Mobile Live Video Broadcasting
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- SDK Download
- Client API
- iOS&Mac
- Integration (No UI)
- Publishing
- Advanced Features
- API Documentation
- iOS
- Android
- Flutter
- Publishing
- FAQs
- OSS information
DocumentationMobile Live Video Broadcasting
Mic Connect
Last updated: 2024-12-16 14:38:05
Mic Connect
Last updated: 2024-12-16 14:38:05
Overview
In RTMP-based mic connect, the MLVB SDK offers the
MLVBLiveRoom component to help you quickly implement the mic connect feature. To better cater to your mic connect needs, Tencent Cloud has launched an RTC-based mic connect scheme and offered simpler and more flexible V2 APIs.MLVB’s V2 APIs support publishing/mic connect via RTMP as well as RTC. You can choose whichever scheme fits your needs. Below is a comparison of the two schemes.
Item | RTMP | RTC |
Protocol | Based on TCP | Based on UDP (more suitable for streaming) |
QoS | Poor adaptability to bad network connection | Video streaming unaffected with 50% packets loss; audio mic connect unaffected with 70% packets loss |
Region | Chinese mainland | Worldwide |
Tencent Cloud products used | MLVB, CSS | MLVB, CSS, TRTC |
Price | 0.0028 USD/min |
Demonstration
The MLVB SDK provides new V2 APIs via
V2TXLivePusher (publishing) and V2TXLivePlayer (playback) to power larger-scale live streaming scenarios with greater flexibility and lower latency. Hosts can use the capabilities provided by the APIs for RTC-based publishing. Audience, by default, play streams via CDNs, whose cost is relatively low. To connect mic with hosts, audience can switch to RTC-based playback, which has lower latency and guarantees better interactive experience. To enable RTC-based mic connect, you must activate TRTC.
Below are the UI views of the MLVB-API-Example demo.UI demonstration
Before streaming
Host (Phone A) | Mic-connecting audience (Phone B) | Audience (Phone C) |
 Loading… |  Loading… |  Loading… |
Mic connecting
Host (Phone A) | Mic-connecting audience (Phone B) | Audience (Phone C) |
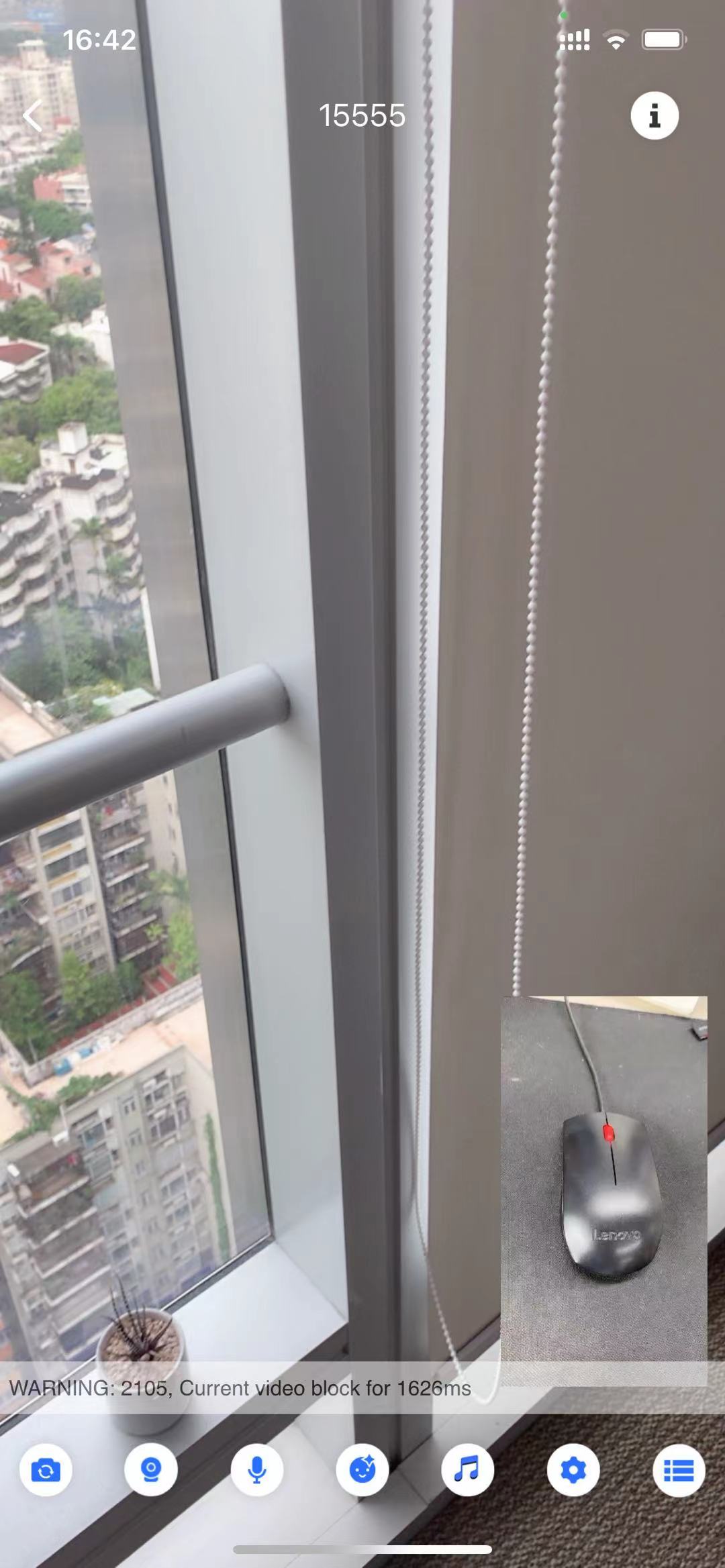 Loading… |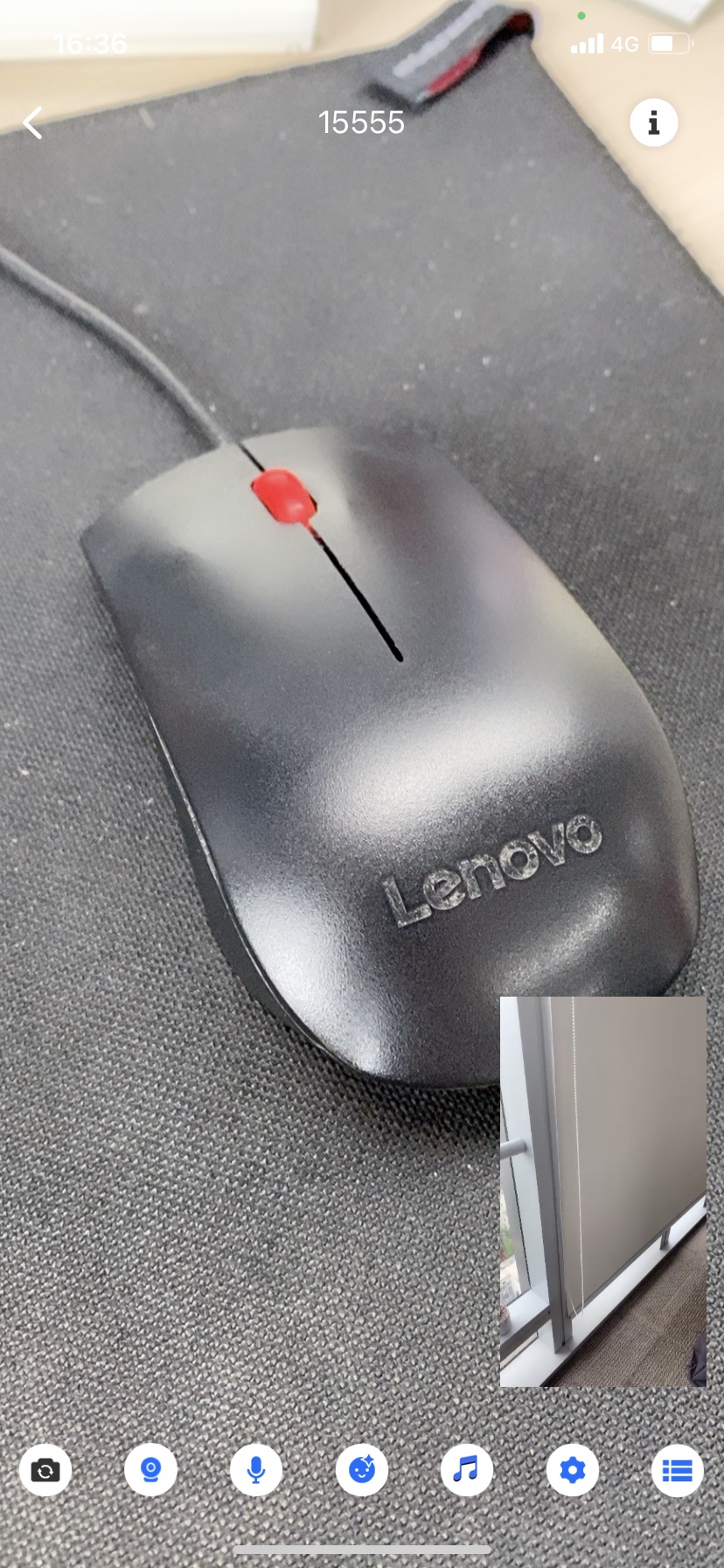  Loading… |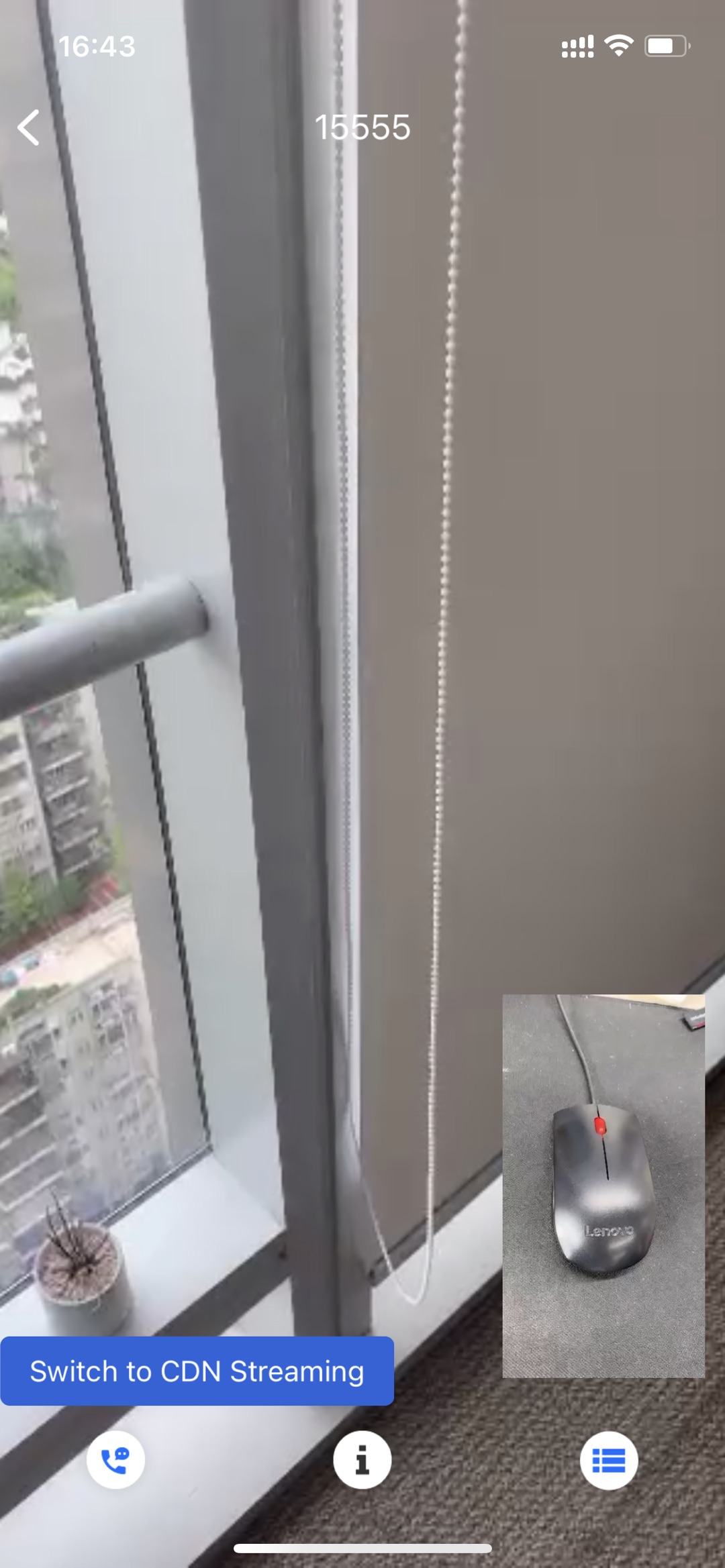  Loading… |
Implementation
As shown in the figure below, user A is the host, while user B and C are the audience. For user B to connect mic with user A, follow these steps:
User B: Start publishing using the
trtc:// protocol and switch from CDN playback to the ultra-low-latency trtc:// protocol.User A: Start playing user B’s stream and initiate a stream mixing task to mix his or her stream with user B’s.
User C can continue to play streams via a CDN and will see the mic connecting images of user A and B after stream mixing.
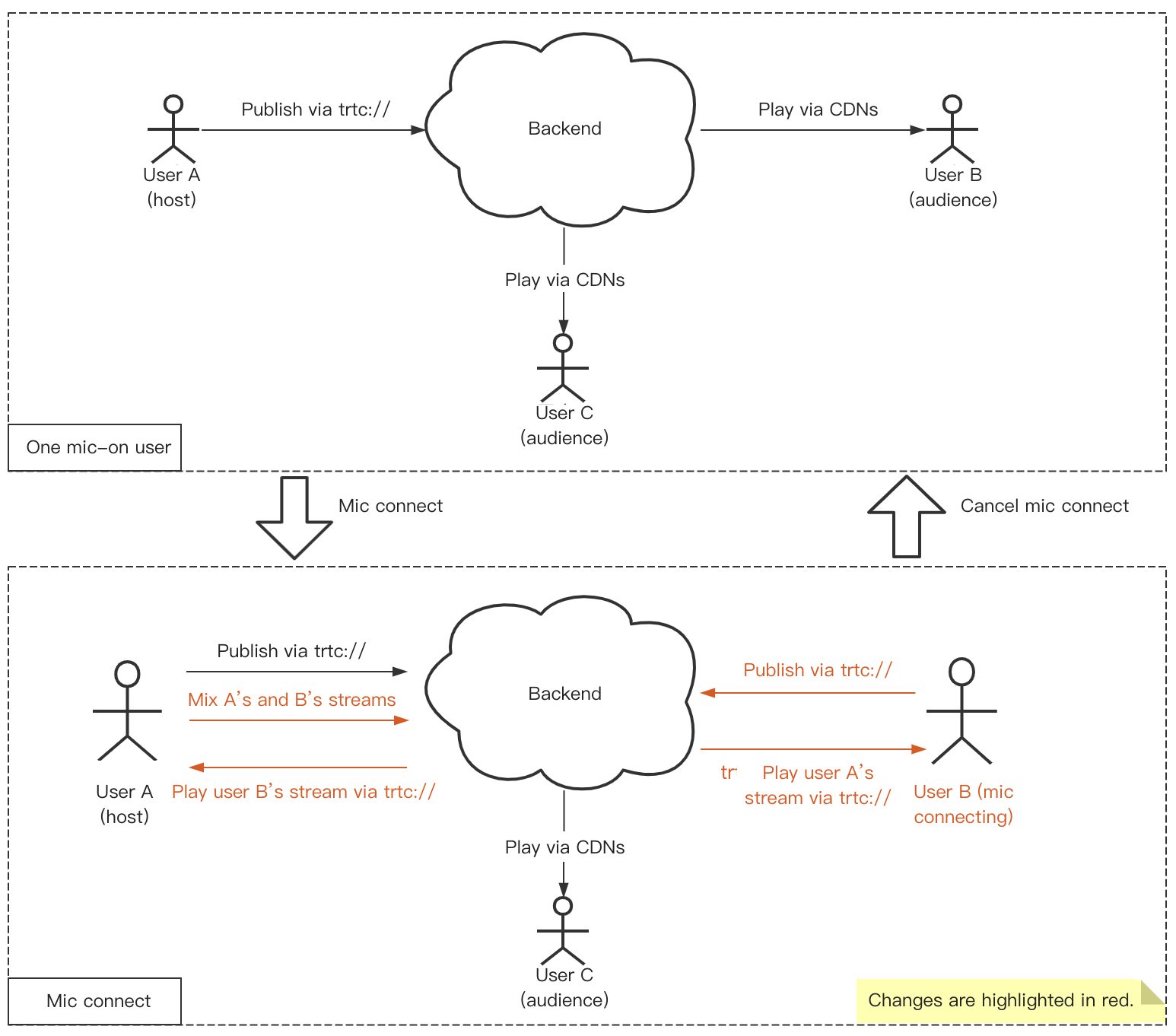
1. Publish streams via RTC (host)
User A calls
V2TXLivePusher to publish a stream. For how to splice a publishing URL, please see Publish/Playback URL.V2TXLivePusher pusher = new V2TXLivePusherImpl(this, V2TXLiveMode.TXLiveMode_RTC);pushURLA= "trtc://cloud.tencent.com/push/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=A&usersig=xxx";pusher.startPush(pushURLA);
V2TXLivePusher *pusher = [[V2TXLivePusher alloc] initWithLiveMode:V2TXLiveMode_RTC];NSString *pushURLA = @"trtc://cloud.tencent.com/push/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=A&usersig=xxx";[pusher startPush:pushURLA];
2. Play streams via CDNs (audience)
All audience call
V2TXLivePlayer to play user A’s stream. For how to splice a playback URL, please see Publish/Playback URL.V2TXLivePlayer player = new V2TXLivePlayerImpl(mContext);/*** Streams are played via CDNs in the example. The protocols supported include FLV, HLS, and WebRTC. Standard protocols such as FLV and HLS are more cost-effective, but WebRTC delivers interactive experience with lower latency.* playURLA= "http://3891.liveplay.myqcloud.com/live/streamidA.flv";* playURLA= "http://3891.liveplay.myqcloud.com/live/streamidA.hls";* playURLA= "webrtc://3891.liveplay.myqcloud.com/live/streamidA"*/player.startPlay(playURLA);
V2TXLivePlayer * player = [[V2TXLivePlayer alloc] init];/*** Streams are played via CDNs in the example. The protocols supported include FLV, HLS, and WebRTC. Standard protocols such as FLV and HLS are more cost-effective, but WebRTC delivers interactive experience with lower latency.* NSString *playURLA= @"http://3891.liveplay.myqcloud.com/live/streamidA.flv";* NSString *playURLA= @"http://3891.liveplay.myqcloud.com/live/streamidA.hls";* NSString *playURLA= @"webrtc://3891.liveplay.myqcloud.com/live/streamidA"*/[player setRenderView:view];[player startPlay:playURLA];
3. Initiate mic connect (audience)
User B (the mic-connecting user B) calls
V2TXLivePusher to publish streams.V2TXLivePusher pusher = new V2TXLivePusherImpl(this,V2TXLiveMode.TXLiveMode_RTC);pushURLB= "trtc://cloud.tencent.com/push/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=B&usersig=xxx";pusher.startPush(pushURLB);
V2TXLivePusher *pusher = [[V2TXLivePusher alloc] initWithLiveMode:V2TXLiveMode_RTC];NSString *pushURLB = @"trtc://cloud.tencent.com/push/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=B&usersig=xxx";[pusher startPush:pushURLB];
4. Start mic connect
User A calls
V2TXLivePlayer to play the stream of the mic-connecting user B via RTC.V2TXLivePlayer player = new V2TXLivePlayerImpl(mContext);playURLB= "trtc://cloud.tencent.com/play/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=B&usersig=xxx&appscene=live";player.startPlay(playURLB);
V2TXLivePlayer * player = [[V2TXLivePlayer alloc] init];NSString* playURLB = @"trtc://cloud.tencent.com/play/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=B&usersig=xxx&appscene=live";[player setRenderView:view];[player startPlay:playURLB];
The mic-connecting user B calls
V2TXLivePlayer to switch to RTC and play user A’s stream.V2TXLivePlayer player = new V2TXLivePlayerImpl(mContext);playURLA= "trtc://cloud.tencent.com/play/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=A&usersig=xxx&appscene=live";player.startPlay(playURLA);
V2TXLivePlayer * player = [[V2TXLivePlayer alloc] init];NSString* playURLA = @"trtc://cloud.tencent.com/play/streamid?sdkappid=1400188888&userId=A&usersig=xxx&appscene=live";[player setRenderView:view];[player startPlay:playURLA];
User A and the mic-connecting user B start ultra-low-latency interaction.
5. Mix streams
To make sure that other audience can see the host and the mic-connecting user interact with each other, user A needs to initiate a stream mixing task to mix his or her stream and user B’s into one stream. Specifically, user A needs to call the
setMixTranscodingConfig API to start On-Cloud MixTranscoding, specifying audio-related parameters including audioSampleRate, audioBitrate, and audioChannels.
If your application involves the transfer of video data, you must also set video-related parameters such as videoWidth, videoHeight, videoBitrate, and videoFramerate.Sample code:
V2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveTranscodingConfig config = new V2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveTranscodingConfig();// Set the resolution to 720 × 1280 px, bitrate 1500 Kbps, and frame rate 20 fpsconfig.videoWidth = 720;config.videoHeight = 1280;config.videoBitrate = 1500;config.videoFramerate = 20;config.videoGOP = 2;config.audioSampleRate = 48000;config.audioBitrate = 64;config.audioChannels = 2;config.mixStreams = new ArrayList<>();// Position of the camera image of the hostV2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveMixStream local = new V2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveMixStream();local.userId = "localUserId";local.streamId = null; // `streamID` is required for the remote user but not for the local userlocal.x = 0;local.y = 0;local.width = videoWidth;local.height = videoHeight;local.zOrder = 0; // When `zOrder` is set to `0`, it indicates that the host’s image is displayed at the bottomconfig.mixStreams.add(local);// Image position of the mic-connecting userV2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveMixStream remoteA = new V2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveMixStream();remoteA.userId = "remoteUserIdA";remoteA.streamId = "remoteStreamIdA"; // `streamID` is required for the remote user but not for the local userremoteA.x = 400; // For reference onlyremoteA.y = 800; // For reference onlyremoteA.width = 180; // For reference onlyremoteA.height = 240; // For reference onlyremoteA.zOrder = 1;config.mixStreams.add(remoteA);// Image position of the mic-connecting userV2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveMixStream remoteB = new V2TXLiveDef.V2TXLiveMixStream();remoteB.userId = "remoteUserIdB";remoteB.streamId = "remoteStreamIdB"; // `streamID` is required for the remote user but not for the local userremoteB.x = 400; // For reference onlyremoteB.y = 800; // For reference onlyremoteB.width = 180; // For reference onlyremoteB.height = 240; // For reference onlyremoteB.zOrder = 1;config.mixStreams.add(remoteB);// Start On-Cloud MixTranscodingpusher.setMixTranscodingConfig(config);
V2TXLiveTranscodingConfig *config = [[V2TXLiveTranscodingConfig alloc] init];// Set the resolution to 720 × 1280 px, bitrate 1500 Kbps, and frame rate 20 fpsconfig.videoWidth = 720;config.videoHeight = 1280;config.videoBitrate = 1500;config.videoFramerate = 20;config.videoGOP = 2;config.audioSampleRate = 48000;config.audioBitrate = 64;config.audioChannels = 2;// Position of the camera image of the hostV2TXLiveMixStream *local = [[V2TXLiveMixStream alloc] init];local.userId = @"localUserId";local.streamId = nil; // `streamID` is required for the remote user but not for the local userlocal.x = 0;local.y = 0;local.width = videoWidth;local.height = videoHeight;local.zOrder = 0; // When `zOrder` is set to `0`, it indicates that the host’s image is displayed at the bottom// Image position of the mic-connecting userV2TXLiveMixStream *remoteA = [[V2TXLiveMixStream alloc] init];remoteA.userId = @"remoteUserIdA";remoteA.streamId = @"remoteStreamIdA"; // `streamID` is required for the remote user but not for the local userremoteA.x = 400; // For reference onlyremoteA.y = 800; // For reference onlyremoteA.width = 180; // For reference onlyremoteA.height = 240; // For reference onlyremoteA.zOrder = 1;// Image position of the mic-connecting userV2TXLiveMixStream *remoteB = [[V2TXLiveMixStream alloc] init];remoteB.userId = @"remoteUserIdB";remoteB.streamId = @"remoteStreamIdB"; // `streamID` is required for the remote user but not for the local userremoteB.x = 400; // For reference onlyremoteB.y = 800; // For reference onlyremoteB.width = 180; // For reference onlyremoteB.height = 240; // For reference onlyremoteB.zOrder = 1;// Specify the streams to mixconfig.mixStreams = @[local,remoteA,remoteB];// Start On-Cloud MixTranscodingpusher.setMixTranscodingConfig(config);
Note:
In On-Cloud MixTranscoding, the default ID for the post-mixing stream is the stream ID of the user who initiates the stream mixing task. To specify an ID for the post-mixing stream, pass in the ID when calling the API.
After the above steps are performed, other audience will be able to see user A and B interact with each other.
Note:
Since you need to maintain room and user status by yourself, the new RTC-based mic connect scheme may seem more complicated than the old one. In fact, there isn’t an always better scheme, only one that better suits your needs.
You can stick to the old mic connect scheme if your application scenarios do not require low latency or high concurrency.
If you want to use V2 APIs without having to manage a room and users, try using Tencent Cloud’s IM SDK to implement the necessary logic.
Billing
FAQs
1. Why is publishing and playback using the same streamid on the same device possible with TXLivePusher and TXLivePlayer but not with V2TXLivePusher and V2TXLivePlayer?
V2TXLivePusher and V2TXLivePlayer are based on Tencent Cloud’s TRTC protocol. This is a UDP-based private protocol that features ultra-low latency and does not support using the same streamid for ultra-low-latency publishing and playback on the same device. We have determined that it’s not necessary to support this given the current use cases, but may consider optimizing the protocol in the future.2. What are the parameters mentioned in Activate TRTC above?
SDKAppID identifies your application, and UserID your user. UserSig is a security signature calculated based on the two parameters using the HMAC SHA256 encryption algorithm. Attackers cannot use your Tencent Cloud traffic without authorization as long as they cannot forge a UserSig. UserSig calculation involves hashing crucial information such as SDKAppID, UserID, and ExpireTime, as shown below.// UserSig formula, in which `secretkey` is the key used to calculate UserSigusersig = hmacsha256(secretkey, (userid + sdkappid + currtime + expire +base64(userid + sdkappid + currtime + expire)))
3. How can I set audio or video quality using V2TXLivePusher and V2TXLivePlayer?
We provide APIs for the setting of audio and video quality. For details, please see setAudioQuality() and setVideoQuality:resolutionMode:().
4. What does the error code -5 mean?
The error code
-5 means failure to call an API due to invalid license. The enumerated value is V2TXLIVE_ERROR_INVALID_LICENSE. For other error codes, please see V2TXLiveCode.5. What is the typical latency of RTC-based mic connect?
In the new RTC-based mic connect scheme, the mic connect latency is lower than 200 ms, and the latency for hosts and audience is 100-1,000 ms.
6. What should I do if the 404 error occurs when I try to play streams via CDNs after successfully publishing streams over RTC?
Check if you have enabled TRTC’s relayed push feature. The feature is needed because, after publishing streams via RTC, to enable CDN playback, you need to relay the streams to CDNs.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
