Cache Purge
Last updated: 2021-08-05 14:43:55
This document is currently invalid. Please refer to the documentation page of the product.
Feature Overview
ECDN is capable of configuring basic cache. Cache expiration time can be configured according to rules such as specified business types, directories, and specific URLs to regularly purge resources cached on nodes, pull latest resources from the origin server and cache them again.
Note:If your application has been migrated to the CDN console, you can go to the console for operation by referring to Content Delivery Network.
In addition, ECDN can purge cache for specified URLs or directories in batches:
- Purge URL: Delete the cache of corresponding resources on all ECDN nodes.
- Purge directory: if you select the "Purge Changed Resources" mode, when an end user accesses a resource under the corresponding directory, the
Last-Modifyinformation of the resource will be obtained from the origin-pull. If it is the same as that of the currently cached resource, the cached resource will be directly returned; otherwise, the changed resource will be pulled from the origin server and cached again. If you select the "Purge All Resources" mode, when the user accesses a resource under the corresponding directory, the latest version of the resource will be directly pulled from the origin server and cached again.
After a purge is successfully executed, the corresponding resource on the node does not have a valid cache. When the user initiates an access request again, the node will pull the required resource from the origin server and cache it on the node again. If you submit a large number of purge tasks, many caches will be cleared, resulting in a surge in origin-pull requests and high pressure on the origin server.
Use Cases
New resource release
After a resource is overwritten by a new one with the same name on the origin server, to prevent users on the entire network from accessing the legacy version of the resource cached on the node, you can submit a request to purge the URL/directory for the resource and clear all caches so users can directly access the latest version of the resource.
Illegal resource cleanup
When illegal resources (such as resources related to pornography, drug, or gambling) are found on your origin server, they may still be accessible even after you delete them on the origin server because of node cache. To protect your network environment security, you can delete the cached resources through URL purge for timely cleanup.
Operation Guide
How to use
Log in to the ECDN Console, click Purge and Prefetch on the left sidebar, and submit a Purge URL or Purge Directory task: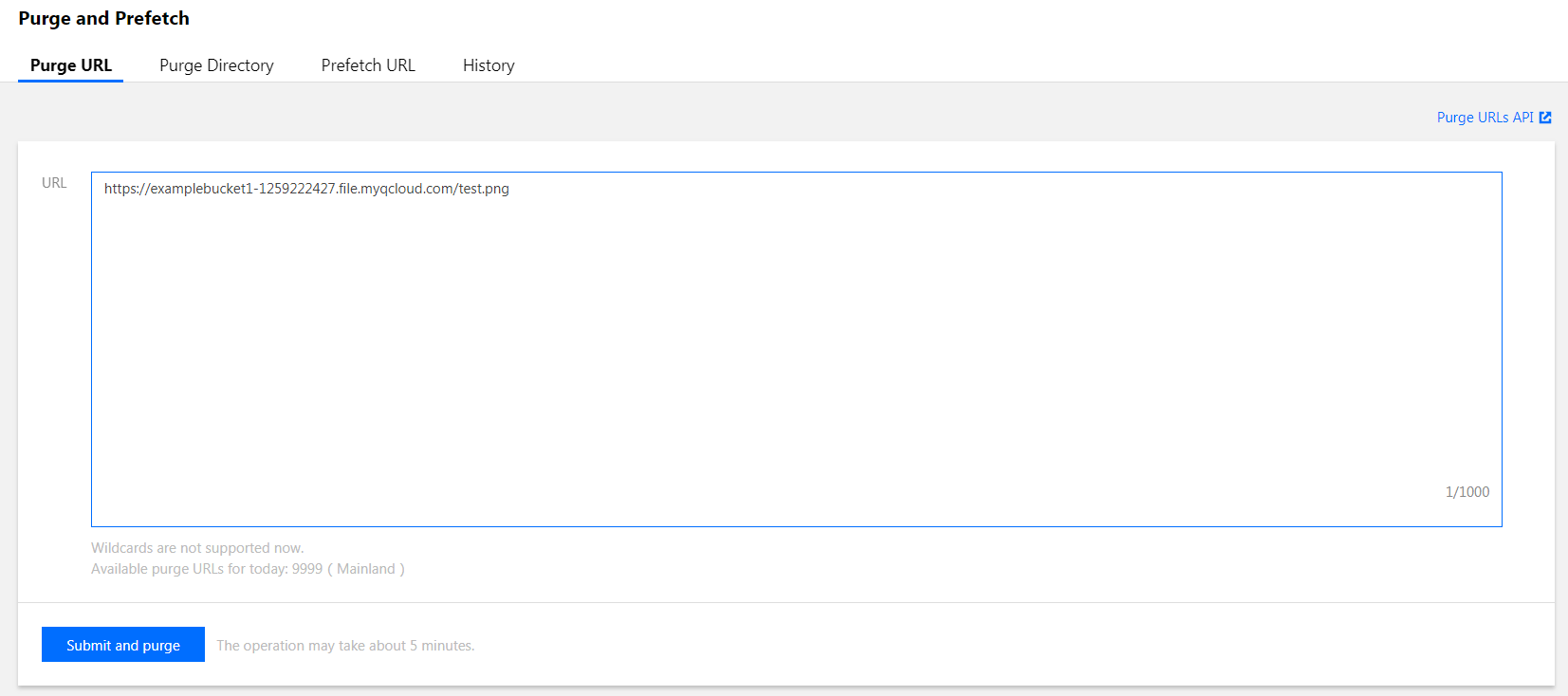
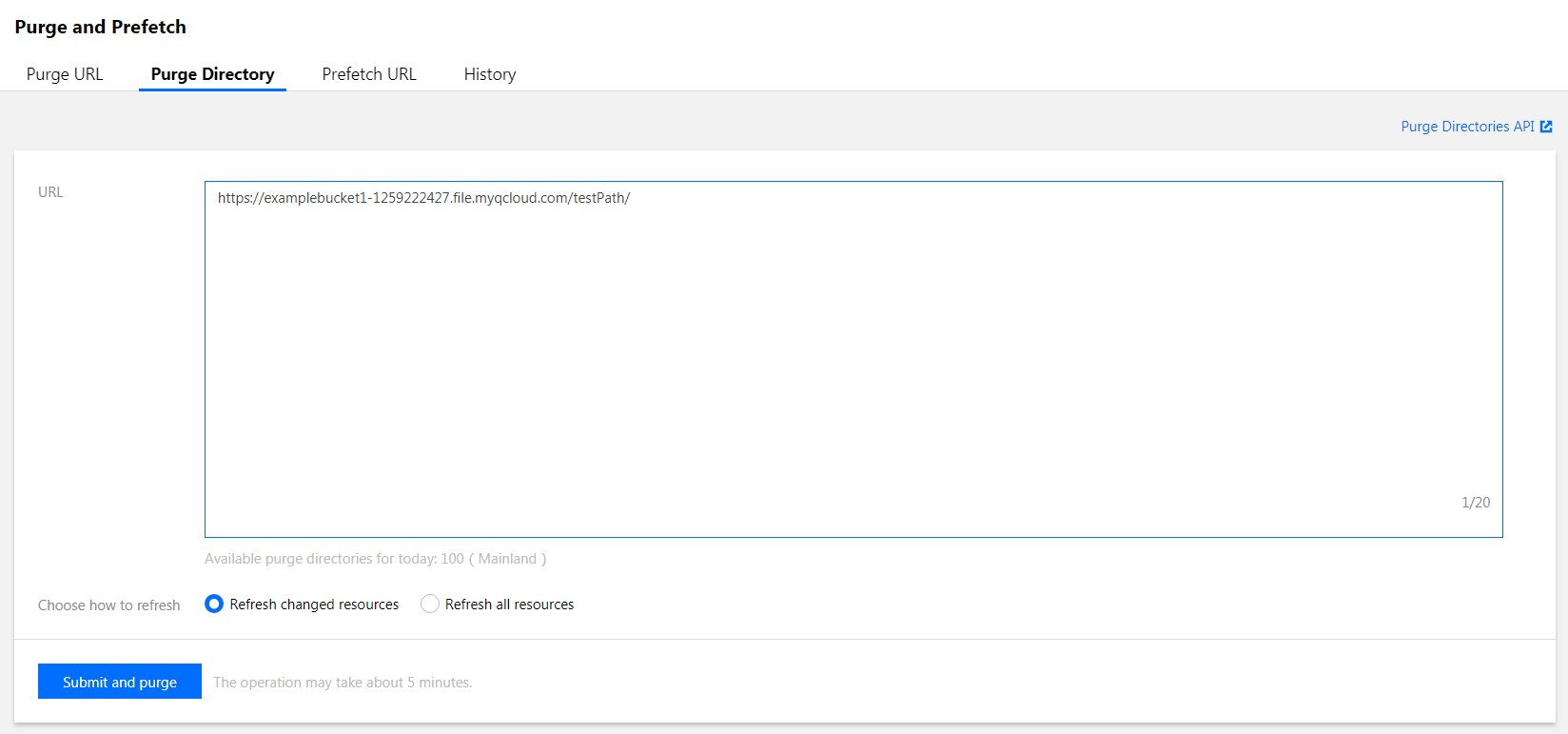
In the History section, you can query tasks by specified time period, keyword, and purge task type. With regard to keyword, you can only query tasks by specifying a domain name or a complete purged URL/directory: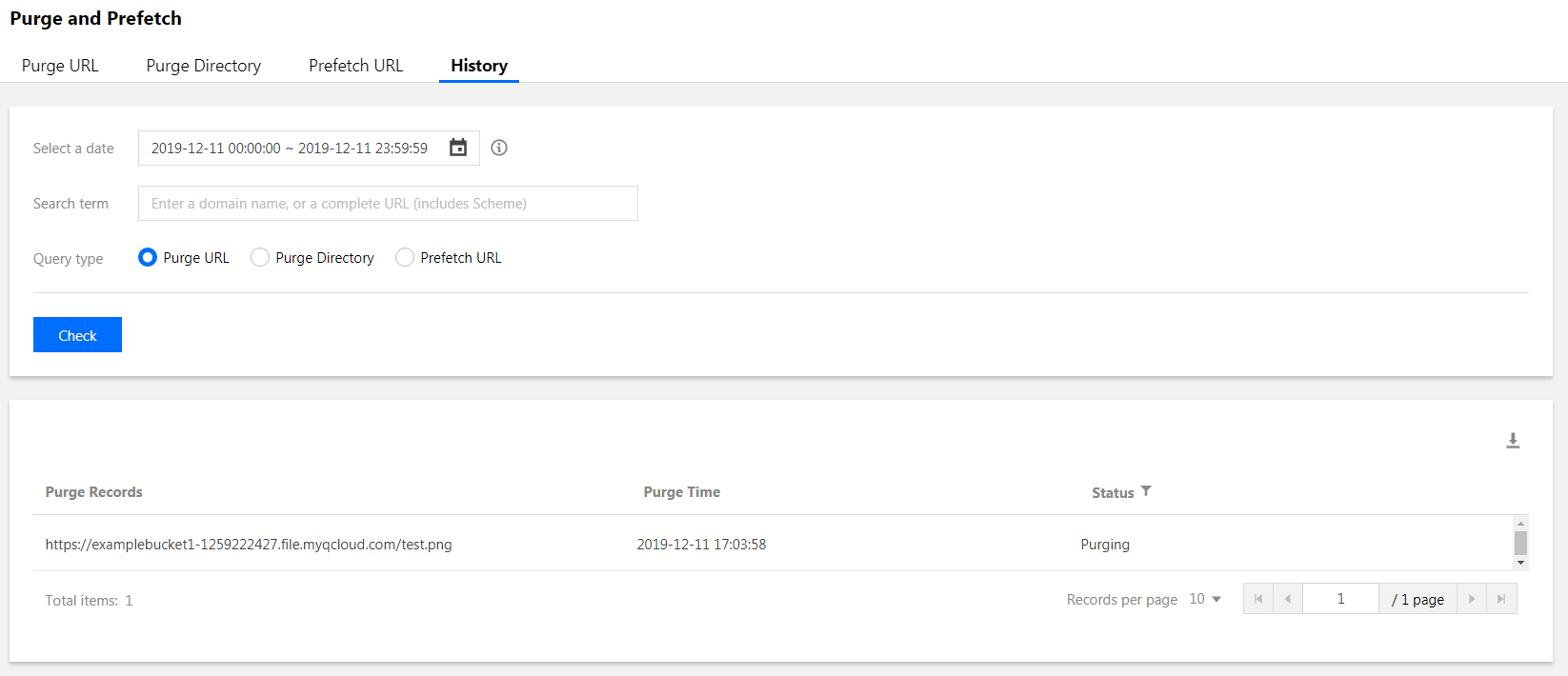
Precautions
URL purge:
- Up to 10,000 URLs can be purged per day for each account, and up to 1,000 URLs can be submitted for purge at a time.
- You need to add the
http://orhttps://protocol identifier when submitting a purge task. - URLs in the format of
http://*.test.com/cannot be purged. Even if you connect a wildcard domain name to CDN, you need to submit the corresponding sub-domain names for purge. - When submitting URLs for purge, domain names should have already been connected to CDN; otherwise, the submission will fail.
- URLs containing Chinese characters cannot be purged.
- By default, URLs will be purged by acceleration regions of domain names in the URLs.
Directory Purge:
- Up to 100 directories can be purged per day per account, and up to 20 directories can be submitted for purge at a time.
- You need to add the
http://orhttps://protocol identifier when submitting a purge task. - Directories in the format of
http://*.test.com/cannot be purged. Therefore, even if you connect a wildcard domain name to CDN, you need to submit the corresponding sub-domain names for purge. - When submitting URLs for purge, domain names should have already been connected to CDN; otherwise, the submission will fail.
- URL directories containing Chinese characters cannot be purged.
Sub-user permissions configuration:
- The operations of directory purge, URL purge, and purge history query must have already been connected to the latest permission system and support permission configuration at the resource (domain name) level.
- For permission assignment method, please see Permission Configuration.
Use Cases
Directory purge - purge changed resources
The acceleration domain name is purge-test-1251991073.file.myqcloud.com, the origin server is Tencent Cloud Object Storage (COS), and resources on the origin server are as follows: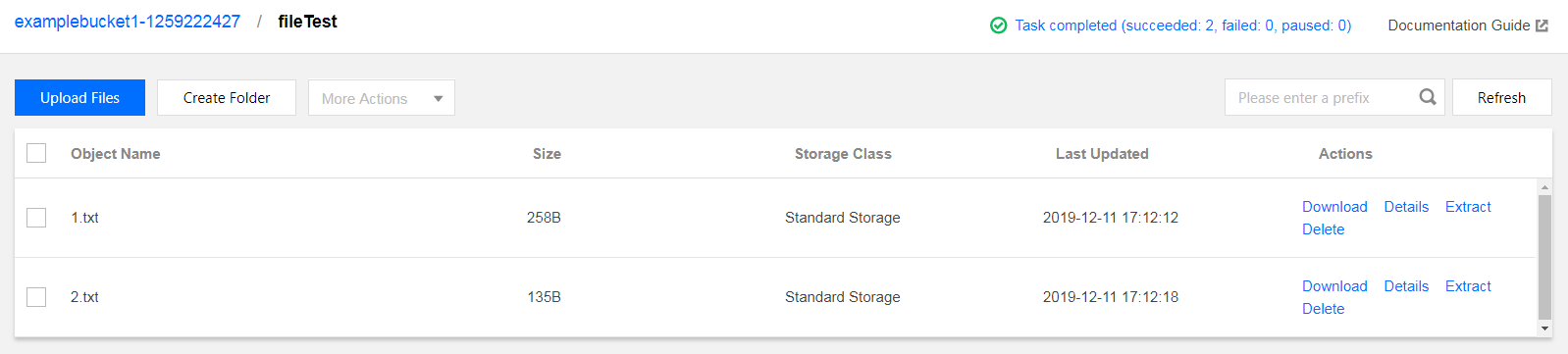
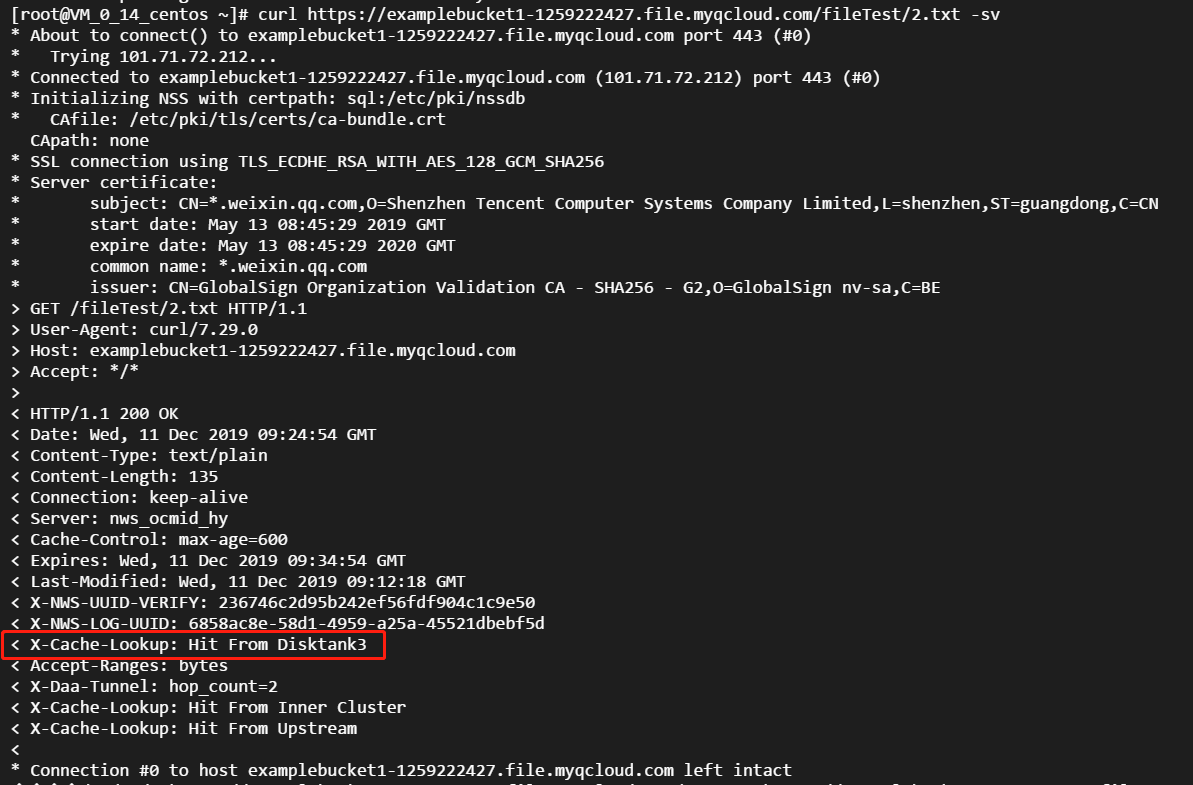
- Initiate requests to access resources
1.txtand2.txtrespectively. Nodes to be hit can be determined based on X-Cache-Lookup: Hit From Disktank3 and Server: NWS_SPMid, resources will be directly returned by the nodes: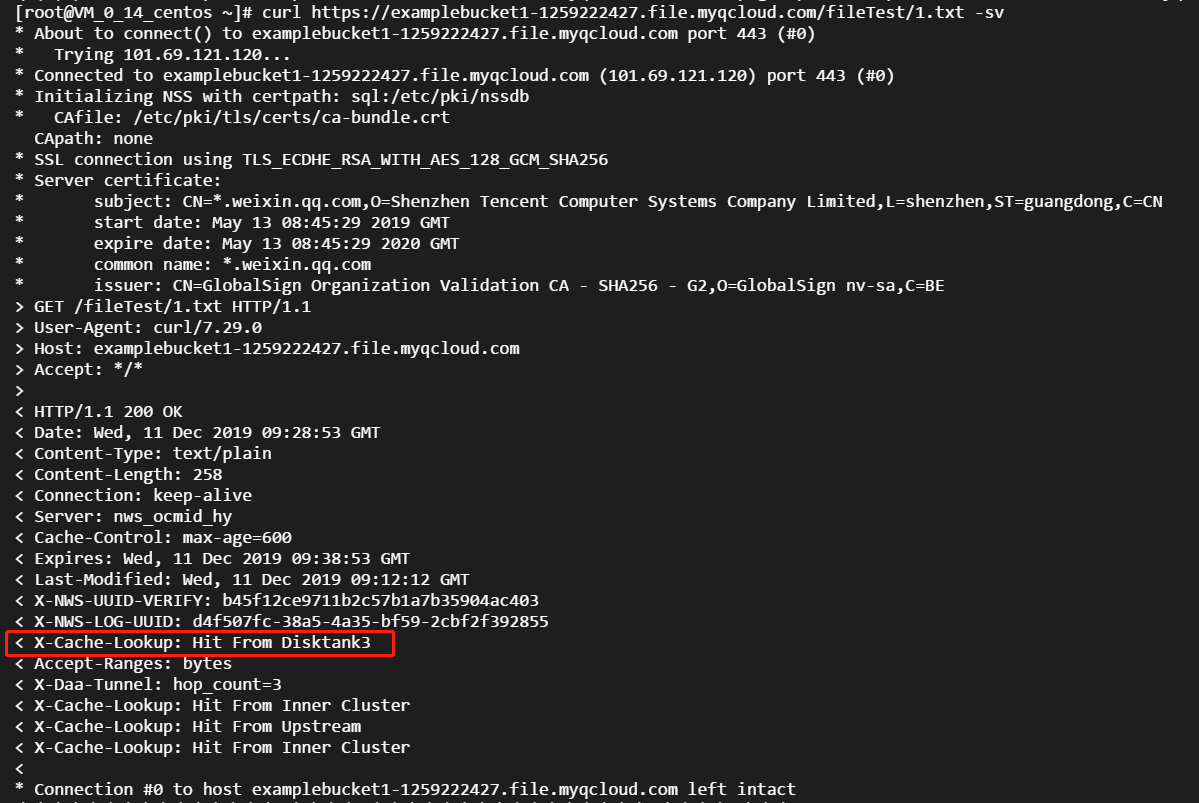
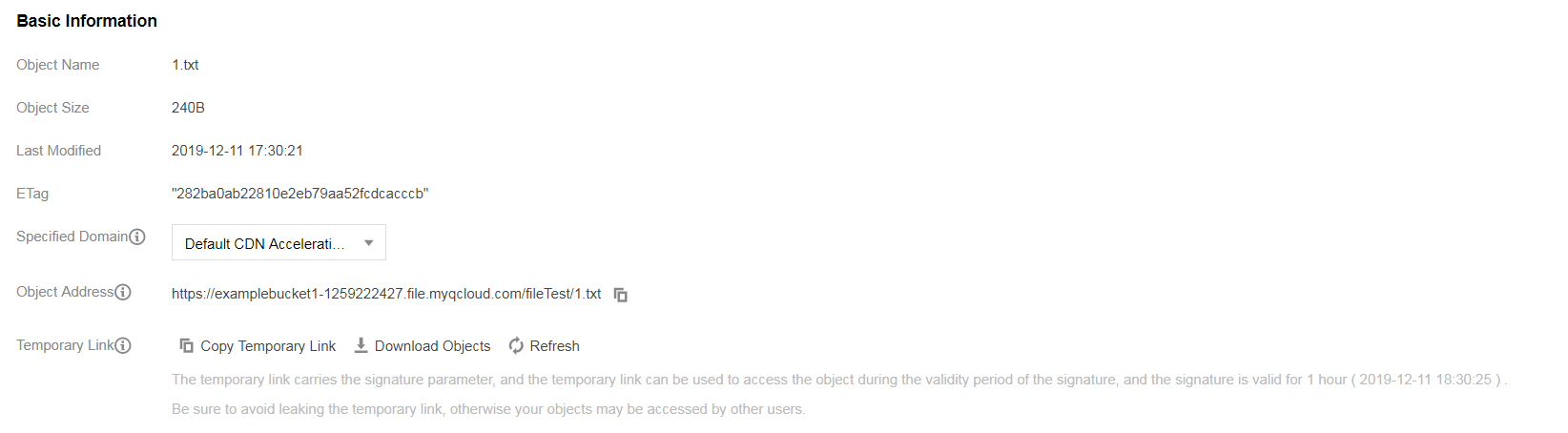
- On the origin server, replace
1.txtwith a file that has the same name, and the file’s last modified time changes, while2.txtstays the same: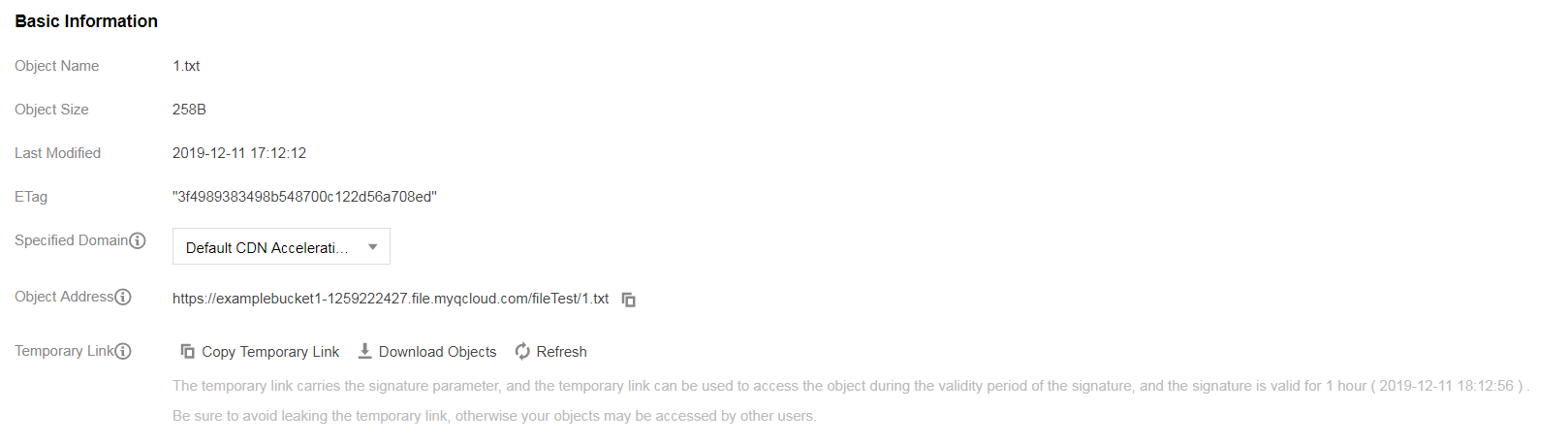
- Initiate requests again. As the cache has not expired, the legacy content of the
1.txtresource will be accessed: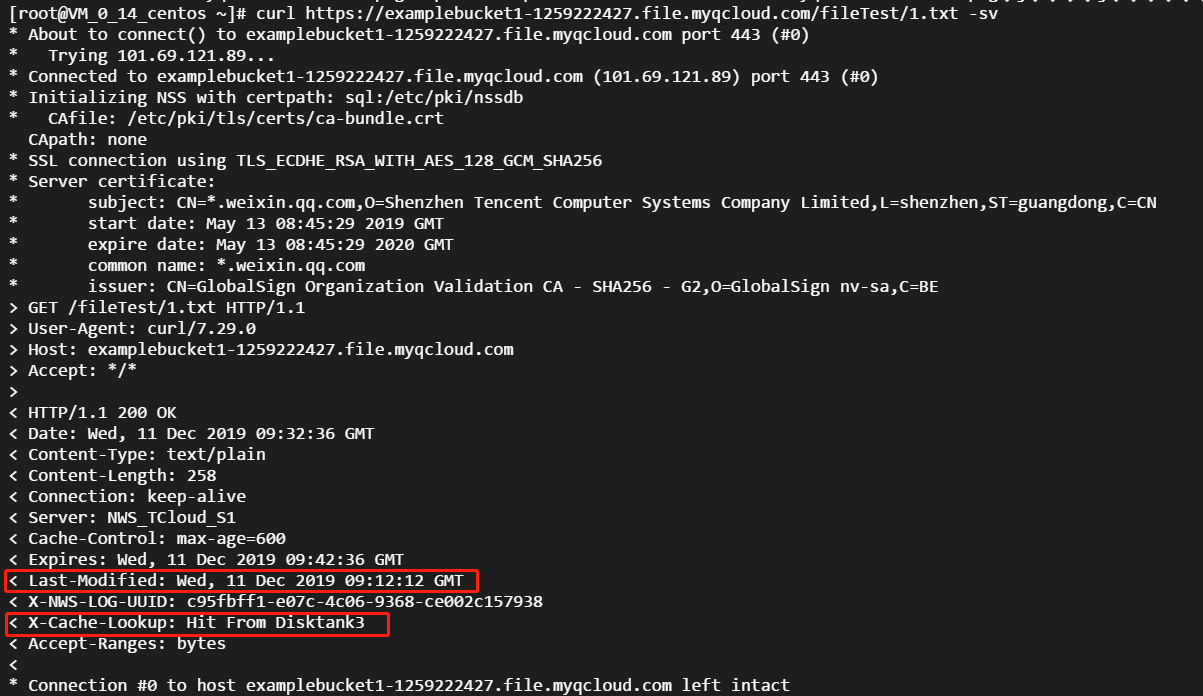
- Submit a directory purge task, select Purge Changed Resources, and wait for the purge to complete:
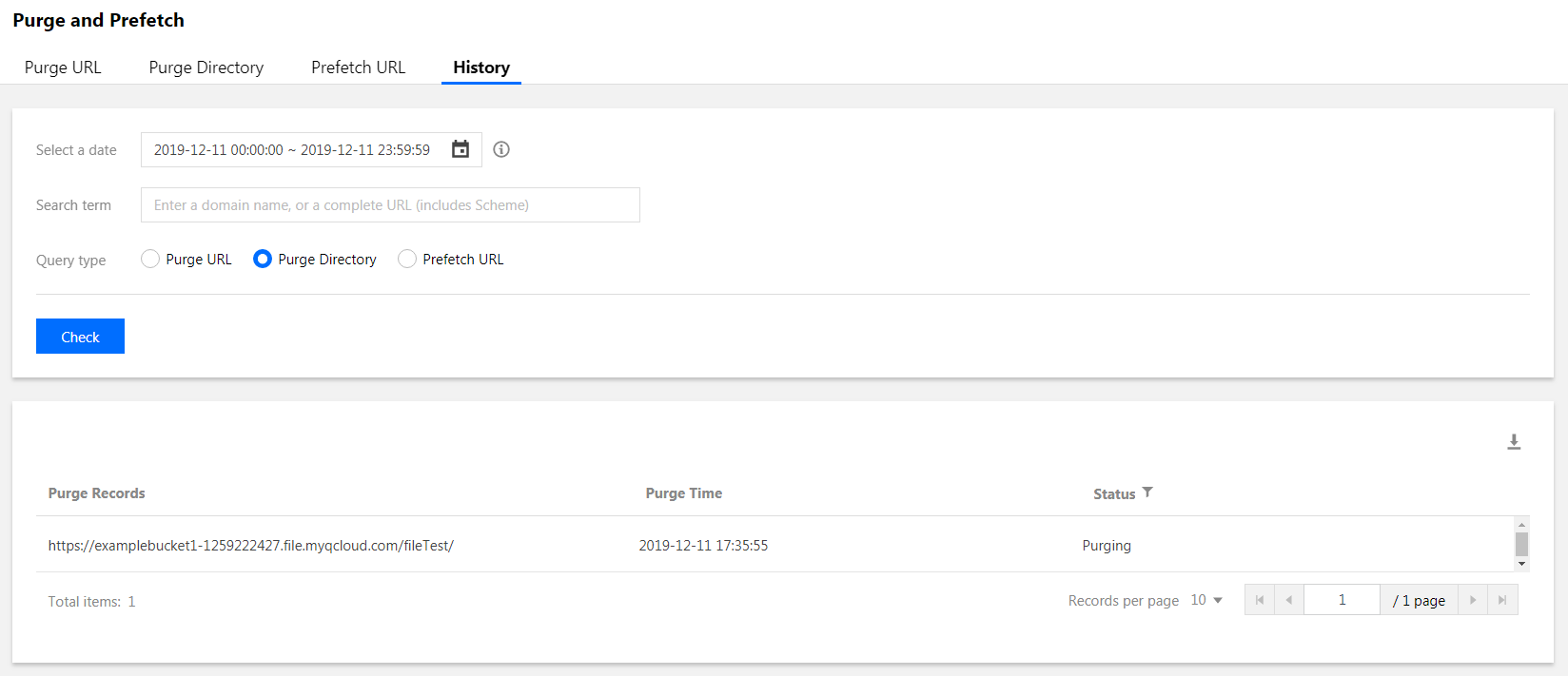
- After the purge is completed, because
Last-Modifiedof1.txthas been changed, the request will be forwarded to the origin server. As2.txthas not been changed, even after a directory purge task is submitted, it will still be hit by nodes and returned: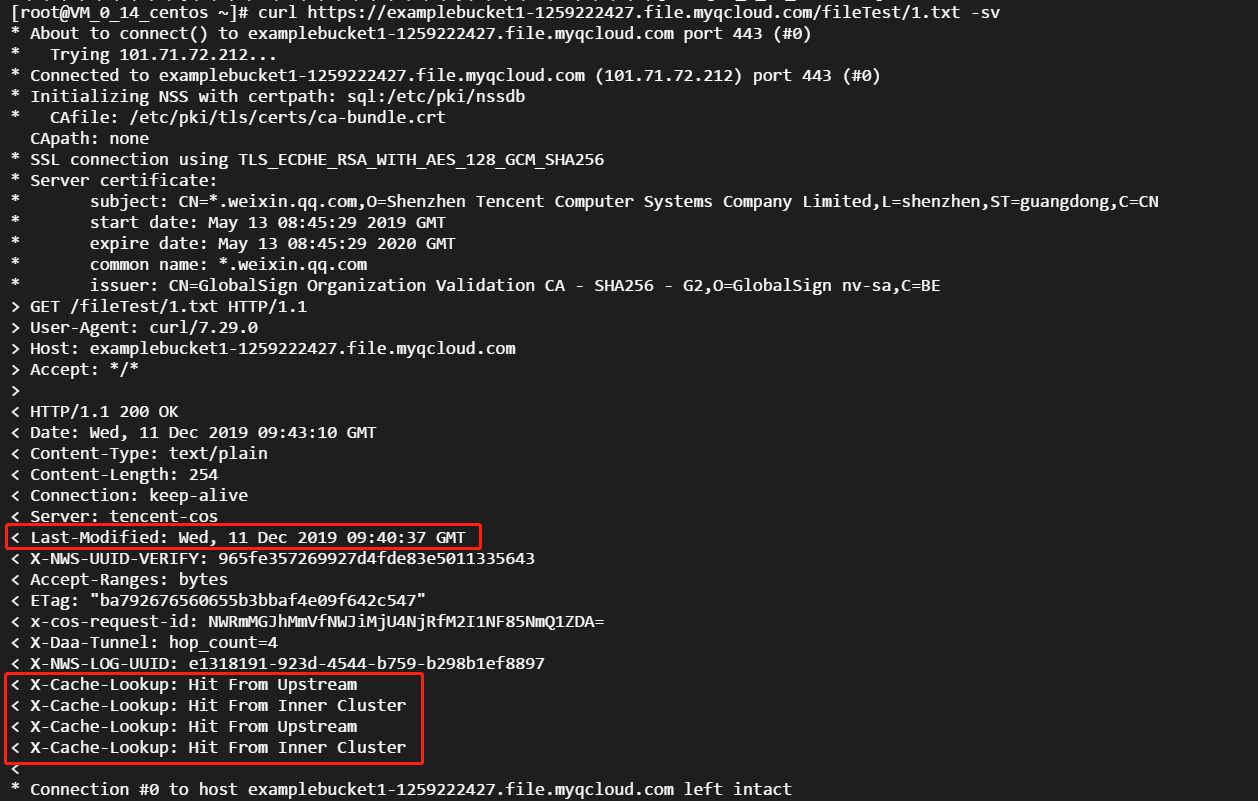
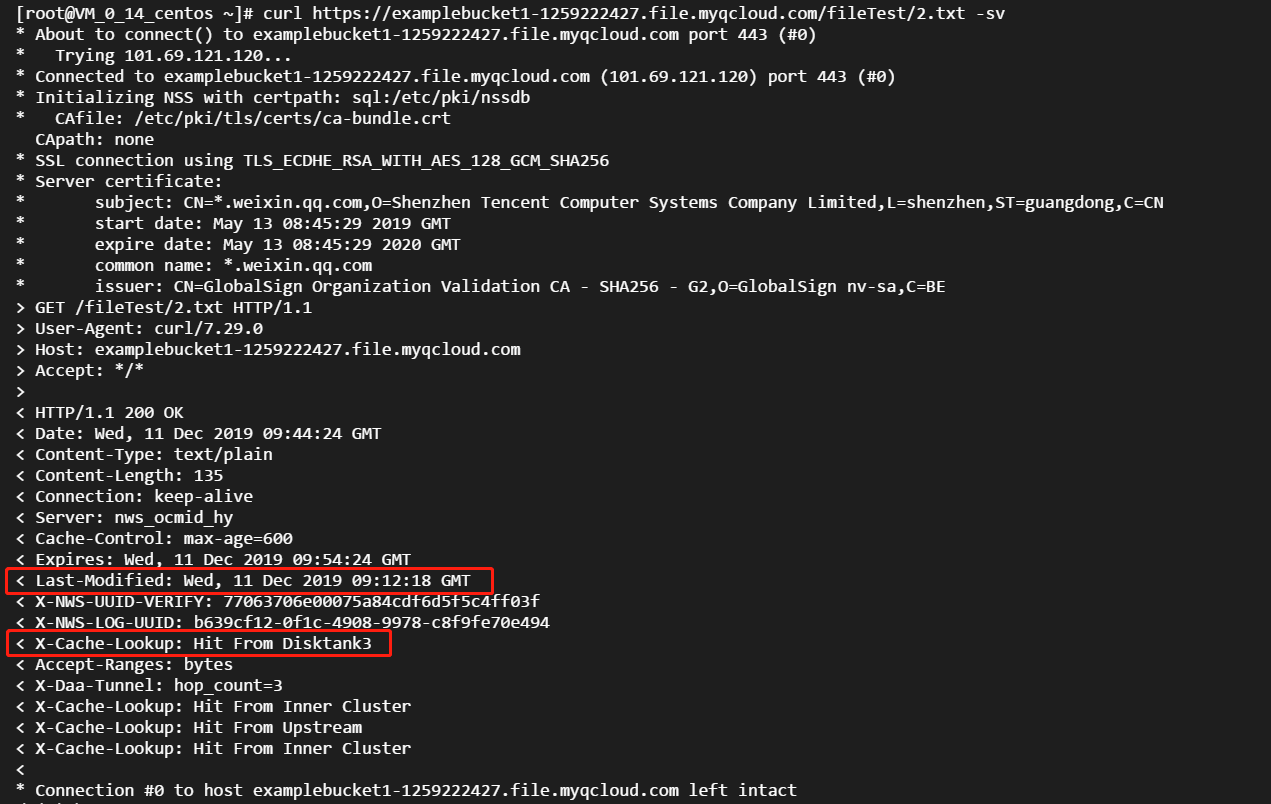

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?