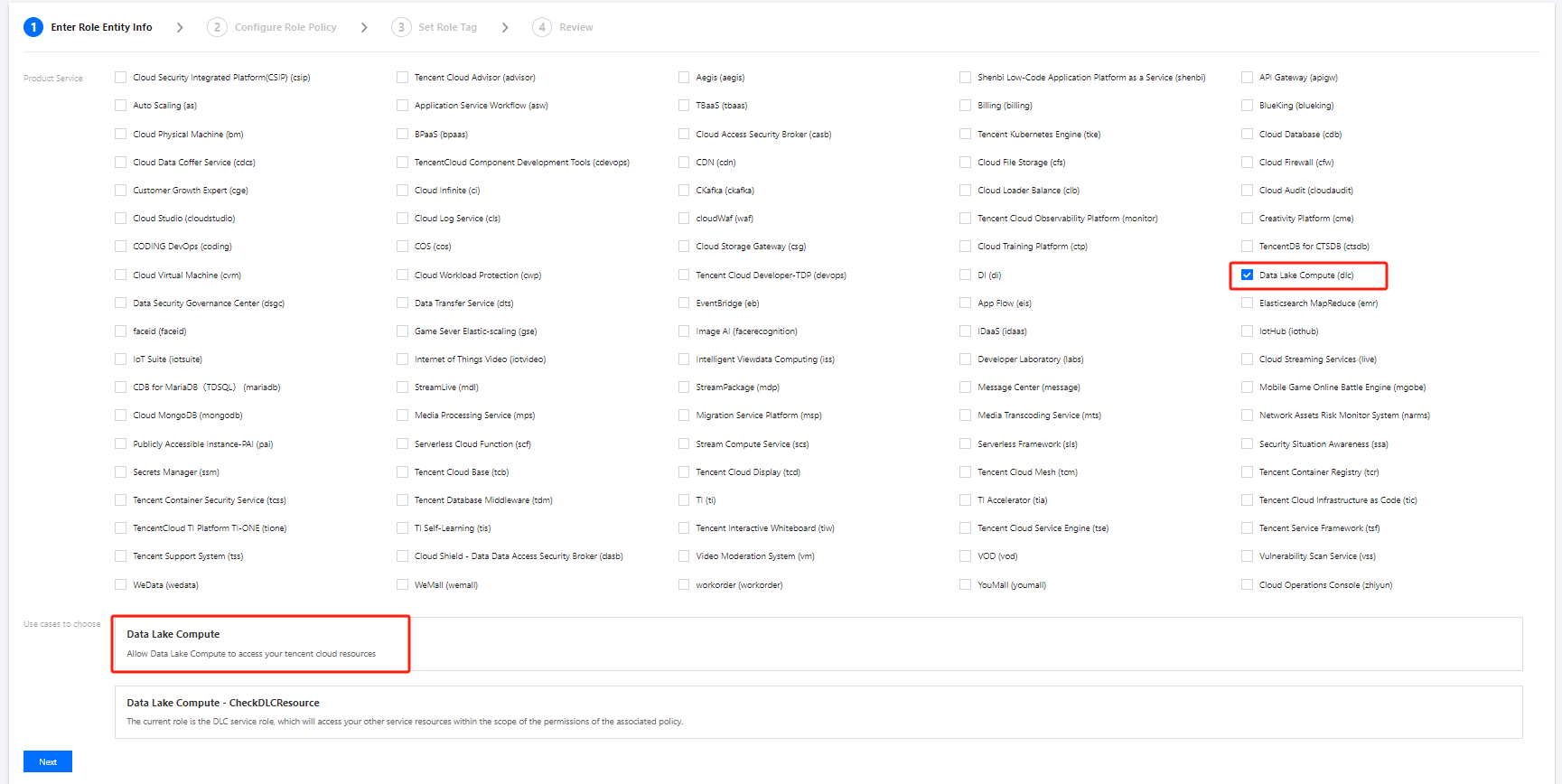
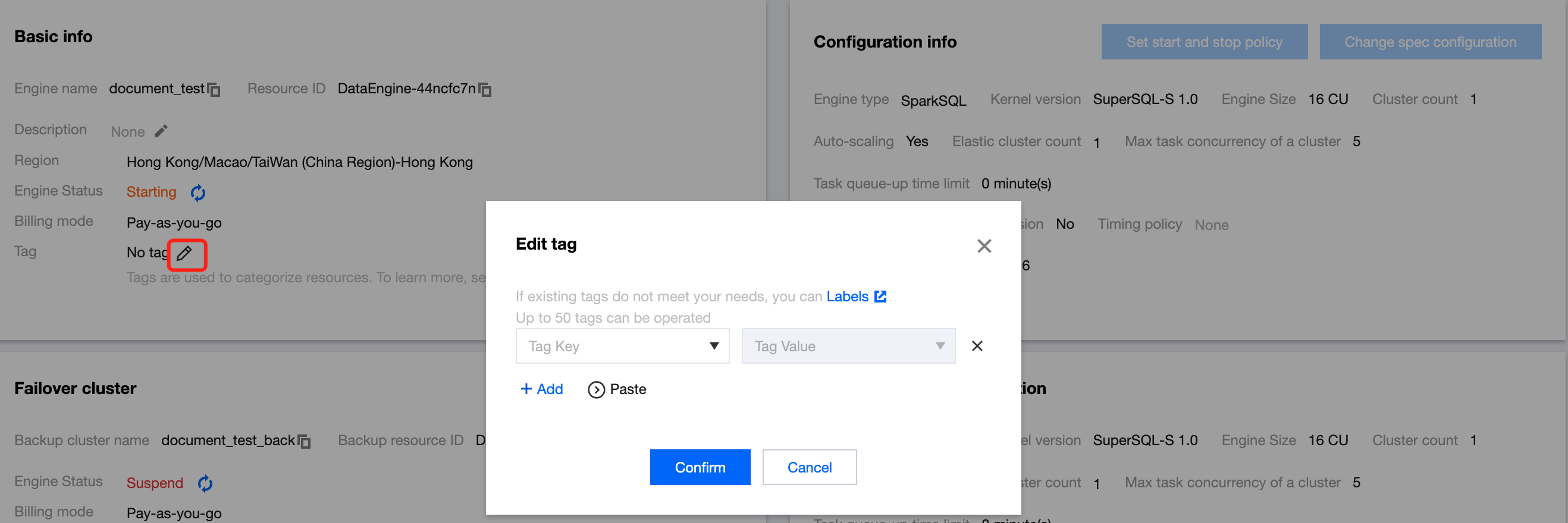
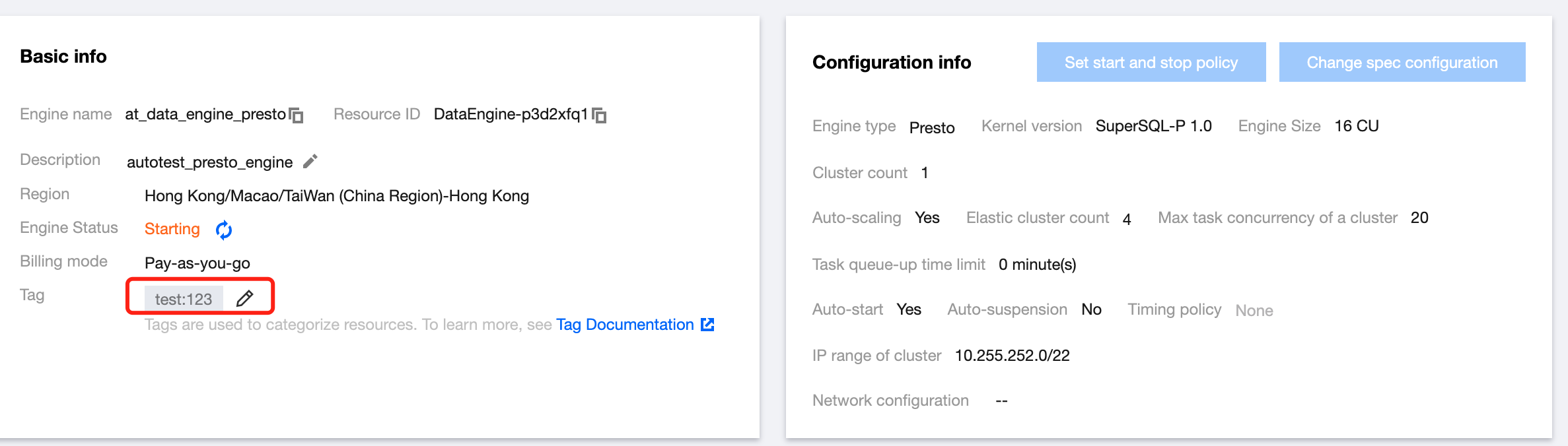
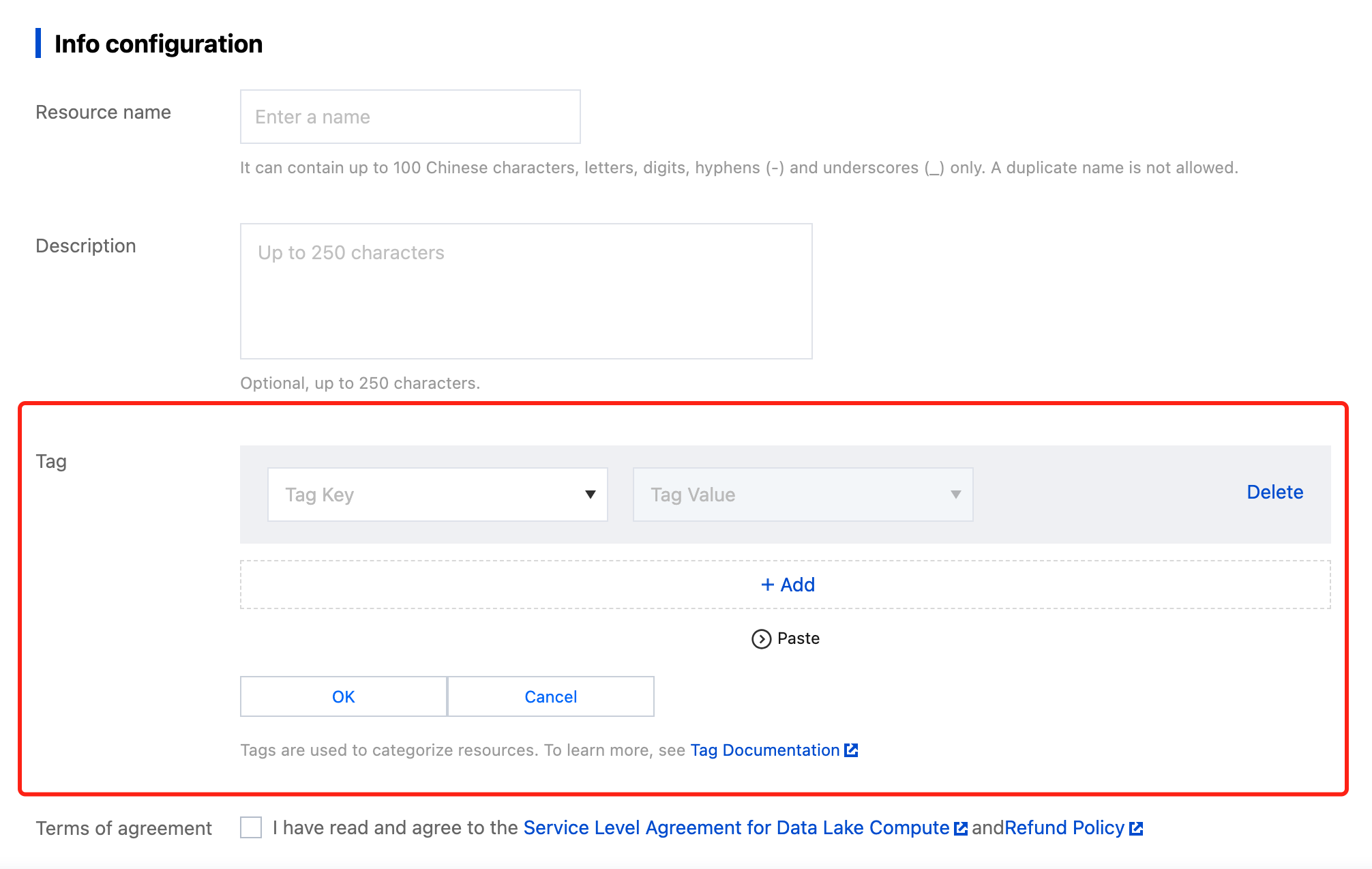
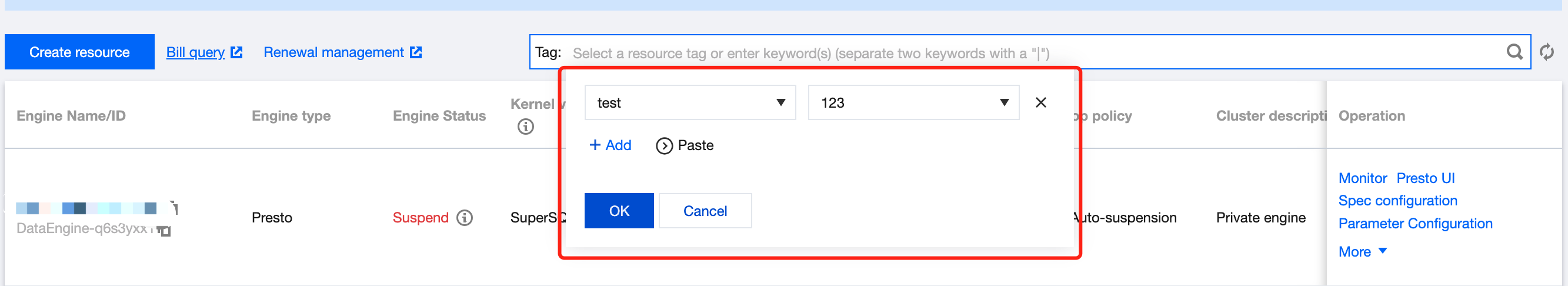
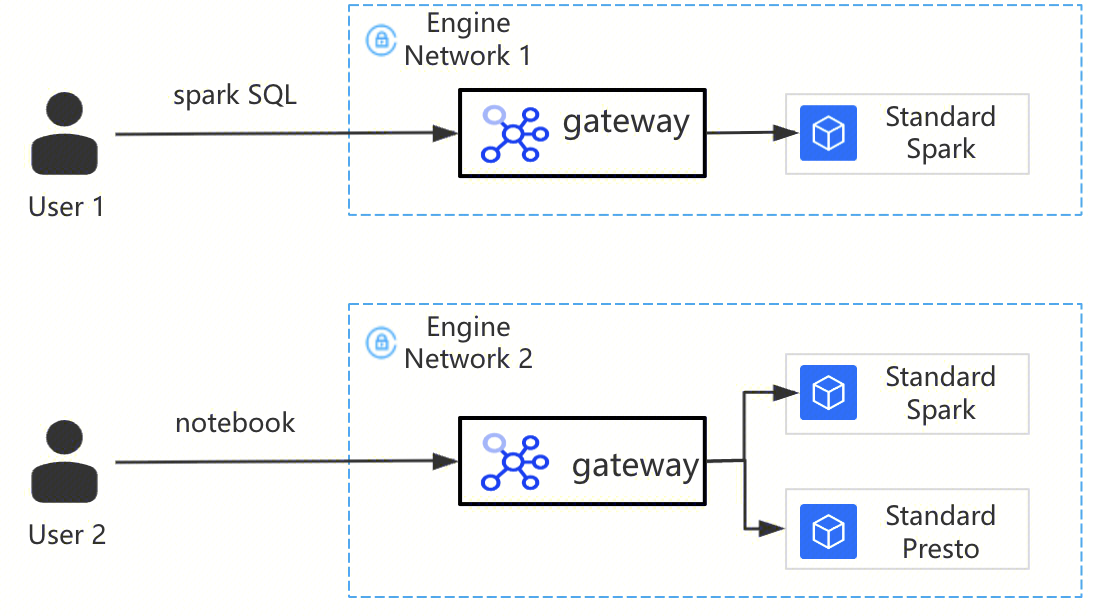
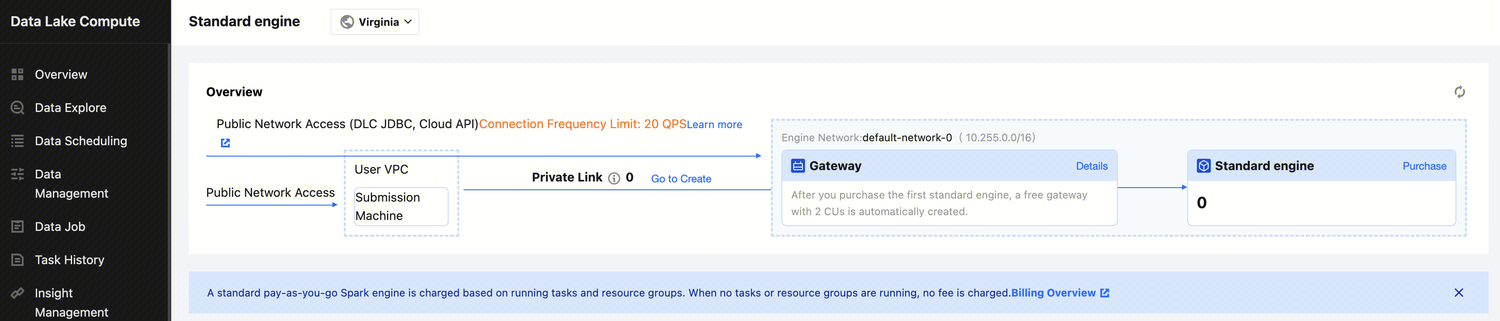
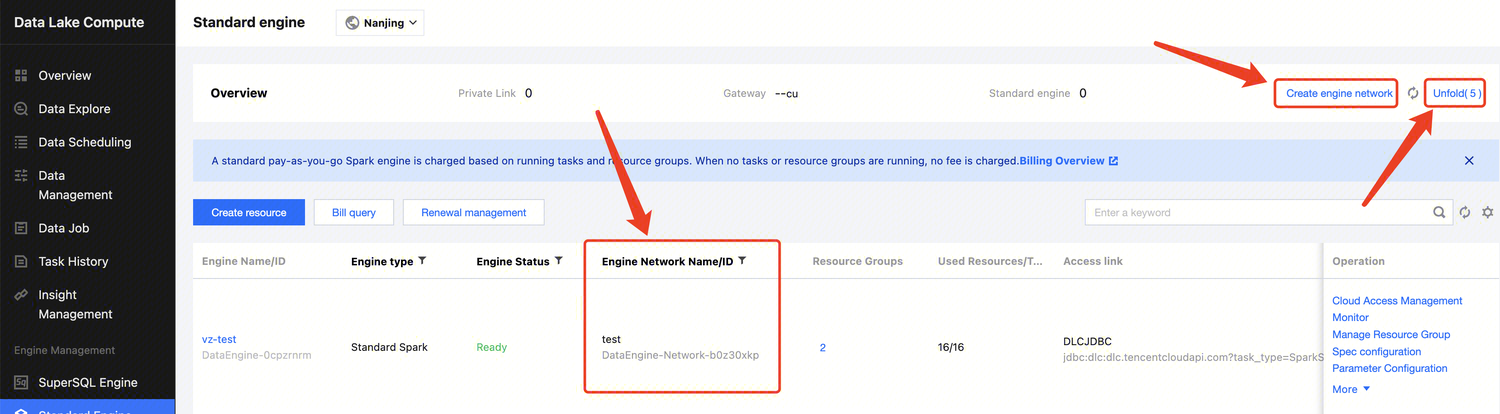
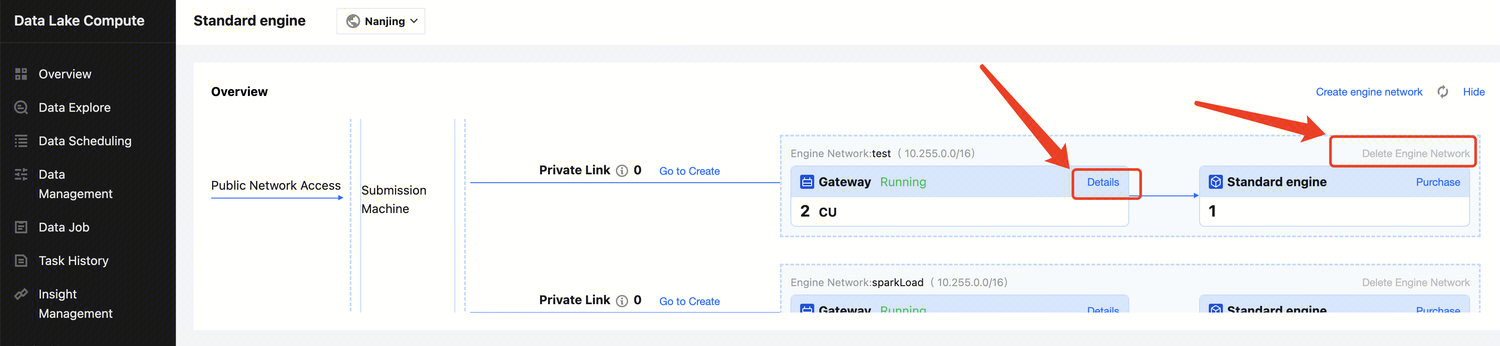
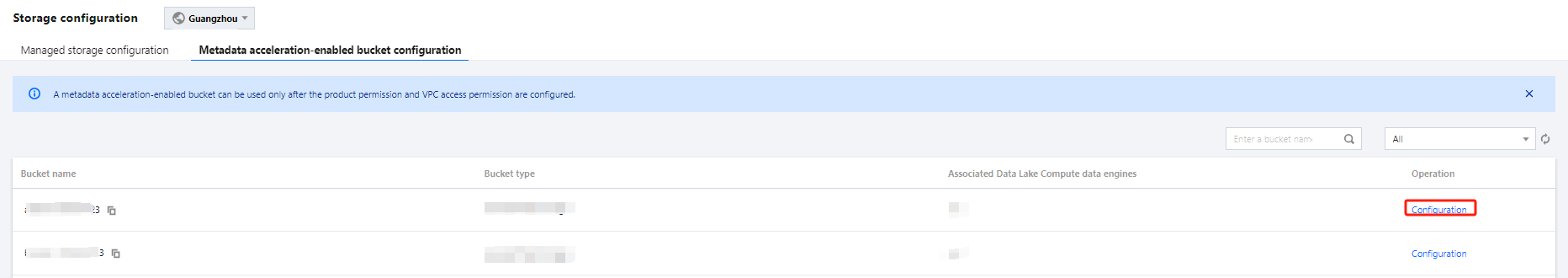
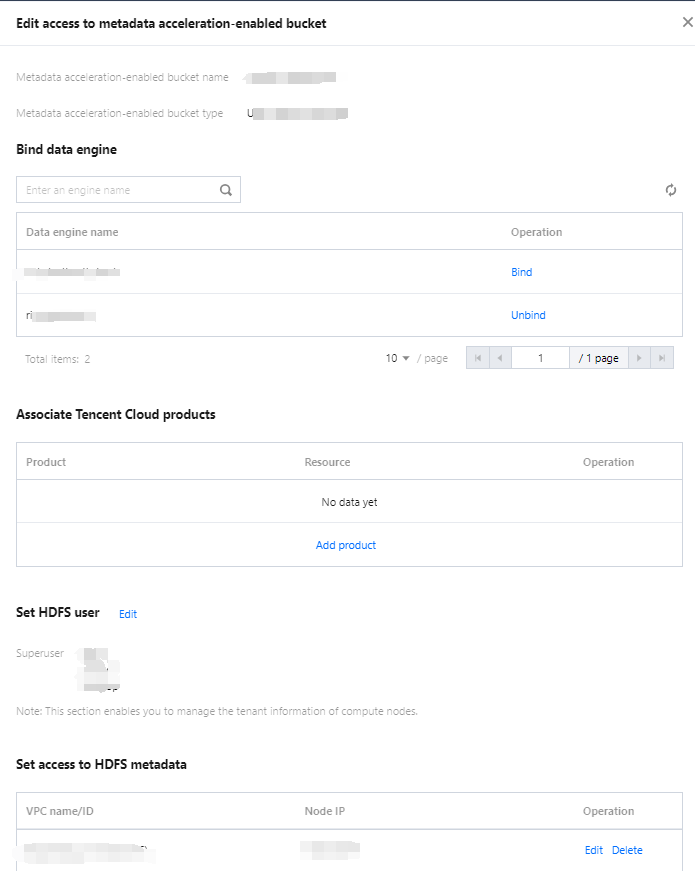
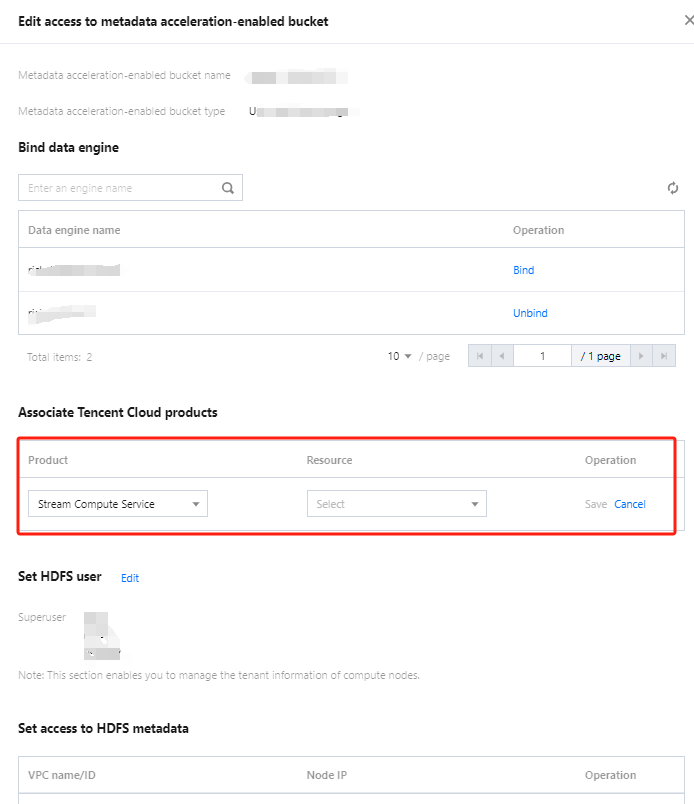
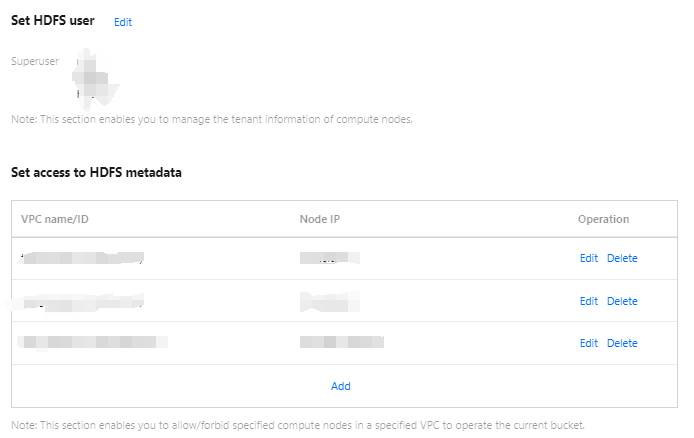
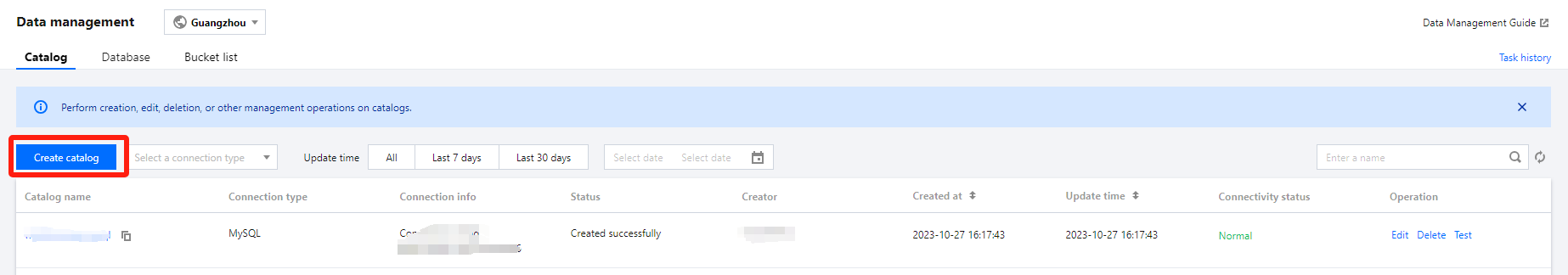
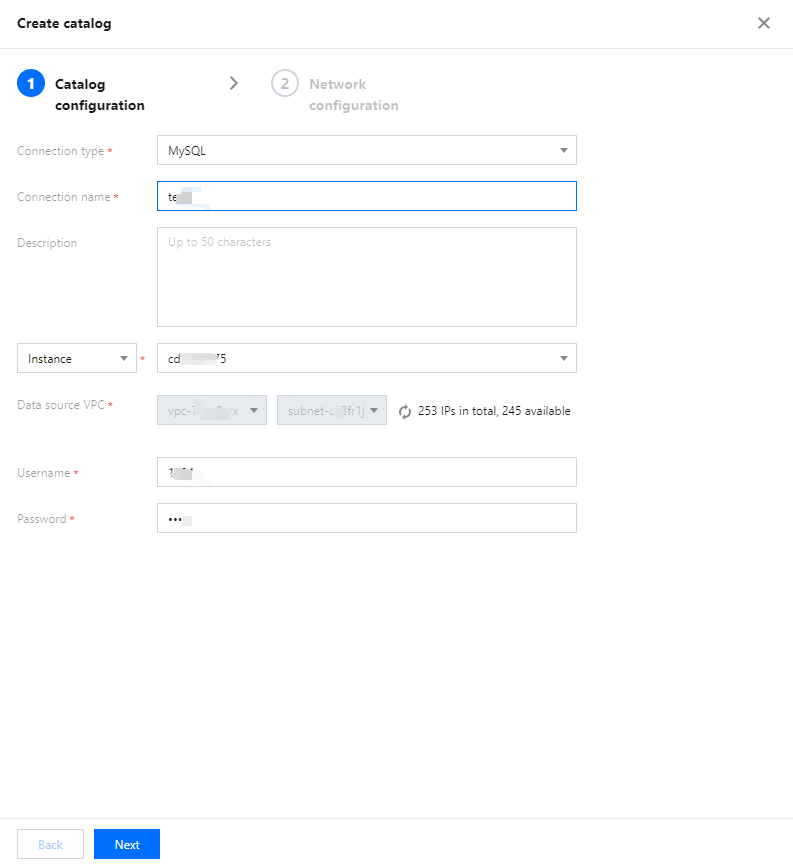
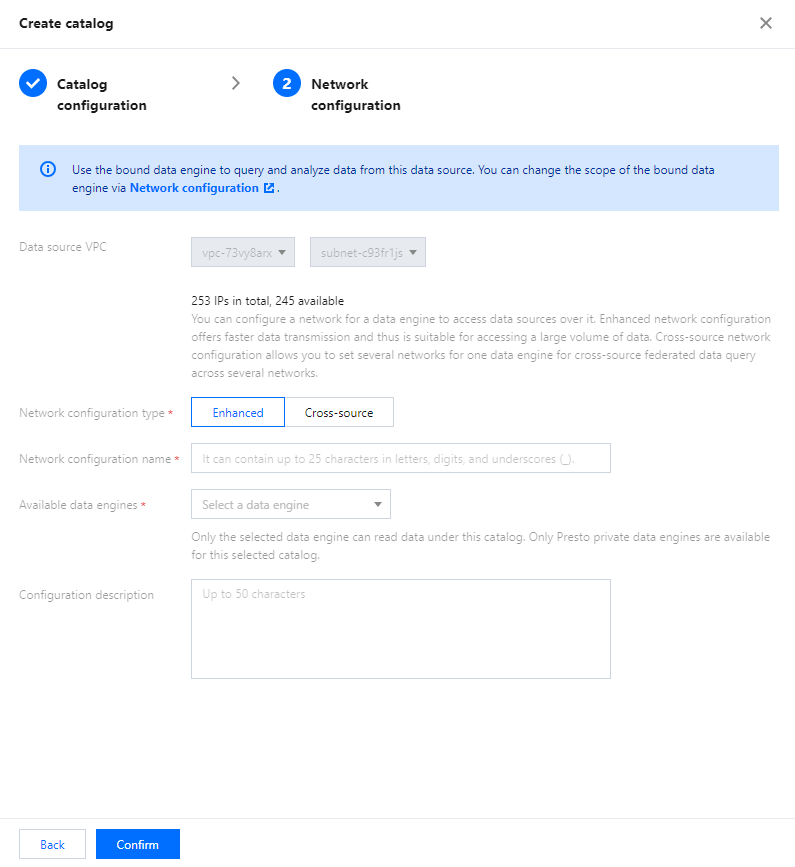
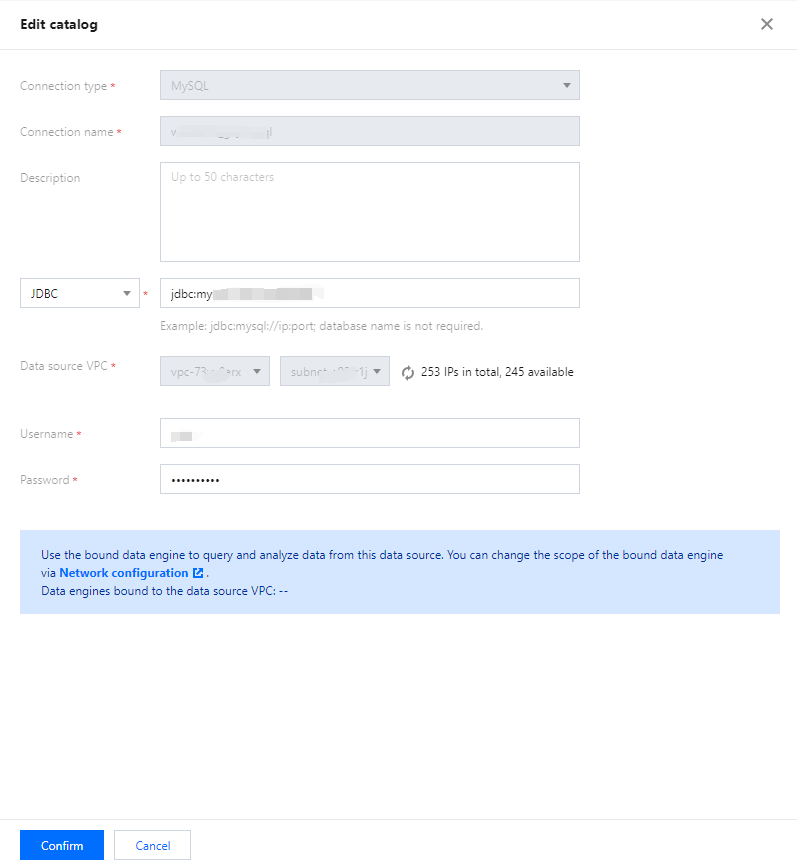
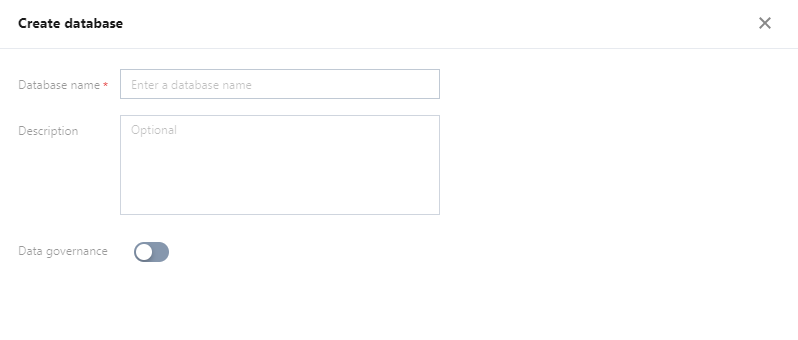
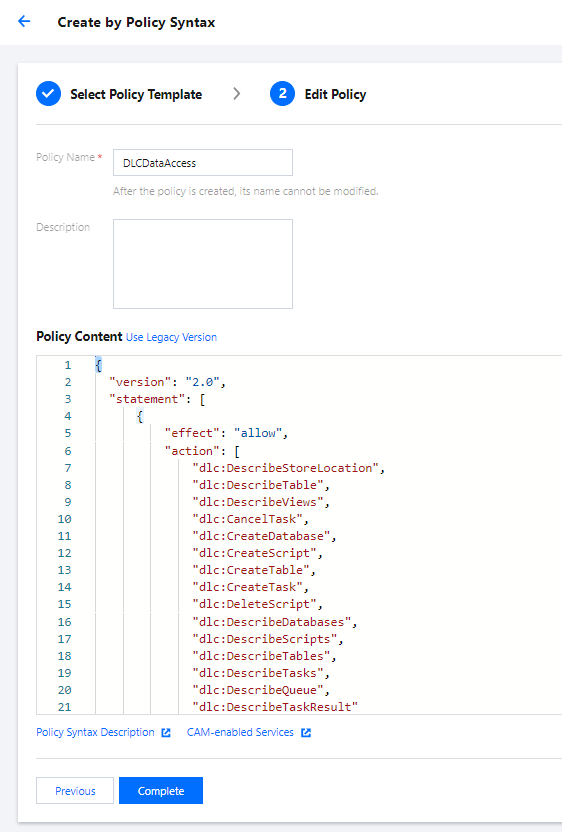
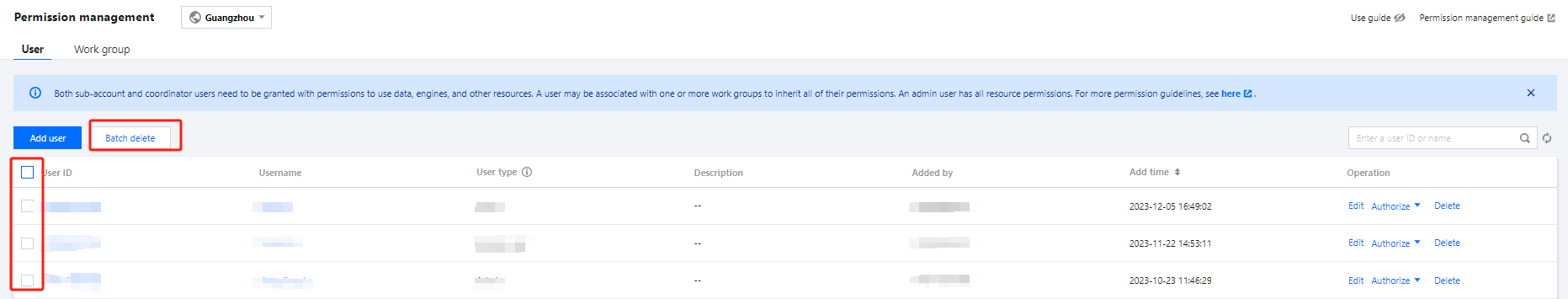
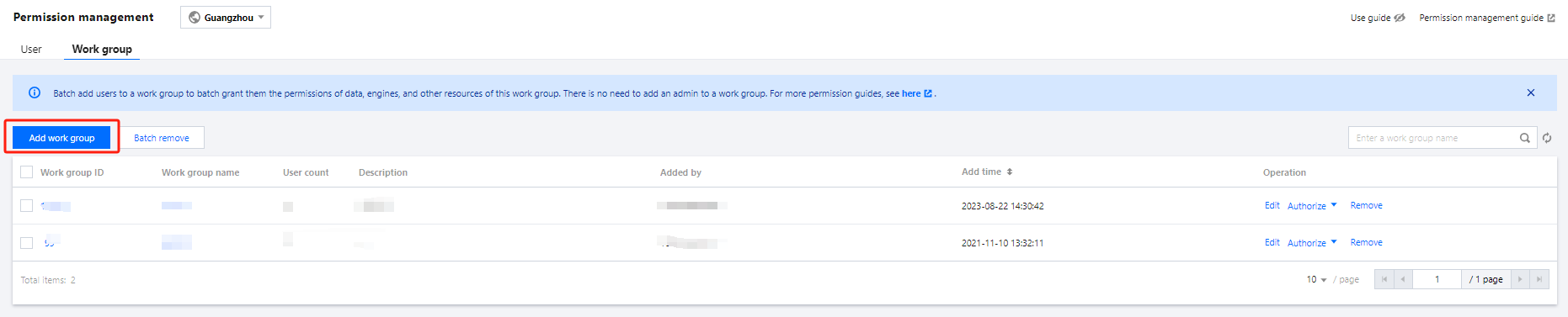
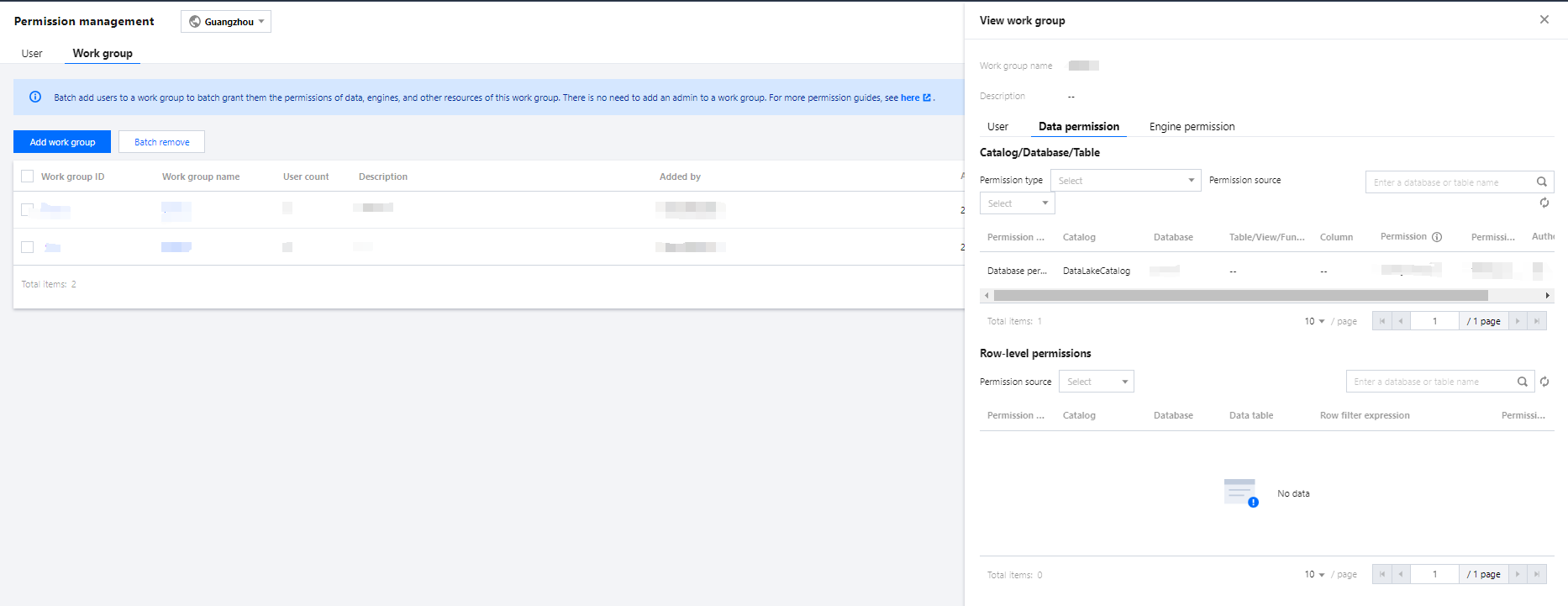
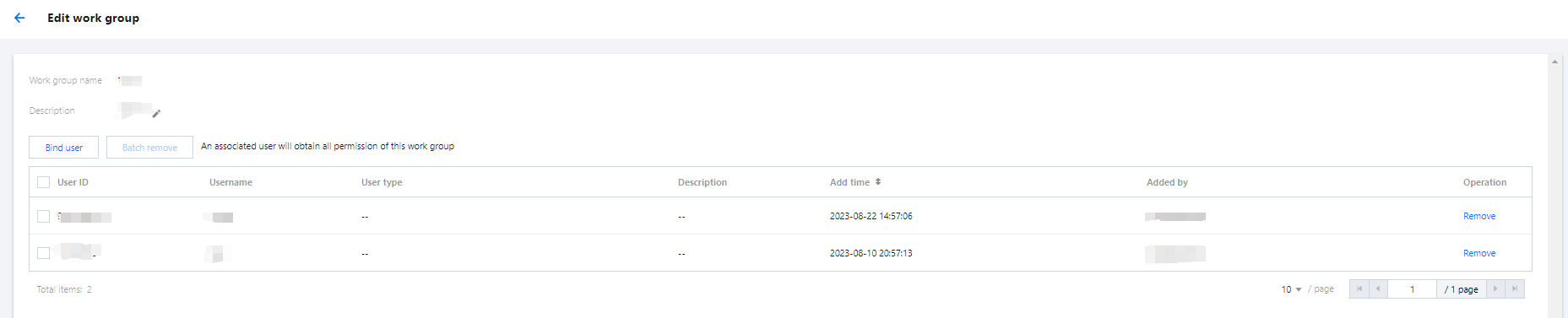
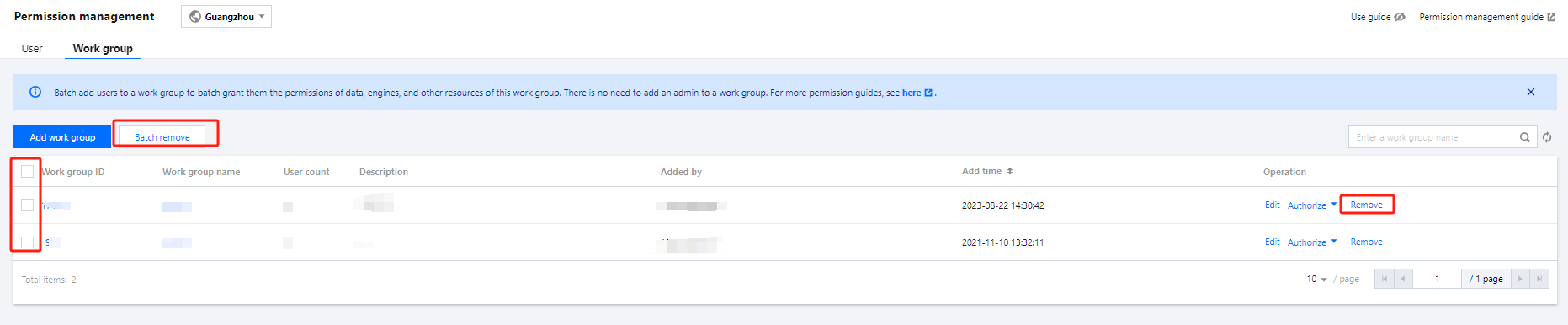
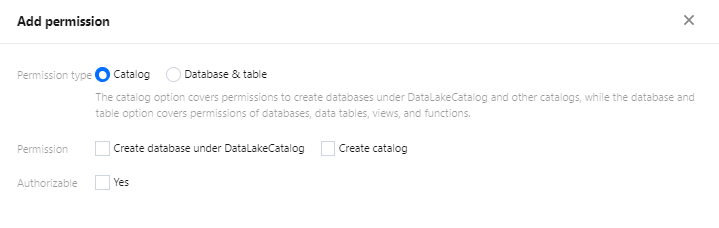
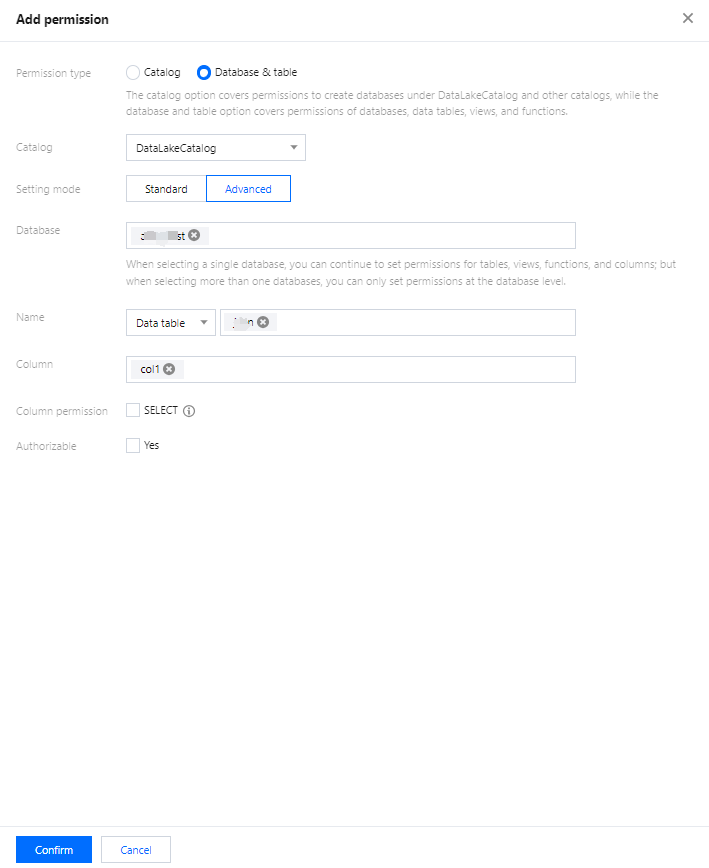
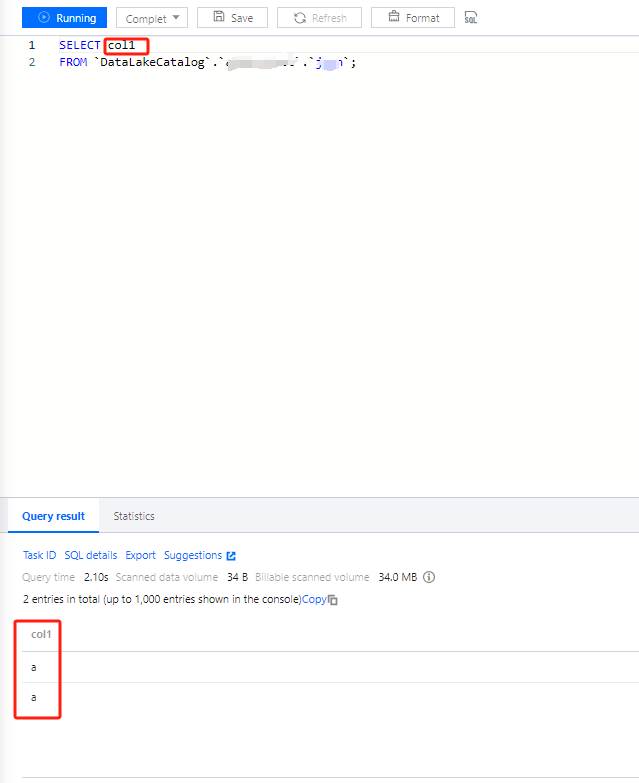
Users can create databases by executing DDL statements using either the DLC Console or the API.
Creating a Data Table
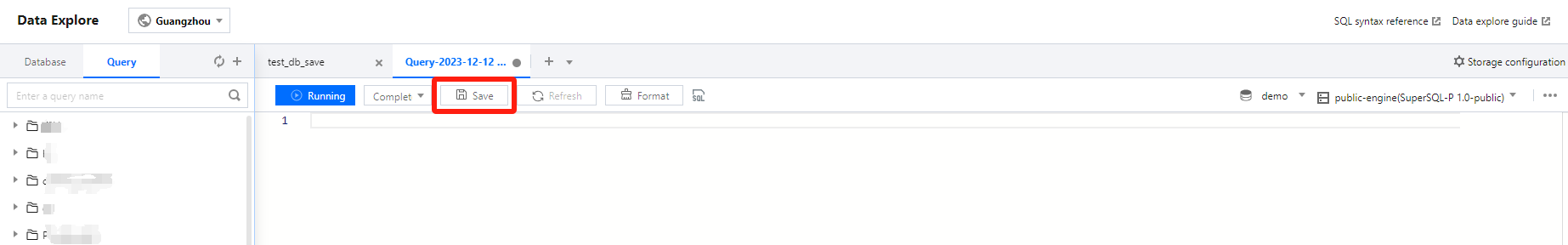
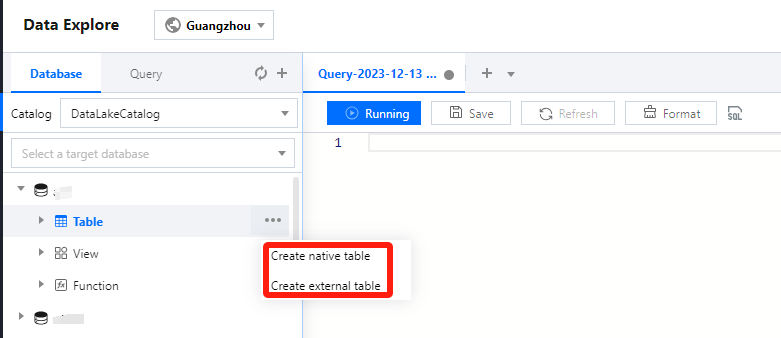
Method I: Creating in Data Exploration
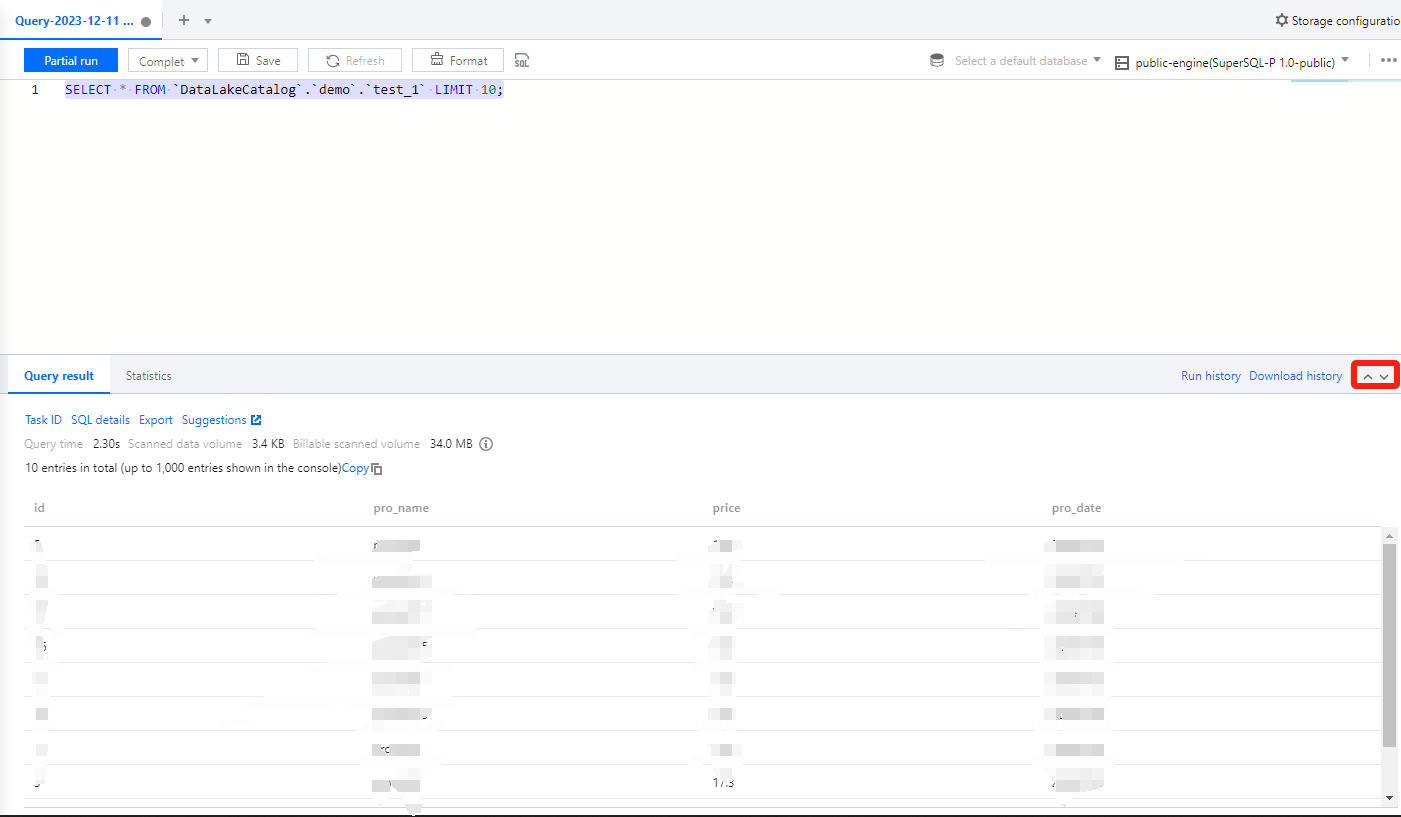
1. Log in to the DLC console and select the service region. Ensure the logged-in user has the permission to create data tables. 2. Navigate to the Data Exploration module. In the left list, click an existing database. Let the mouse pointer over the table row and click the icon. Then click Create Native Table or Create External Table. Note:
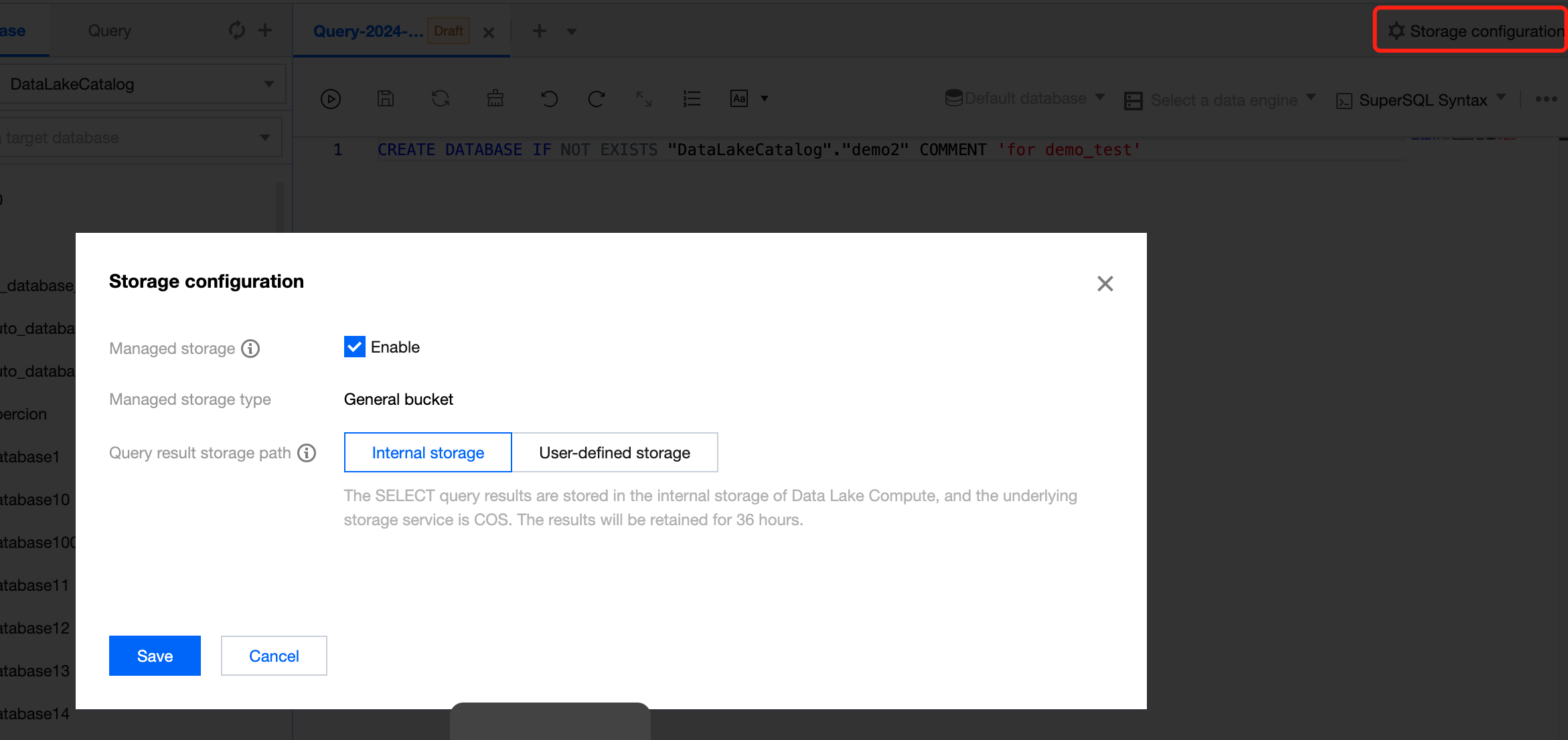
Native tables are stored in DLC managed storage. You do not need to worry about the underlying Iceberg storage format and it supports data optimization capabilities. To use native tables, managed storage must be enabled. For more details, see Managed Storage Configuration. The underlying data of an external table is stored in your own Cloud Object Storage. You need to specify the data path when creating an external table.
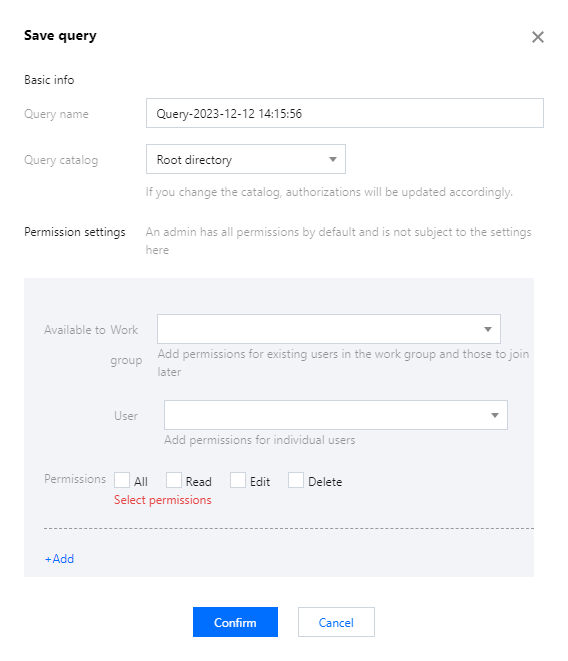
3. After you click Create Native Table/Create External Table, the system will automatically generate an SQL template for creating the data table. Users can modify the SQL template to create the data table. Click Run to execute the SQL statement and complete the creation.
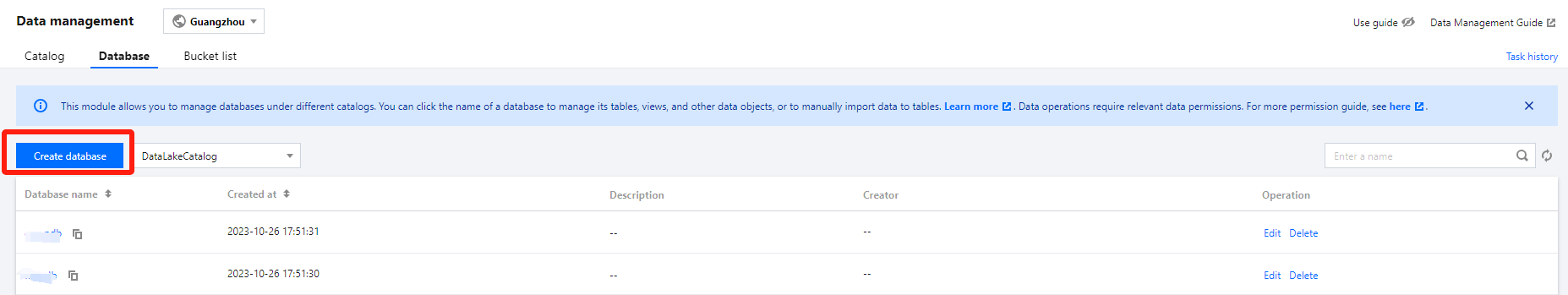
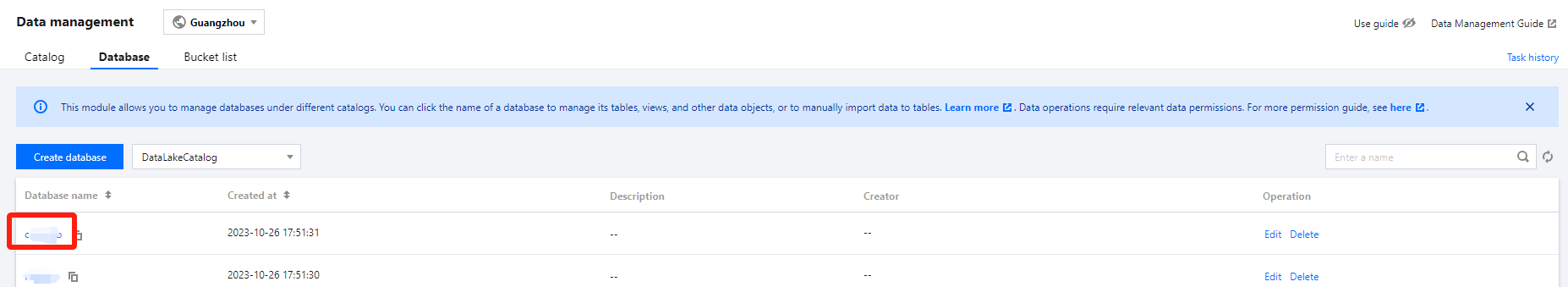
Method II: Creating in Data Management
The Data Management module supports managing both native tables and external tables in DLC managed storage.
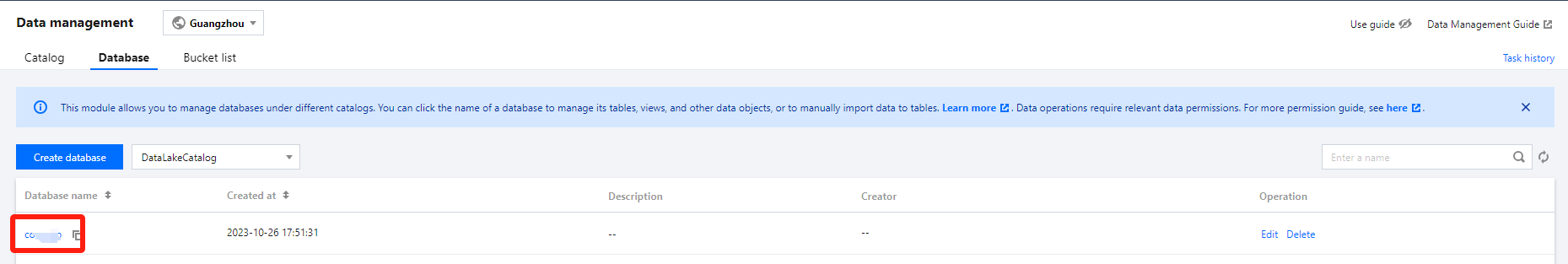
1. Log in to the DLC console and select the service region. Ensure the logged-in user has the permission to create data tables. 2. Go to Data Management through the menu on the left, enter Database, and click the name of the database where the data table will be located to enter the database management center page.
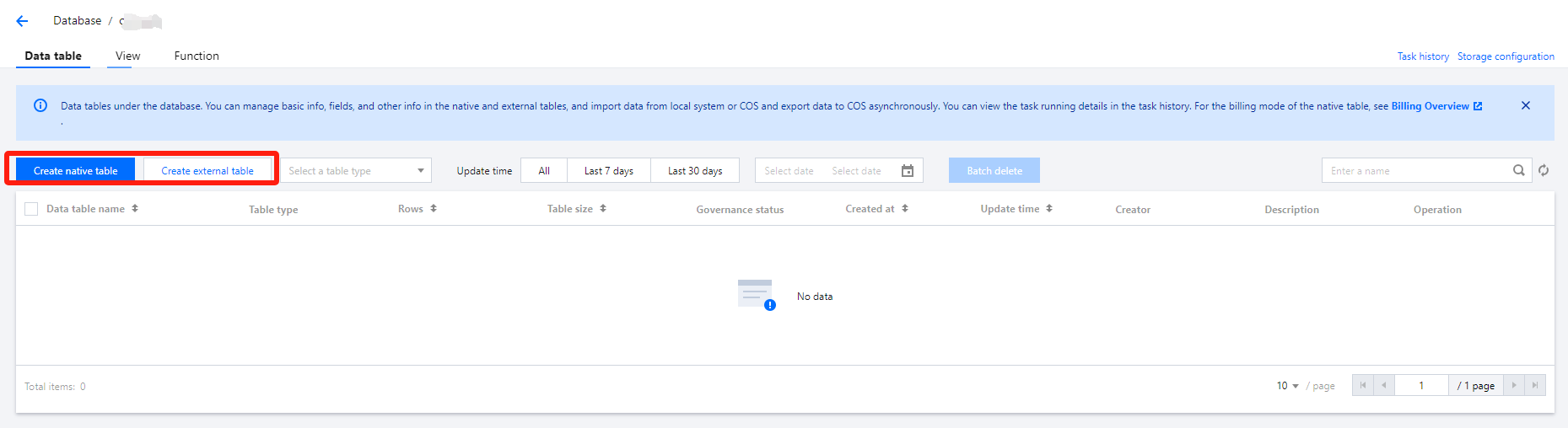
3. Click Create Native Table or Create External Table button to enter the data table configuration page.
4. Native tables support three types of data sources: empty table, local upload, and Cloud Object Storage (COS). Different data sources have different creation processes. Native tables also support data optimization capabilities, which can be set to inherit the database governance rules or managed independently.
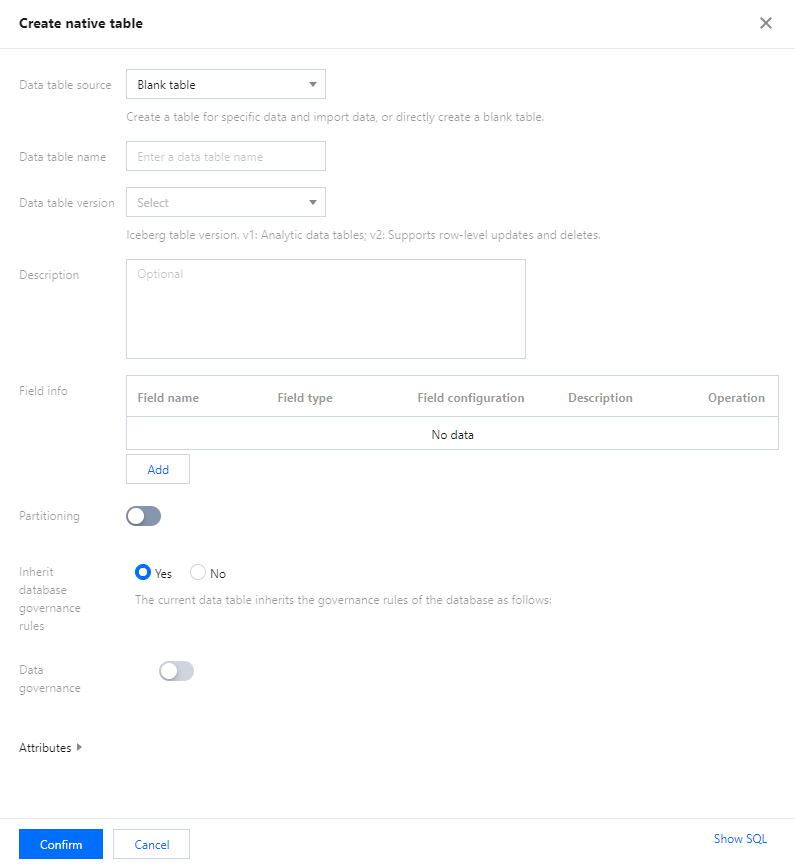
4.1 Create Empty Table: Create an empty table with no records.
Table Name: Cannot start with a digit, supports uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and underscores (_), up to 128 characters.
You can provide a description for the data table.
You can manually add and input column names and data types. Supports configuring complex field types such as array, map, and struct.
4.2 Local Upload: Upload a local file to DLC to create a data table, supporting files up to 100 MB.
CSV: Supports visual configuration of CSV parsing rules, including compression format, column delimiter, and field enclosure. It can automatically infer the schema of the data file and parse the first row as column names.
JSON: DLC only recognizes the first level of JSON as columns. It supports automatic schema inference for JSON files, and the system will treat the first level fields as column names.
Supports common big data formats such as Parquet, ORC, and AVRO.
You can manually add and input column names and data types.
If automatic structure inference is selected, DLC will fill in the recognized columns, column names, and data types. If they are incorrect, please modify them manually.
4.3 Create a data table through Cloud Object Storage (COS).
Create a data table by reading the COS data bucket under the current account.
CSV: Supports visual configuration of CSV parsing rules, including compression format, column delimiter, and field enclosure. It can automatically infer the schema of the data file and parse the first row as column names.
JSON: DLC only recognizes the first level of JSON as columns. It supports automatic schema inference for JSON files, and the system will treat the first level fields as column names.
Supports common big data formats such as Parquet, ORC, and AVRO.
You can manually add and input column names and data types.
If automatic structure inference is selected, DLC will fill in the recognized columns, column names, and data types. If they are incorrect, please modify them manually.
5. Data partitioning is typically used to improve query performance by partitioning tables with large quantities of data. DLC supports querying data by partitions. Users need to add partition information at this step. By partitioning your data, you can limit the amount of data scanned by each query, thus improving query performance and reducing usage costs. DLC follows the partitioning rules of Apache Hive.
The partition column corresponds to a subcatalog under the table's COS path, and the catalog naming rule is Partition Column Name=Partition Column Value.
Note:
The example code is for reference only and should be modified based on the actual business scenario. For example, replace "bucket_name" with your bucket name.
cosn://nanjin-bucket/CSV/year=2021/month=10/day=10/demo1.csv
cosn://nanjin-bucket/CSV/year=2021/month=10/day=11/demo2.csv
If there are multiple partition columns, they need to be nested in the order specified in the CREATE TABLE Statement.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `COSDataCatalog`.`dlc_demo`.`table_demo` (
`_c0` string,
`_c1` string,
`_c2` string,
`_c3` string
) PARTITIONED BY (`year` string, `month` string, `day` string)
ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ('separatorChar' = ',', 'quoteChar' = '"')
STORED AS TEXTFILE
LOCATION 'cosn://bucket_name/folder_name/';
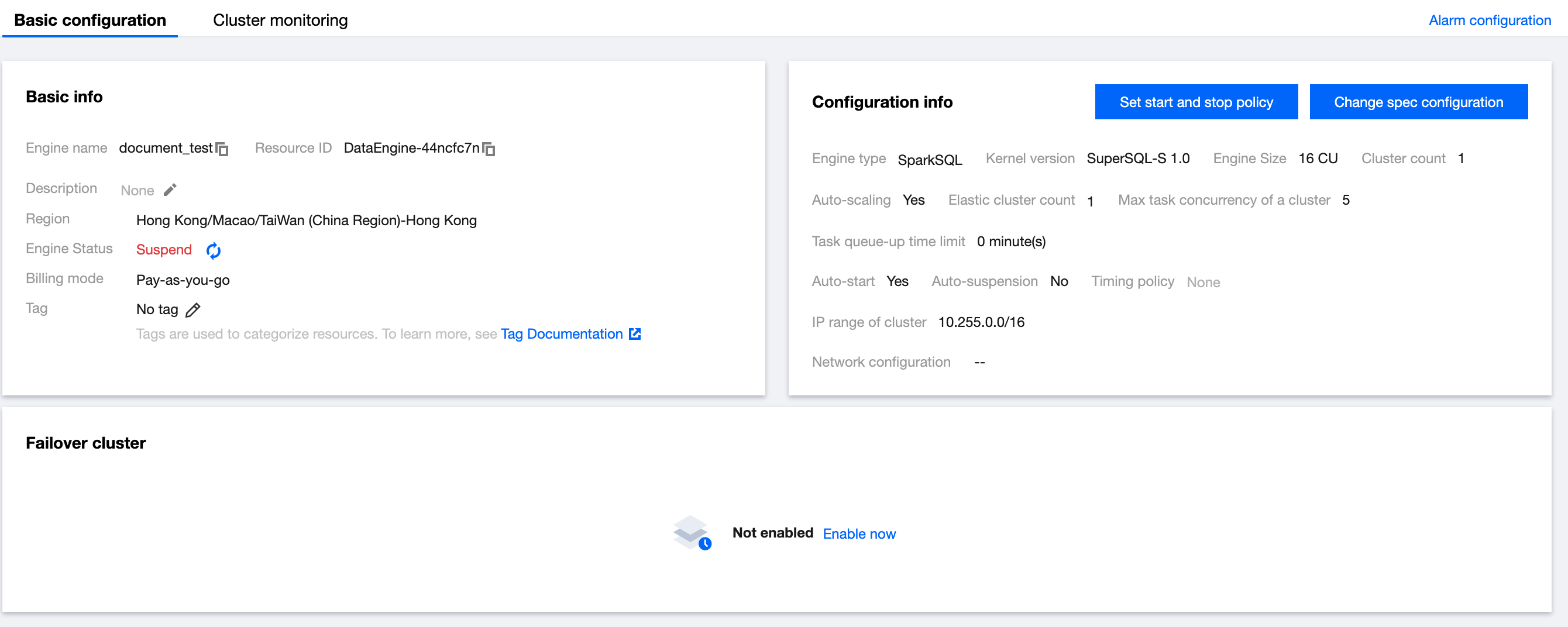
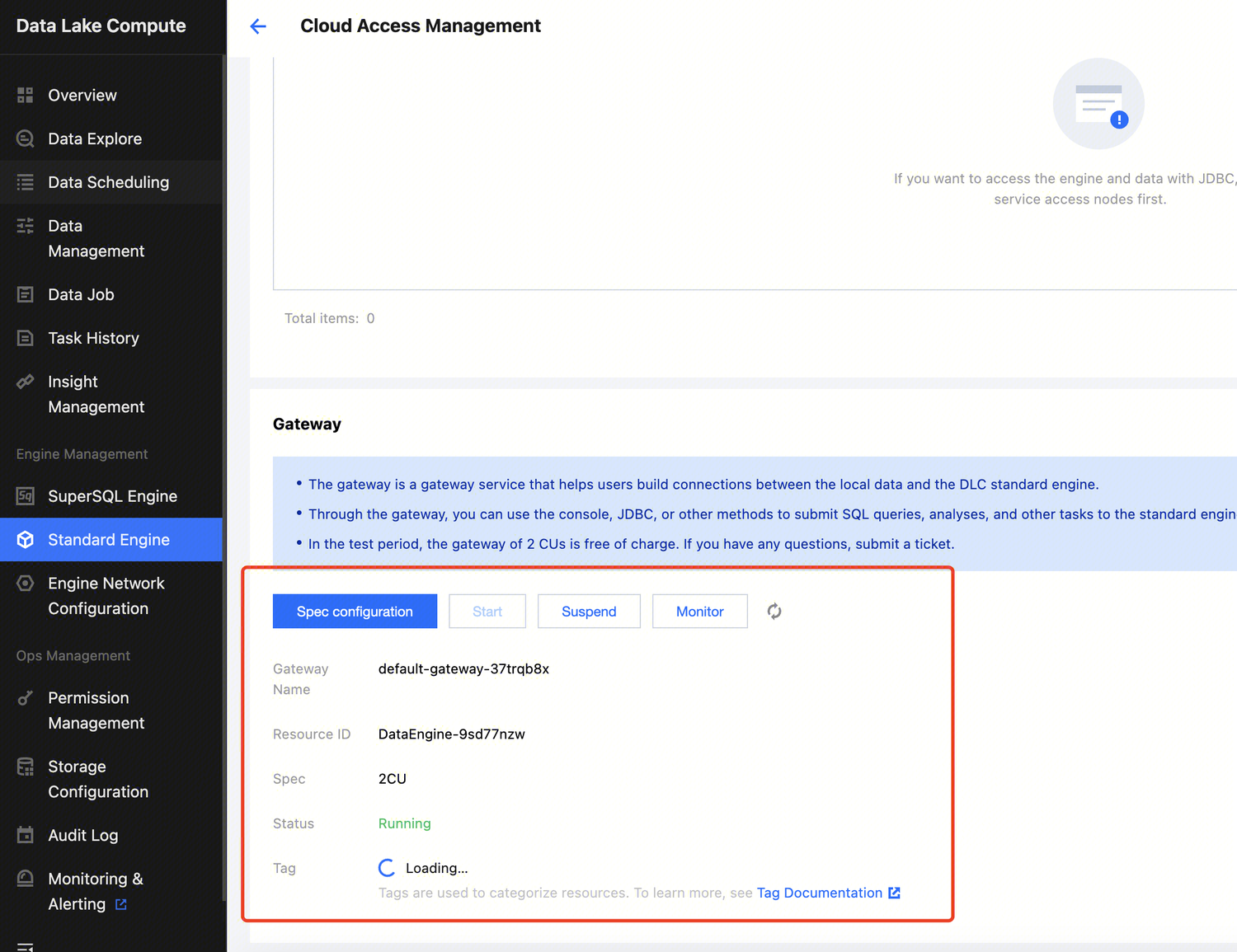
Querying Basic Information of Data Tables
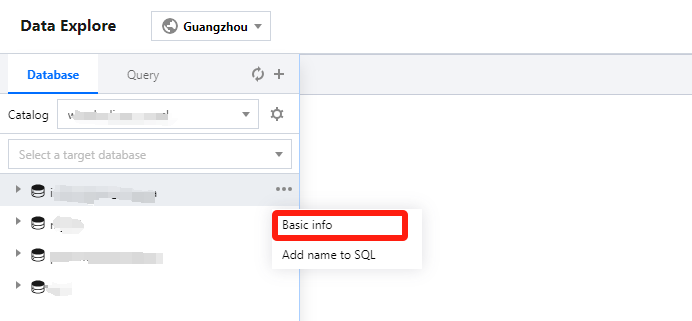
Method I: Querying in Data Exploration
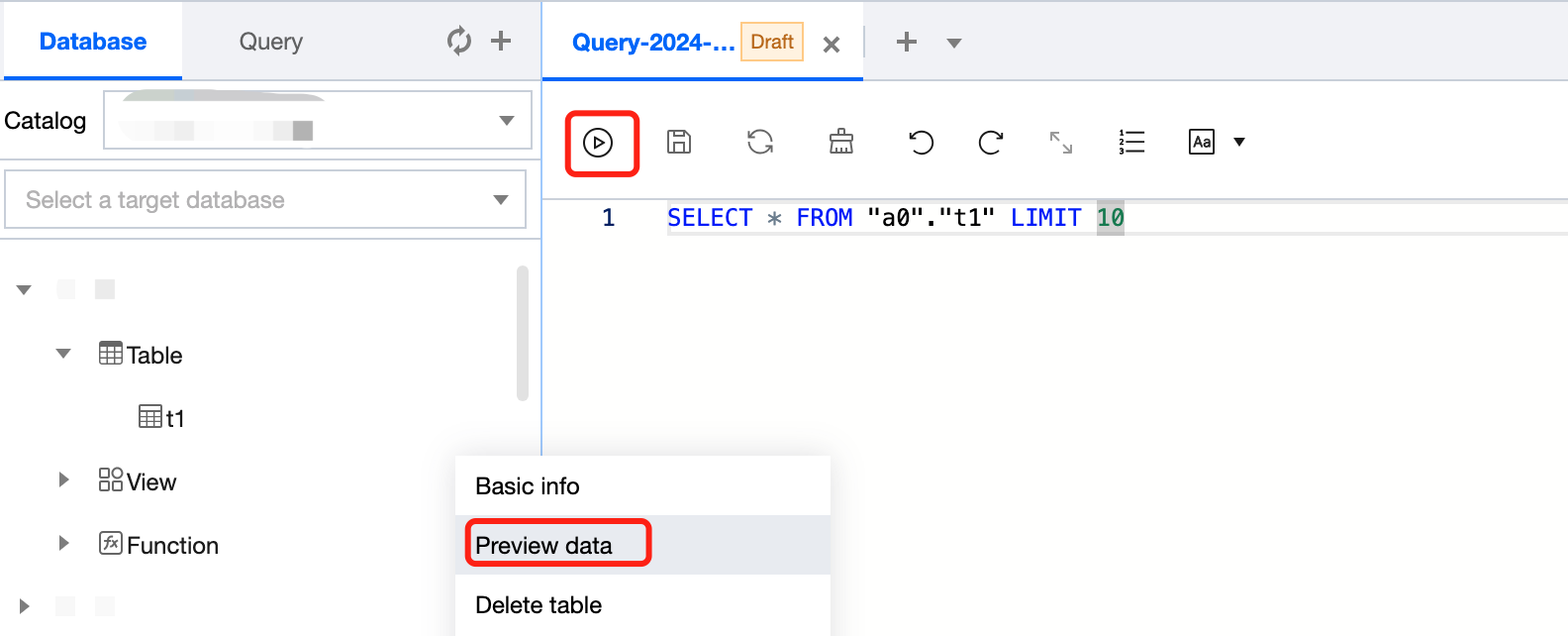
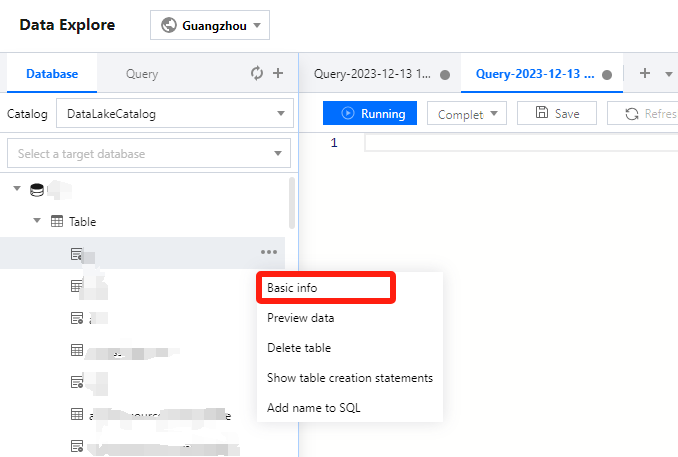
In the data table project, let the mouse pointer hover over the Data Table Name row, then click the icon. From the pull-down menu, click Basic Information to view the basic information of the created data table. Basic information of the data table includes:
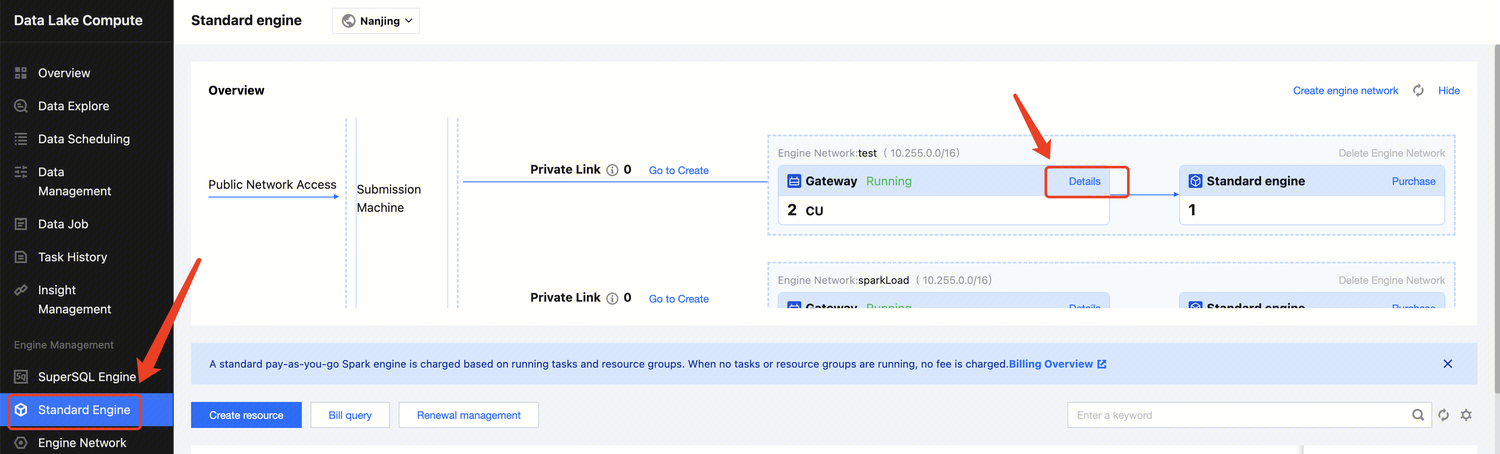
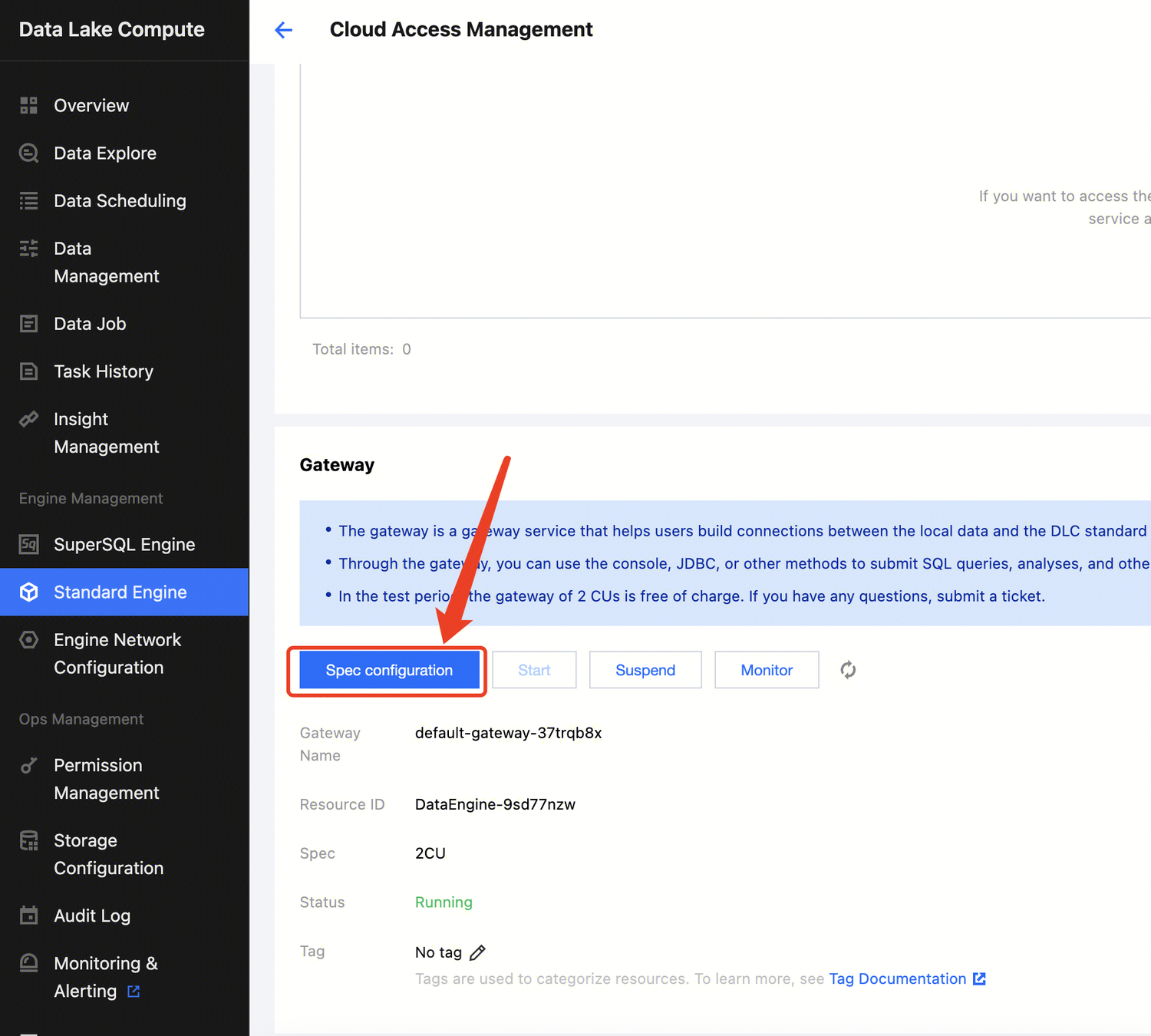
Method II: Viewing in Data Management
1. Log in to the DLC Console and select the service region. Ensure the logged-in user has the permission to view the data table. 2. Go to the metadata management module via the left sidebar. On the database page, click the name of the database where the data table resides. Enter the database management center page. Here, you can query information such as the number of rows, storage space, creator, fields, partitions, etc.
Self-Service Querying for Data Table Partition Information
Note:
Replace the database name and table name in the example below according to your actual business scenario.
SuperSQL Spark SQL Engine:
select * from `DataLakeCatalog`.`db`.`tb$partitions`
SuperSQL Job Engine and Standard Engine:
select * from `DataLakeCatalog`.`db`.`tb`.`partitions`
Querying Data Table Partition Information
Data table management supports querying partition information related to data tables. With the partition information, you can view details, including record quantity, file quantity, data storage capacity, and update time for each partition of the table.
1. Go to DLC console, select the service region. Login user should have the permission to view data tables. 2. Go to Metadata Management via the left sidebar, enter the Database, and click the name of the database where the data table resides to access the Database Management page. 3. Select Database to go to the Data Table management page. Select and click the Data Table, and then select Partition Information to go to the Partition Information page.
The data partition page displays partition information of the table in paginated form. You can query partition details through sorting partitions by fields, including names, record quantity, file data size, and file storage. For example, to view a certain fixed partition, enter the partition name to search.
Note:
1. Partition information statistics are currently only available for DLC native tables.
2. Partition information statistics are currently in the Beta testing phase. To enable the partition information statistics, you may contact us.
Previewing Data Table Data
In the data table project, let the mouse pointer hover over the Data Table Name row, then click the icon. From the pull-down menu, click Preview Data, and DLC will automatically generate an SQL statement to preview the first 10 rows of data. Execute the SQL statement to query the first 10 rows of the data table. By default, the data preview feature displays the first 100 rows of data.
Editing Data Table Information
You can edit the description information of a data table in the data management module.
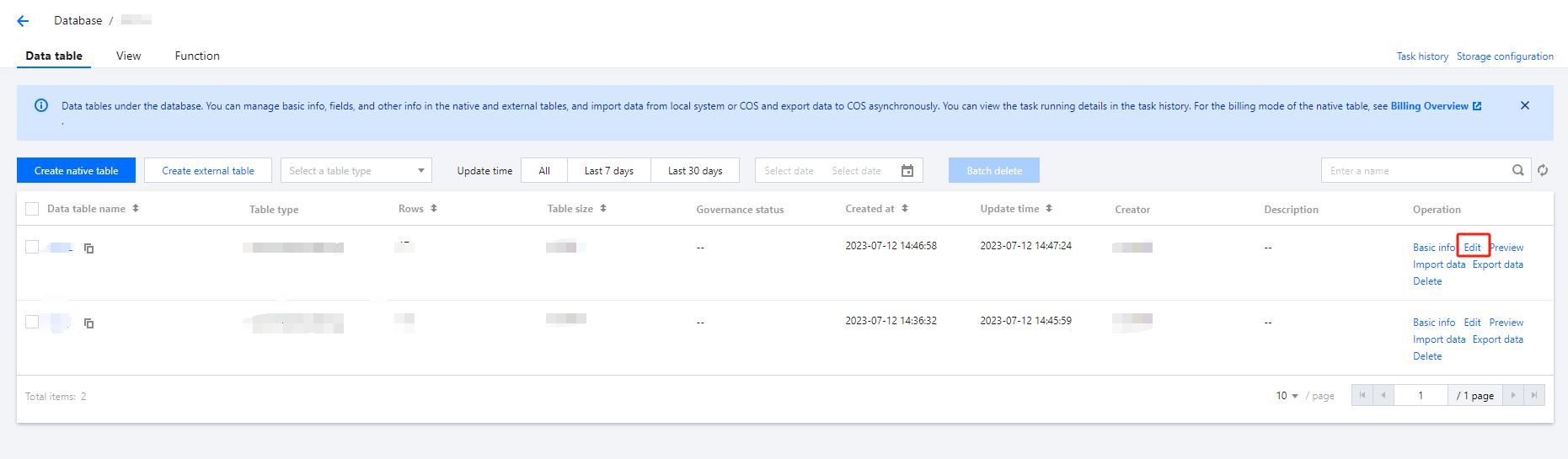
1. Log in to the DLC console and select the service region. Ensure the logged-in user has the permission to edit the data table. 2. Go to Metadata Management > Database via the left sidebar, and click the database name where the data table is located to enter the database management center page. 3. Find the data you need to edit, and click the Edit button on the right to make changes.
4. After modification, click the Confirm button to complete the edit.
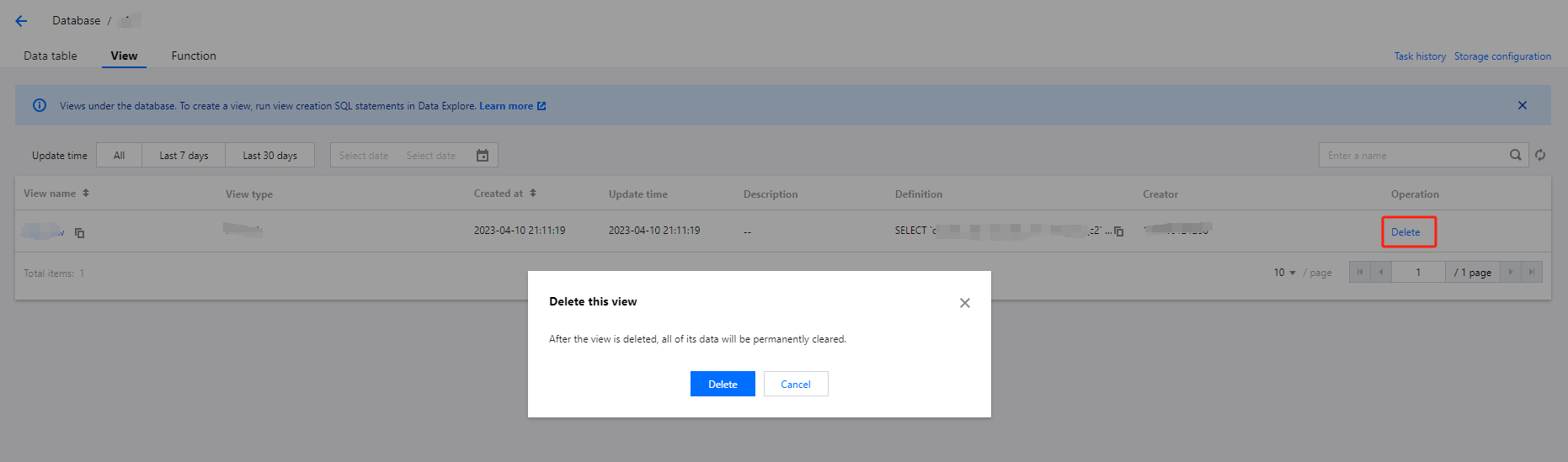
Deleting a Data Table
Method I: Deleting in Data Exploration
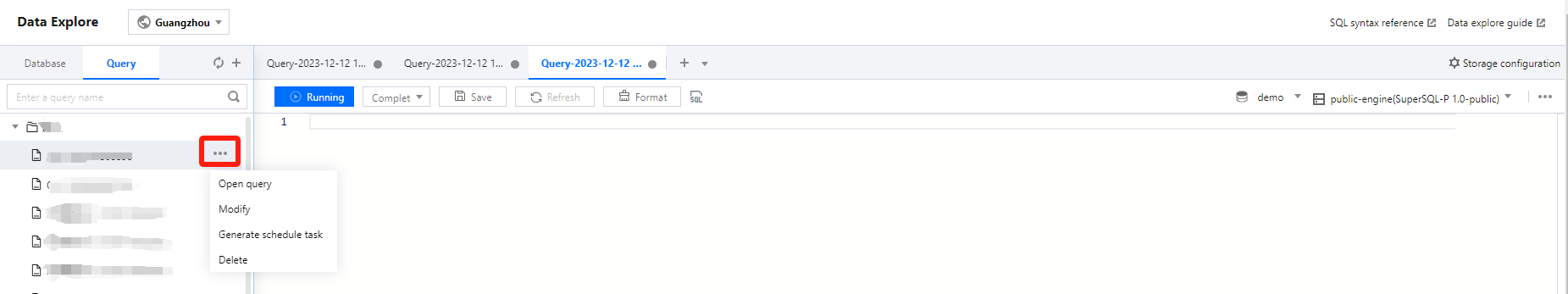
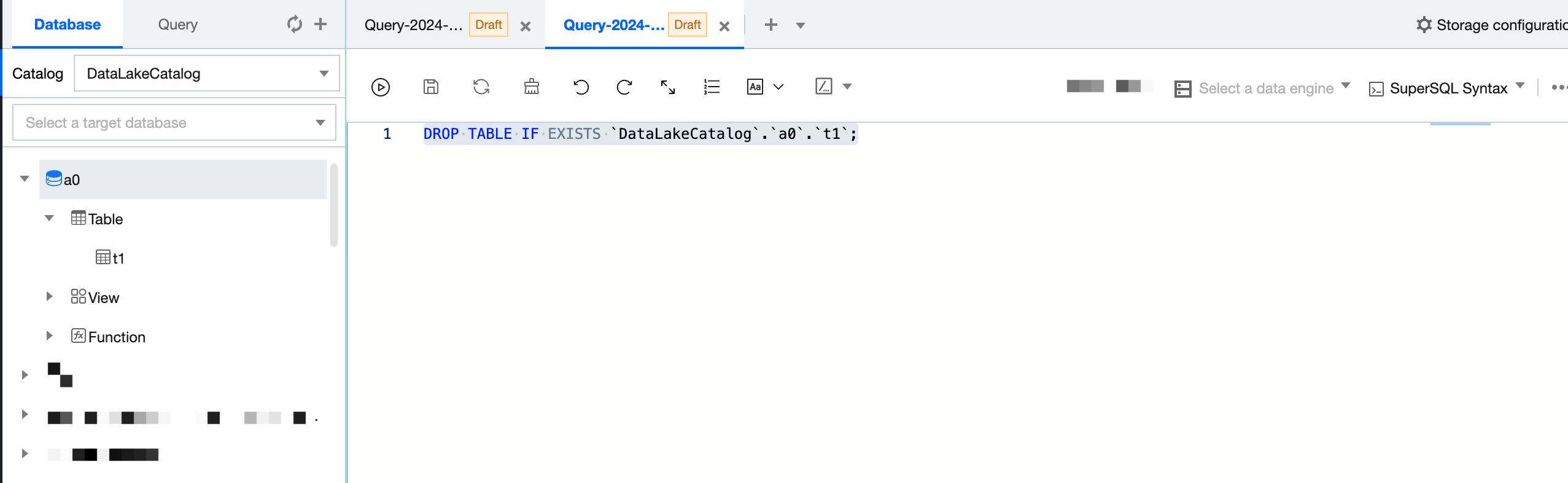
In the data table project, let the mouse pointer hover over the Data Table Name row, then click the icon. From the pull-down menu, click Delete Table. DLC will automatically generate an SQL statement to delete the data table. Execute the SQL statement to delete the data table. When an external table is deleted, only the metadata stored in DLC is deleted. The data source files are not affected.
When a data table under the DataLakeCatalog directory is deleted, all data in the data table will be cleared. Please operate with caution.
Method II: Deleting in Data Management
Currently, Data Management only supports managing database and tables stored in DLC. For external tables, use Method I to delete.
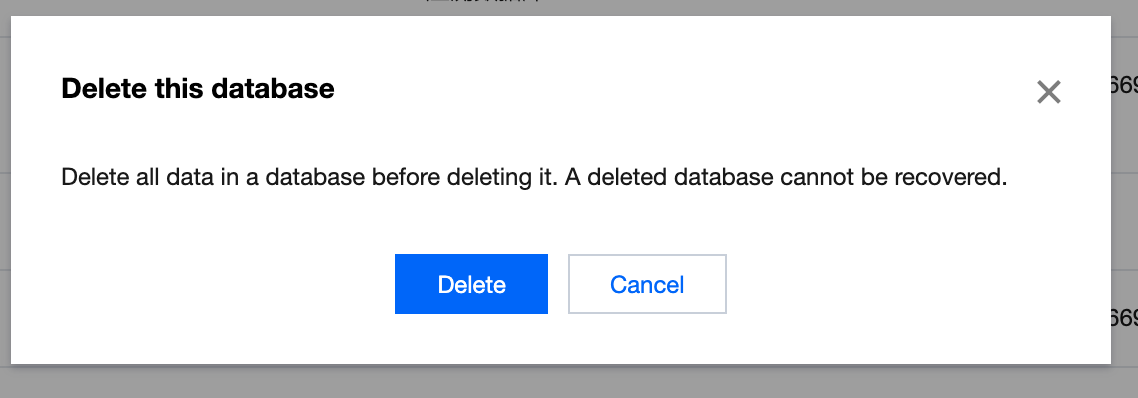
1. Log in to the DLC console and select the service region. Ensure the logged-in user has the permission to delete the data table. 2. Go to Metadata Management > Database via the left sidebar., and click the database name where the data table is located to enter the database management center page. 3. Click the Delete button on the right of the data table that you want to delete. After a second confirmation, the corresponding data table will be deleted, and the data in the data table will be cleared.
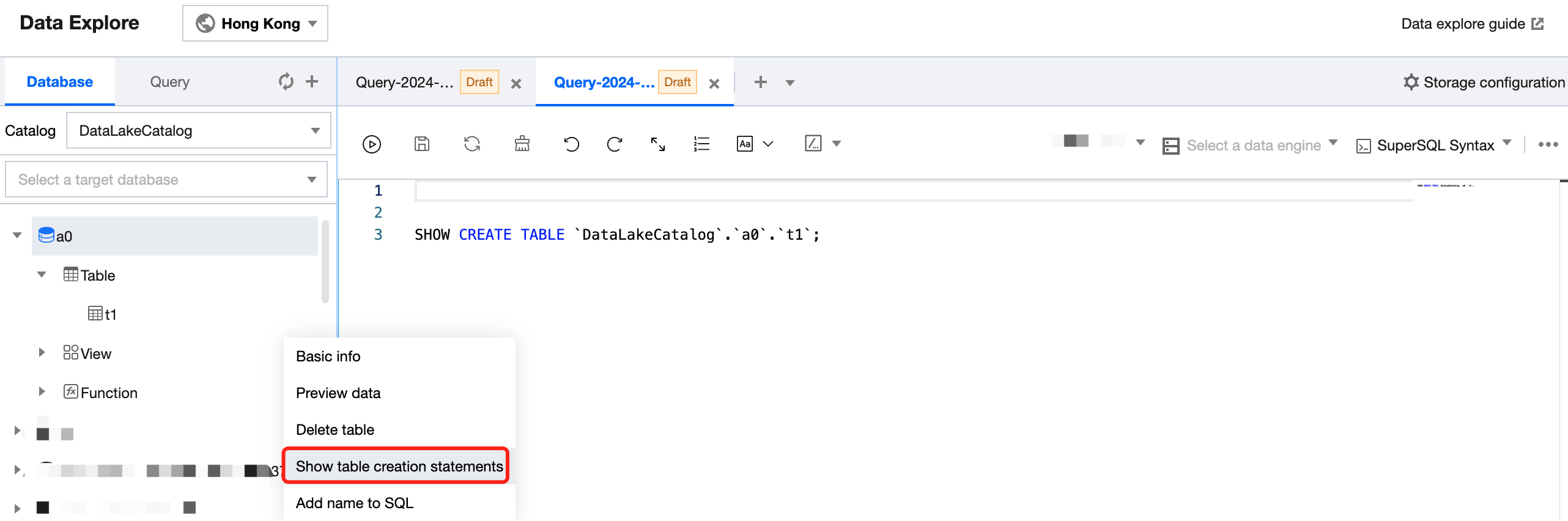
Showing Table Creation Statements
In the data table project, let the mouse pointer hover over the Data Table Name row, then click the icon. From the pull-down menu, click Show table creation statements. DLC will automatically generate and display the SQL statement used to create the data table. Execute the SQL statement to view the CREATE TABLE statement. System Constraints
DLC allows a maximum quantity of 4096 data tables per database, up to 100,000 partitions per data table, and up to 4096 columns of attributes per data table.
DLC will recognize data files under the same COS path as belonging to the same table. Please ensure that data for separate tables is stored in separate directory structures.
DLC does not support multiple versions of data in COS and only the latest version of data in the COS bucket can be queried.
All tables created in DLC are external tables and the CREATE TABLE SQL statement must include the EXTERNAL keyword.
Table names must be unique within the same database.
Table names are case-insensitive and can only include English letters, digits, and underscores (_), with a maximum length of 128 characters.
For partitioned tables, you must manually implement the ADD PARTITION statement or the MSCK statement to add partition information before you can query the partition data. For more details, see Query partitioned table. When CSV is used to create a table, DLC will default all field types to string. However, this does not affect the computation and query of the original data fields.