Tencent Cloud Mesh
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Announcements
- Getting Started
- Application Configuration
- Traffic Control
- Service HA
- Multi-cluster Disaster Recovery and Multi-active
- Security Reinforcement
- Operation Guide
- Mesh Instance Management
- Service Discovery Management
- Traffic Management
- Observability
- Access Management
- Extended Features
- FAQs
DocumentationTencent Cloud Mesh
Deploying Wasm Filters in Batches
Last updated: 2022-08-17 11:43:14
This document is currently invalid. Please refer to the documentation page of the product.
Deploying Wasm Filters in Batches
Last updated: 2022-08-17 11:43:14
Tencent Cloud Mesh provides two tools to help you deploy wasm filters quickly. The tools support wasm filters in the binary and image formats, and can filter the deployment scope by label.
Prerequisites
- Tencent Cloud Mesh is equal to or later than v1.8.
- K8s is equal to or later than v1.16.
How It Works
At present, the main implementation in the industry is to mount a wasm file into a container by mounting the hostPath. There are two shortcomings in this implementation:
- An existing pod cannot mount the file. You must restart the pod and mount the path.
- The file mounting method requires that the corresponding file exists on the machine. Otherwise, Envoy may be abnormal after an EnvoyFilter is created, and there is a potential timing problem.
Based on remoteSource natively supported by Envoy, Tencent Cloud Mesh can pull wasm after the pod is started, so that it can support wasm without restarting the pod. In addition, the architecture is simplified, and each node no longer needs a DaemonSet pod, which saves node resources to a certain extent. Tencent Cloud Mesh defines a CRD named AutoWasm, which allows users to pull a wasm extension file from an image registry or other data sources. The controller provided by Tencent Cloud Mesh performs List/Watch of the custom resource, generates the final EnvoyFilter, and pulls and caches the wasm file at the same time. The controller supports horizontal extension.
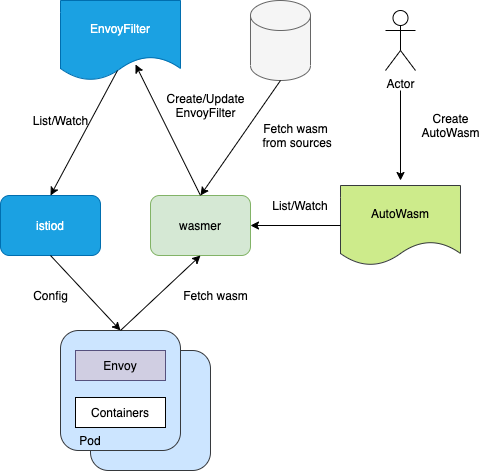
Required Components
wasmc: Similar to Docker, this tool can upload a .wasm file to an OCI image registry.
wasmer: A server program used for quick wasm deployment.
Component Deployment
- wasmc: Click to download
- wasmer:
helm repo add servicemesh-tcm https://servicemesh.tencentcloudcr.com/chartrepo/tcm helm install servicemesh-tcm/wasmer --generate-name
Note:In a multi-cluster scenario, the components must be deployed on each cluster and AutoWasm must be created on the multiple clusters.
Examples
In the following example, wasm is used to add KEY hello:world to the header of the details application.
Pushing wasm to an image registry
# Push the **example.wasm** file you prepared to the OCI image registry, which supports the binary or image format.
wasmc push ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/{$repoName}/wasm-add-header:v0.3 -f ./example.wasm
Pushed ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/***/wasm-add-header:v0.3
Digest: sha256:***
# Pull the file from the registry to the local host
wasmc pull ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/{$repoName}/wasm-add-header-wadecai:v0.3
Pulled ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/***/wasm-add-header-wadecai:v0.3
Sha256: ***
Location: ***/filter.wasm
Obtaining a wasm extension file from the image registry and deploying wasm
The wasm deployment file aw.yaml is as follows:
apiVersion: wasm.tcm.io/v1alpha1
kind: AutoWasm
metadata:
name: test
namespace: default
spec:
filter:
applyPorts:
- 9080
rootID: test
source:
registry:
image: ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/{Your image registry}/wasm-add-header:v0.3
vmID: test
secret: test # Image registry's secret
selector:
matchLabels:
app: details
Parameters are described as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| spec.filter.applyPorts | Port on which the deployment will take effect. (This field is optional, and the deployment will take effect on all ports by default.) |
| spec.filter.rootID | Unique ID, which is used to share wasm's RootContext and Contexts. (This field is optional.) |
| spec.filter.vmID | wasm VM ID. (This field is optional. If this field is left blank, a wasm VM ID is automatically generated.) |
| spec.filter.sourc | wasm file source. The values registry and object are supported, which indicate an image registry and object storage, respectively. |
| spec.selector.matchLabels | Label used to match a pod on which the deployment needs to take effect. |
| spec.secret | Image registry's secret. For a public image, this field can be left blank. |
The source.registry part indicates to obtain the wasm extension file from the image registry.
Obtaining a wasm extension file from COS and deploying wasm
apiVersion: wasm.tcm.io/v1alpha1
kind: AutoWasm
metadata:
name: test
namespace: default
spec:
filter:
applyPorts:
- 9080
rootID: test
source:
object:
url: https://aaaa.com/bbb
vmID: test
selector:
matchLabels:
app: details
Note:At present, you are allowed to obtain a wasm extension file only from public object storage.
Creating a resource and checking results
kubectl apply -f aw.yaml
Note:The content of the aw.yaml file is shown above. The wasm file is obtained from the image registry.
- Check aw CR.
kubectl get aw
NAME SECRET MATCH SOURCE APPLYPORTS TIME PHASE
test test {"app":"details"} {"registry":{"image":"ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/xxx/wasm-add-header:v0.3"}} [9080] 2021-10-27T10:00:36Z Synced
- View EnvoyFilter.
kubectl get envoyfilter test -o yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2021-10-28T08:25:24Z"
name: test
namespace: default
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
subFilter:
name: envoy.filters.http.router
portNumber: 9080
patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: envoy.filters.http.wasm
typedConfig:
'@type': type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
typeUrl: type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.wasm.v3.Wasm
value:
config:
name: test
rootId: test
vmConfig:
code:
remote:
httpUri:
cluster: outbound|8081||wasmer.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
timeout: 600s
uri: wasmer.istio-system:8081/wasm/750d63889653e7117fcbc0831f10f0e1d3f7ec0c82fe5787b71d08a783e3393f
sha256: 750d63889653e7117fcbc0831f10f0e1d3f7ec0c82fe5787b71d08a783e3393f
runtime: envoy.wasm.runtime.v8
vmId: test
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: details
- Check results.
kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
details-v1-79f774bdb9-2vhjx 2/2 Running 0 4m 172.16.0.10 cwd-dev <none> <none>
curl -s 172.16.0.10:9080 -vvv
* About to connect () to 10.244.0.157 port 9080 (#0)
* Trying 10.244.0.157...
* Connected to 10.244.0.157 (10.244.0.157) port 9080 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> User-Agent: curl/7.29.0
> Host: 172.16.0.10:9080
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
< content-type: text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1
< server: istio-envoy
< date: Thu, 28 Oct 2021 06:16:22 GMT
< content-length: 273
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 1
< hello: world
< x-envoy-decorator-operation: details.default.svc.cluster.local:9080/*
<
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD><TITLE>Not Found</TITLE></HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1>Not Found</H1>
`/' not found.
<HR>
<ADDRESS>
WEBrick/1.6.0 (Ruby/2.7.1/2020-03-31) at
172.16.0.10:9080
</ADDRESS>
</BODY>
</HTML>
It is found that hello: world has been added.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
