基本概念
最后更新时间:2020-11-09 15:54:32
CNAME 记录
CNAME 记录是指域名解析中的别名记录(Canonical Name)。
例如,有一台服务器名为
host.example.com,它同时提供 WWW 和 MAIL 服务,为了方便用户访问服务。这台服务器可以在 DNS 解析服务商分别添加www.example.com和mail.example.com两个 CNAME,所有访问这两个 CNAME 的请求都会被转到host.example.com。CNAME 域名
CNAME 域名(CNAME domain name)在腾讯云 ECDN 控制台接入加速域名后,系统会为加速域名分配一个“CNAME 域名”(域名后缀为: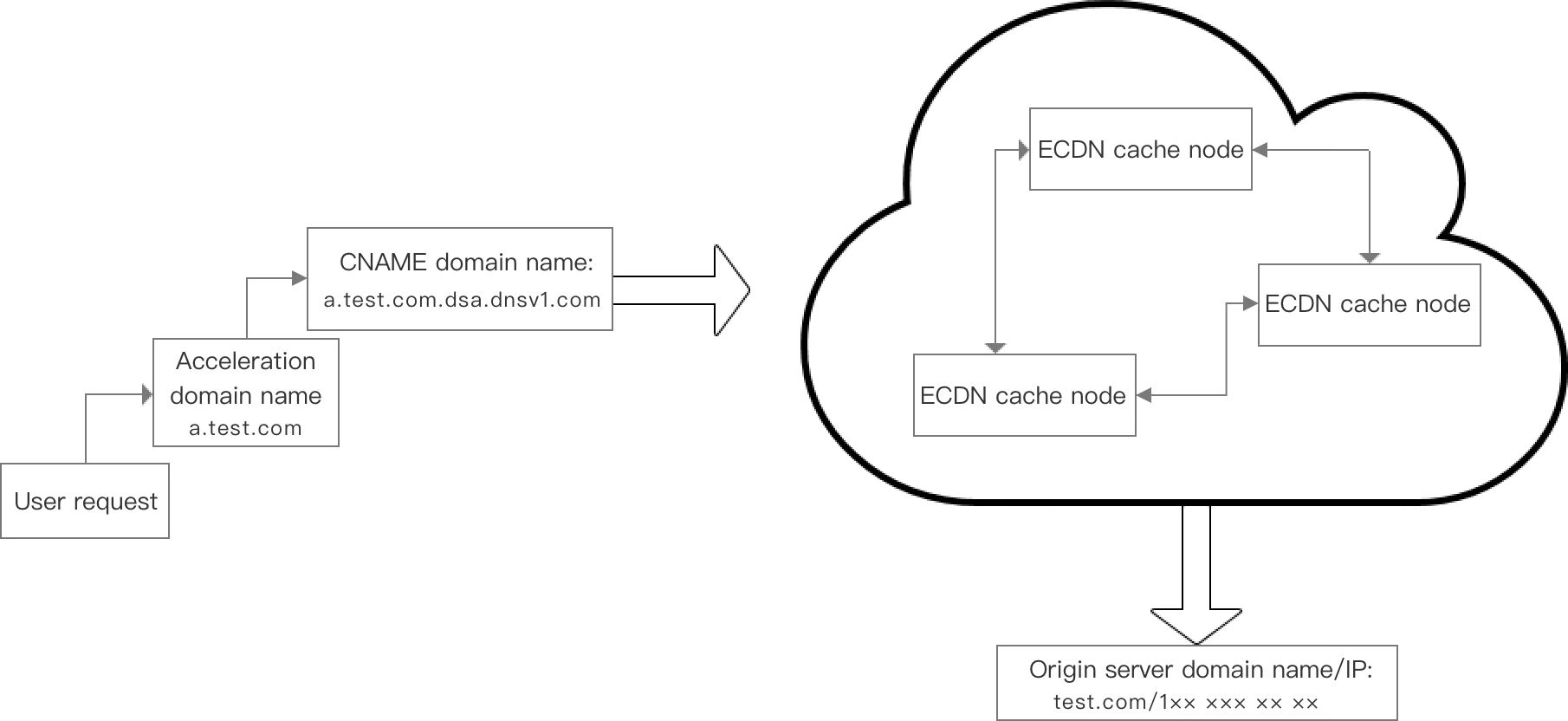
``.ecdn.dnsv1.com``)。用户需要在域名服务商处,添加一条 CNAME 记录,记录生效后,域名解析的工作就正式转向腾讯云 ECDN,该域名所有的请求都将转向腾讯云 ECDN 的节点。
下图描述了 源站域名/IP、加速域名、CNAME 域名,三者在用户发起一次请求到达源站过程中出现的次序:

加速域名
加速域名(accelerated domain name)区别于源站域名(domain name of origin server),是您提供给 ECDN 加速节点进行 CNAME 的域名。
注意:
源站域名不能与加速域名相同。
源站域名
源站域名(domain name of origin server)即客户的业务服务器的域名。
源站 IP
源站 IP(IP of origin server)即客户的业务服务器的 IP 地址。
静态内容
指用户多次访问某一资源,响应返回的数据都是相同的内容。例如:html、css 和 js 文件、图片、视频、软件安装包、apk 文件、压缩包文件等。
动态内容
指用户多次访问某一资源,响应返回的数据是不相同的内容。例如:API 接口、.jsp、.asp、.php、.perl 和 .cgi 文件等。
中间源
是位于业务服务器(源站)和边缘节点的一个中间层的回源服务器,中间源服务器可缓存多个边缘节点的回源请求,对同一内容的请求,中间源服务器只需进行一次回源即可将内容分发至各边缘节点,降低业务服务器(即源站)的访问压力。
文档反馈

