Android
最后更新时间:2025-12-10 11:45:00
业务流程
本节汇总了语聊房中一些常见的业务流程,帮助您更好地理解整个场景的实现流程。
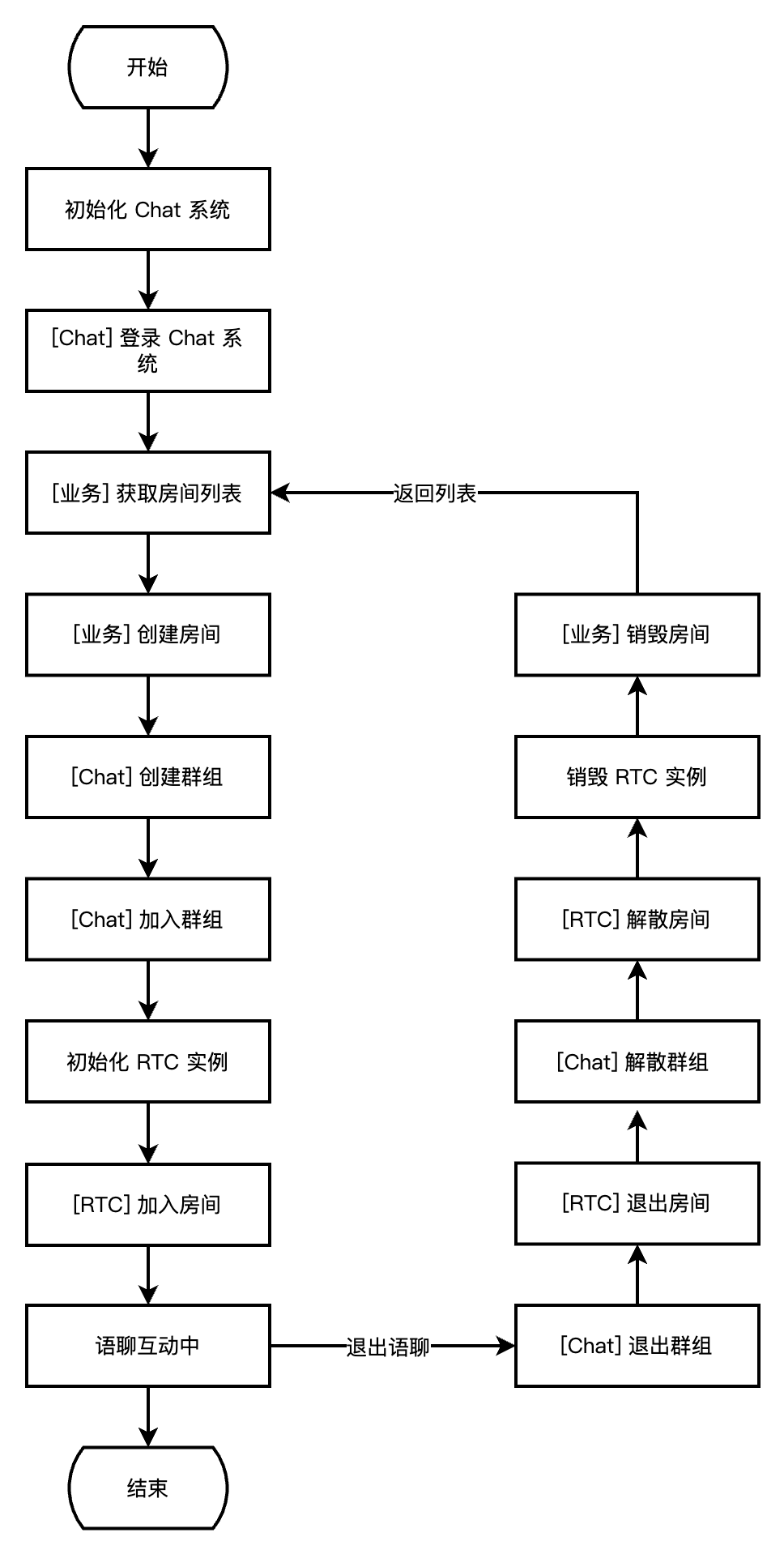
下图展示了房间管理流程,包含创建、加入、退出、解散房间的实现流程。

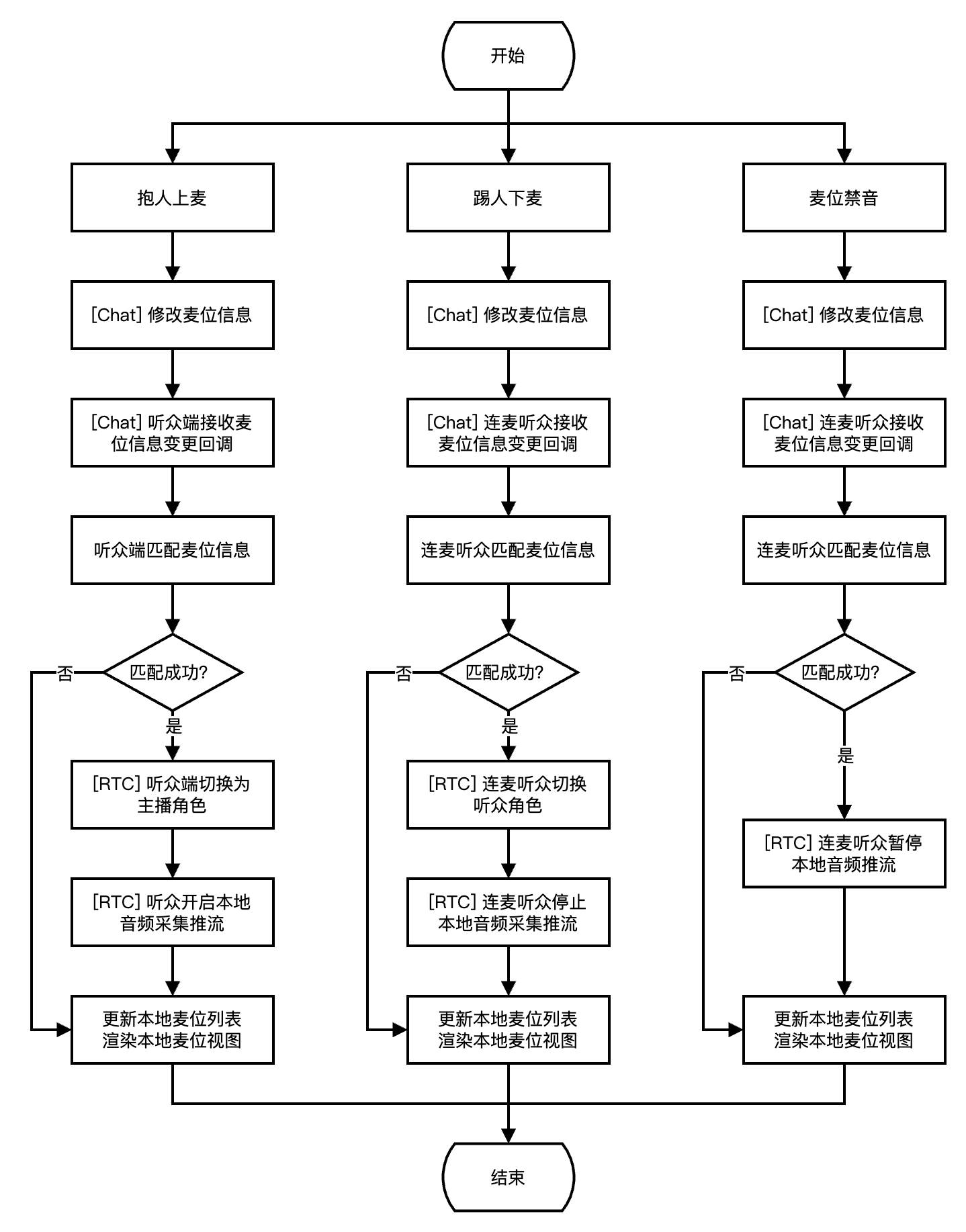
下图展示了房主麦位管理流程,包含抱人上麦、踢人下麦、麦位禁音的实现流程。

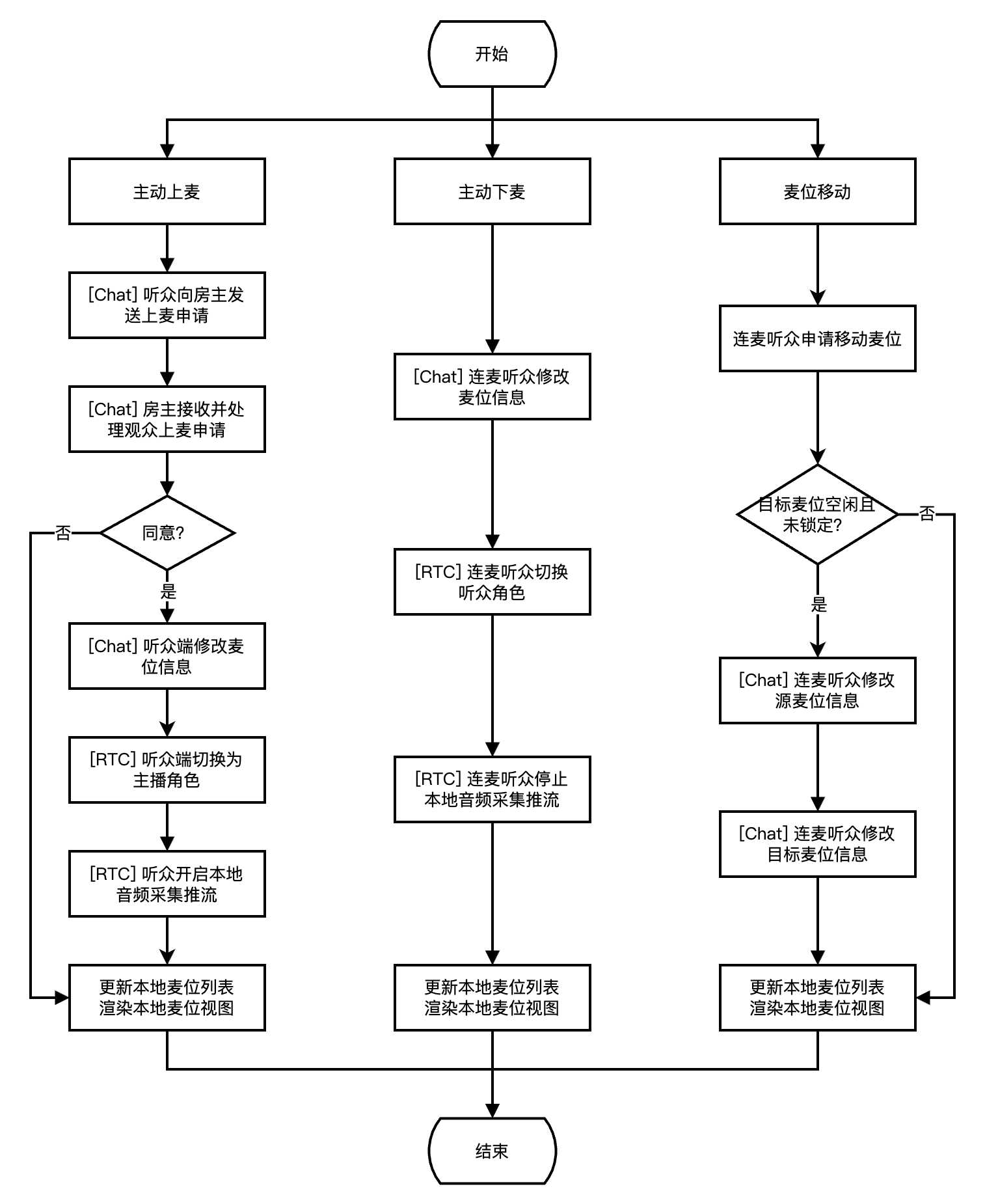
下图展示了听众麦位管理流程,包含主动上麦、主动下麦、麦位移动的实现流程。

接入准备
步骤一:开通服务
1. 首先您需要登录 控制台 创建应用,创建一个RTC Engine 的应用,然后再创建一个 Chat 应用。
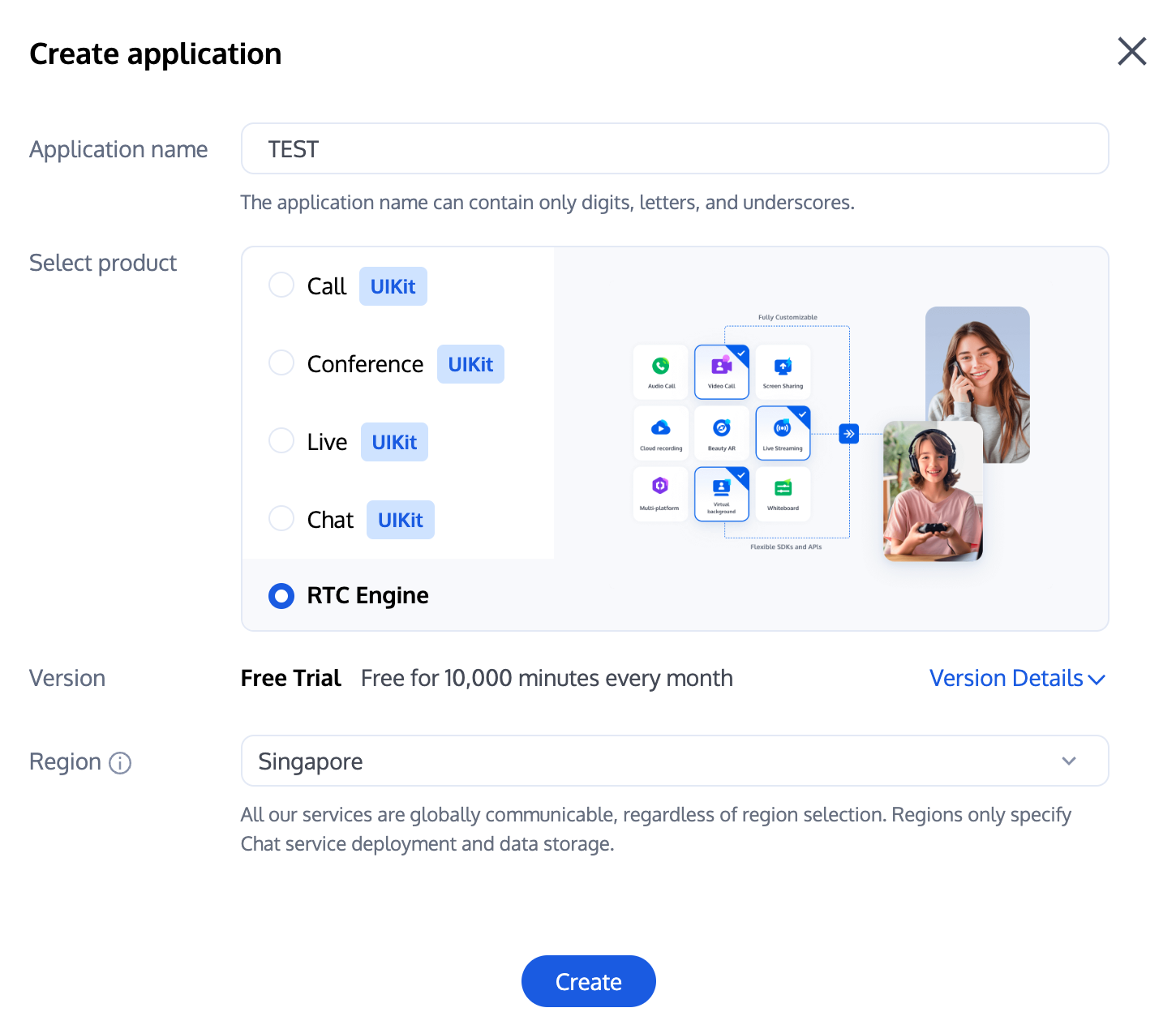

说明:
建议创建两个应用分别用于测试环境和生产环境,一年内每个账号(UIN)每月赠送10,000分钟免费时长。
RTC Engine 包月套餐分为体验版(默认)、轻量版、标准版、专业版,可解锁不同的增值功能服务,详情可见 版本功能与包月套餐说明。
2. 创建应用完毕之后,您可以在应用管理-应用概览栏目看到该应用的基本信息,其中需要您保管好 SDKAppID、SDKSecretKey 便于后续使用,同时应避免密钥泄露造成流量盗刷。


步骤二:导入 SDK
RTC Engine SDK 和 Chat SDK 已经发布到 mavenCentral 库,您可以通过配置 gradle 自动下载更新。
1. 在 dependencies 中添加合适版本 SDK 的依赖。
dependencies {// TRTC 精简版 SDK, 包含 TRTC 和直播播放两项功能implementation 'com.tencent.liteav:LiteAVSDK_TRTC:latest.release'// 添加 Chat SDK,推荐填写最新的版本号implementation 'com.tencent.imsdk:imsdk-plus:Version number'// 如果您需要添加 Quic 插件,请取消下一行的注释(注意:要求插件版本号和 Chat SDK 版本号相同)// implementation 'com.tencent.imsdk:timquic-plugin:Version number'}
说明:
除了推荐的自动加载方式,您还可以选择下载 SDK 并手动导入,详见 手动集成 RTC Engine SDK 和 手动集成 Chat SDK。
Quic 插件,提供 axp-quic 多路传输协议,弱网抗性更优,网络丢包率达到 70% 的条件下,仍然可以提供服务。仅对专业版、专业版 plus 和企业版用户开放,请 购买专业版 、专业版 plus 或企业版后可使用。为确保功能正常使用,请将终端 SDK 更新至7.7.5282及其以上的版本。
2. 在 defaultConfig 中,指定 App 使用的 CPU 架构。
defaultConfig {ndk {abiFilters "armeabi-v7a", "arm64-v8a"}}
说明:
RTC Engine SDK 支持 armeabi/armeabi-v7a/arm64-v8a 架构,另外支持模拟器专用的 x86/x86_64 架构。
Chat SDK 支持 armeabi-v7a/arm64-v8a/x86/x86_64 架构,为了缩减安装包体积,您可以选择只打包部分架构的 SO 文件。
步骤三:工程配置
1. 在 AndroidManifest.xml 中配置 App 权限,语聊场景下 RTC Engine SDK 及 Chat SDK 需要以下权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
注意:
RTC Engine SDK 没有内置权限申请逻辑,需要您自行声明相应的权限和特性,部分权限(如存储、录音等)还需要在运行时动态申请。
若 Android 项目
targetSdkVersion 为 31 或者目标设备涉及到 Android 12 及更高系统版本,官方要求需要在代码中动态申请 android.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT 权限,以正常使用蓝牙功能,具体信息请参见 蓝牙权限。2. 由于我们在 SDK 内部使用了 Java 的反射特性,需要您在 proguard-rules.pro 文件中将 RTC Engine SDK 相关类加入不混淆名单。
-keep class com.tencent.** { *; }
接入过程
步骤一:生成鉴权凭证
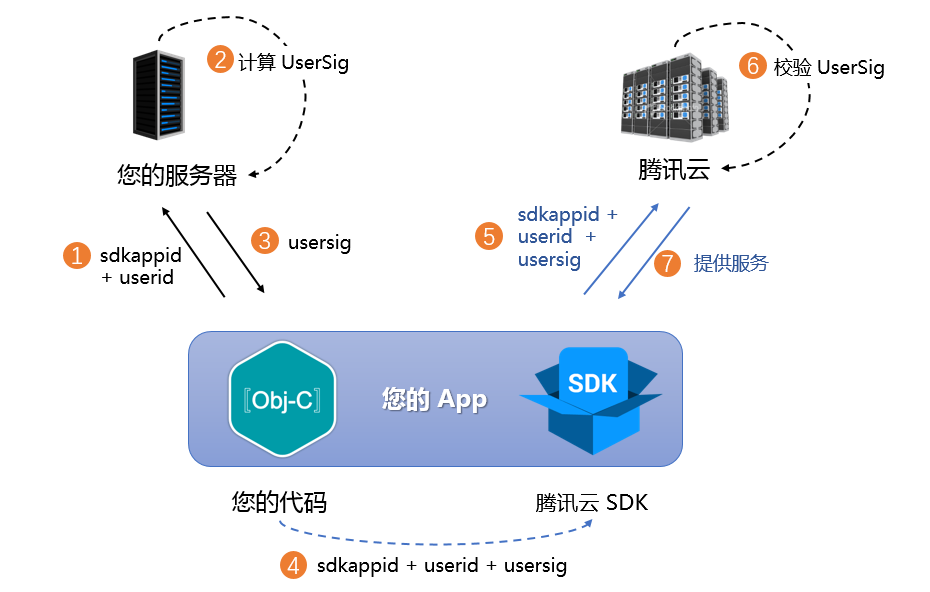
UserSig 是腾讯实时通信服务设计的一种安全保护签名,目的是为了阻止恶意攻击者盗用您的云服务使用权。RTC Engine、Chat 服务都采用了该套安全保护机制,RTC Engine 在进房时鉴权,Chat 在登录时鉴权。
正式运行阶段:推荐安全等级更高的服务端计算 UserSig 方案,防止客户端被逆向破解泄露密钥。
具体实现流程如下:
1. 您的 App 在调用 SDK 的初始化函数之前,首先要向您的服务器请求 UserSig。
2. 您的服务器根据 SDKAppID 和 UserID 计算 UserSig。
3. 服务器将计算好的 UserSig 返回给您的 App。
4. 您的 App 将获得的 UserSig 通过特定 API 传递给 SDK。
5. SDK 将 SDKAppID + UserID + UserSig 提交给腾讯云服务器进行校验。
6. 腾讯云校验 UserSig,确认合法性。
7. 校验通过后,会向 Chat SDK 提供即时通信服务、RTC Engine SDK 提供实时音视频服务。

注意:
调试跑通阶段的本地 UserSig 计算方式不推荐应用到线上环境,容易被逆向破解导致密钥泄露。
我们提供了多个语言版本(Java/Go/PHP/Node.js/Python/C#/C++)的 UserSig 服务端计算源代码,详见 服务端计算 UserSig。
步骤二:初始化与监听
时序图

1. Chat SDK 初始化与添加事件监听器。
// 添加事件监听器V2TIMManager.getInstance().addIMSDKListener(imSdkListener);// 初始化 Chat SDK,调用这个接口后,可以立即调用登录接口V2TIMManager.getInstance().initSDK(context, sdkAppID, null);// SDK 初始化后会抛出一些事件,例如连接状态、登录票据过期等private V2TIMSDKListener imSdkListener = new V2TIMSDKListener() {@Overridepublic void onConnecting() {Log.d(TAG, "Chat SDK 正在连接到腾讯云服务器");}@Overridepublic void onConnectSuccess() {Log.d(TAG, "Chat SDK 已经成功连接到腾讯云服务器");}};// 移除事件监听器V2TIMManager.getInstance().removeIMSDKListener(imSdkListener);// 反初始化 Chat SDKV2TIMManager.getInstance().unInitSDK();
说明:
如果您的应用生命周期跟 SDK 生命周期一致,退出应用前可以不进行反初始化。若您只在进入特定界面后才初始化 SDK,退出界面后不再使用,可以对 SDK 进行反初始化。
2. RTC Engine SDK 创建实例与设置事件监听器
// 创建 RTC Engine SDK 实例(单例模式)TRTCCloud mTRTCCloud = TRTCCloud.sharedInstance(context);// 设置事件监听器mTRTCCloud.setListener(trtcSdkListener);// 来自 SDK 的各类事件通知(比如:错误码,警告码,音视频状态参数等)private TRTCCloudListener trtcSdkListener = new TRTCCloudListener() {@Overridepublic void onError(int errCode, String errMsg, Bundle extraInfo) {Log.d(TAG, errCode + errMsg);}@Overridepublic void onWarning(int warningCode, String warningMsg, Bundle extraInfo) {Log.d(TAG, warningCode + warningMsg);}};// 移除事件监听器mTRTCCloud.setListener(null);// 销毁 RTC Engine SDK 实例(单例模式)TRTCCloud.destroySharedInstance();
说明:
步骤三:登录与登出
初始化 Chat SDK 后,您需要调用 SDK 登录接口验证账号身份,获得账号的功能使用权限。因此在使用其他功能之前,请务必确保登录成功,否则可能导致功能异常或不可用。如您仅需使用 RTC Engine 音视频服务,可忽略此步骤。
时序图

1. 登录。
// 登录:userID 可自定义,userSig 参考步骤一生成获取V2TIMManager.getInstance().login(userID, userSig, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {Log.i("imsdk", "success");}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {// 如果返回以下错误码,表示使用 UserSig 已过期,请您使用新签发的 UserSig 进行再次登录。// 1. ERR_USER_SIG_EXPIRED(6206)// 2. ERR_SVR_ACCOUNT_USERSIG_EXPIRED(70001)// 注意:其他的错误码,请不要在这里调用登录接口,避免 Chat SDK 登录进入死循环。Log.i("imsdk", "failure, code:" + code + ", desc:" + desc);}});
2. 登出。
// 登出V2TIMManager.getInstance().logout(new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {Log.i("imsdk", "success");}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {Log.i("imsdk", "failure, code:" + code + ", desc:" + desc);}});
说明:
如果您的应用生命周期跟 Chat SDK 生命周期一致,退出应用前可以不登出。若您只在进入特定界面后才使用 Chat SDK,退出界面后不再使用,可以进行登出操作和对 Chat SDK 进行反初始化。
步骤四:房间管理
时序图

1. 创建房间。
V2TIMManager.getInstance().createGroup(V2TIMManager.GROUP_TYPE_AVCHATROOM, groupID, groupName, new V2TIMValueCallback<String>() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess(String s) {// 创建群组成功}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {// 创建群组失败}});// 监听群组创建通知V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupCreated(String groupID) {// 群创建回调,groupID 为新创建群组的 ID}});
注意:
语聊房场景创建 Chat 群组需要选用直播群类型:
GROUP_TYPE_AVCHATROOM。RTC Engine 没有创建房间的 API,当用户要加入的房间不存在时,后台会自动创建一个房间。
2. 加入房间。
加入 Chat 群组。
V2TIMManager.getInstance().joinGroup(groupID, message, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 加入群组成功}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {// 加入群组失败}});// 监听加入群组事件V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onMemberEnter(String groupID, List<V2TIMGroupMemberInfo> memberList) {// 有人加入群组}});
加入 RTC Engine 房间。
private void enterRoom(String roomId, String userId) {TRTCCloudDef.TRTCParams params = new TRTCCloudDef.TRTCParams();// 以字符串房间号为例,建议和 Chat 群组号保持一致params.strRoomId = roomId;params.userId = userId;// 从业务后台获取到的 UserSigparams.userSig = getUserSig(userId);// 替换成您的 SDKAppIDparams.sdkAppId = SDKAppID;// 语聊互动场景进房需指定用户角色params.role = TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAudience;// 以语聊互动进房场景为例mTRTCCloud.enterRoom(params, TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_APP_SCENE_VOICE_CHATROOM);}// 进房结果事件回调@Overridepublic void onEnterRoom(long result) {if (result > 0) {// result 代表加入房间所消耗的时间(毫秒)Log.d(TAG, "Enter room succeed");} else {// result 代表进房失败的错误码Log.d(TAG, "Enter room failed");}}
注意:
RTC Engine 房间号分为整型
roomId 和字符串类型 strRoomId,两种类型的房间不互通,建议统一房间号类型。语聊互动场景进房时须指定用户角色(主播/观众),只有主播才有推流权限,如未指定则默认为主播角色。
语聊互动进房场景建议选用
TRTC_APP_SCENE_VOICE_CHATROOM。3. 退出房间。
退出 Chat 群组。
V2TIMManager.getInstance().quitGroup(groupID, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 退出群组成功}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {// 退出群组失败}});V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onMemberLeave(String groupID, V2TIMGroupMemberInfo member) {// 群成员离开回调}});
注意:
直播群(AVChatRoom)中,群主是不可以退群的,群主只能调用
dismissGroup 解散群组。退出 RTC Engine 房间。
private void exitRoom() {mTRTCCloud.stopLocalAudio();mTRTCCloud.exitRoom();}// 离开房间事件回调@Overridepublic void onExitRoom(int reason) {if (reason == 0) {Log.d(TAG, "主动调用 exitRoom 退出房间");} else if (reason == 1) {Log.d(TAG, "被服务器踢出当前房间");} else if (reason == 2) {Log.d(TAG, "当前房间整个被解散");}}
注意:
待 SDK 占用的所有资源释放完毕后,SDK 会抛出
onExitRoom 回调通知到您。如果您要再次调用
enterRoom 或者切换到其他的音视频 SDK,请等待 onExitRoom 回调到来后再执行相关操作。否则可能会遇到例如摄像头、麦克风设备被强占等各种异常问题。4. 解散房间。
解散 Chat 群组。
V2TIMManager.getInstance().dismissGroup(groupID, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 解散群组成功}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {// 解散群组失败}});V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupDismissed(String groupID, V2TIMGroupMemberInfo opUser) {// 群被解散回调}});
解散 RTC Engine 房间
服务端解散:RTC Engine 提供了 服务端解散房间 API
DismissRoom(区分数字房间 ID 和字符串房间 ID),您可以调用此接口把房间所有用户从房间移出,并解散房间。客户端解散:通过各个客户端的退出房间
exitRoom 接口,将房间内的所有主播和听众完成退房,退房后,根据 RTC Engine 房间生命周期规则,房间将会自动解散,详情请参见 退出房间。警告:
建议当您的一次直播任务结束后,可以调用解散房间 API 确保房间解散,防止听众意外进房导致产生非期望的费用。
步骤五:麦位管理
时序图

首先,我们可以创建一个用于保存麦位信息的 JavaBean。
public class SeatInfo implements Serializable {public static final transient int STATUS_UNUSED = 0;public static final transient int STATUS_USED = 1;public static final transient int STATUS_LOCKED = 2;// 座位状态,对应三种状态public int status;// 座位是否禁言public boolean mute;// 座位占用时,存储用户信息public String userId;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "TXSeatInfo{"+ "status=" + status+ ", mute=" + mute+ ", user='" + userId + '\\''+ '}';}}
1. 主动上麦。
主动上麦是指麦下听众向房主或管理员发送上麦申请,待接收到同意信令后上麦。如为自由上麦模式,则可忽略信令请求部分。
听众发送上麦请求。
// 听众发送上麦请求,userId 为主播 ID,data 可传入标识信令的 jsonprivate String sendInvitation(String userId, String data) {return V2TIMManager.getSignalingManager().invite(userId, data, true, null, 0, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int i, String s) {Log.e(TAG, "sendInvitation error " + i);}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {Log.i(TAG, "sendInvitation success ");}});}// 主播收到上麦请求, inviteID 为该条请求 ID,inviter 为请求者 IDV2TIMManager.getSignalingManager().addSignalingListener(new V2TIMSignalingListener() {@Overridepublic void onReceiveNewInvitation(String inviteID, String inviter,String groupId, List<String> inviteeList, String data) {Log.i(TAG, "received invitation: " + inviteID + " from " + inviter);}});
主播处理上麦请求。
// 同意上麦请求private void acceptInvitation(String inviteID, String data) {V2TIMManager.getSignalingManager().accept(inviteID, data, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int i, String s) {Log.e(TAG, "acceptInvitation error " + i);}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {Log.i(TAG, "acceptInvitation success ");}});}// 拒绝上麦请求private void rejectInvitation(String inviteID, String data) {V2TIMManager.getSignalingManager().reject(inviteID, data, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int i, String s) {Log.e(TAG, "rejectInvitation error " + i);}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {Log.i(TAG, "rejectInvitation success ");}});}
听众上麦。
如果主播同意听众的上麦请求,听众可以通过修改群属性的方式添加麦位信息,其他用户会收到群属性变更回调,更新本地麦位信息。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;// 同意上麦请求的回调V2TIMManager.getSignalingManager().addSignalingListener(new V2TIMSignalingListener() {@Overridepublic void onInviteeAccepted(String inviteID, String invitee, String data) {Log.i(TAG, "received accept invitation: " + inviteID + " from " + invitee);takeSeat(seatIndex);}});// 听众开始上麦private void takeSeat(int seatIndex) {// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的麦位信息SeatInfo localInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(seatIndex);SeatInfo seatInfo = new SeatInfo();seatInfo.status = SeatInfo.STATUS_USED;seatInfo.mute = localInfo.mute;seatInfo.userId = mUserId;// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(seatInfo, SeatInfo.class);HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("seat" + seatIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,上麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,切换 TRTC 角色并开始推流mTRTCCloud.switchRole(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAnchor);mTRTCCloud.startLocalAudio(TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_AUDIO_QUALITY_DEFAULT);}});}
2. 抱人上麦。
主播抱人上麦(无需听众同意),直接修改群属性保存的麦位信息,对应听众收到群属性变更回调后匹配 userId 成功即可切换 RTC Engine 角色并开始推流。如为邀请上麦模式,可参照主动上麦的实现逻辑,只需调换信令的发送方与接收方即可。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;// 主播端调用该接口修改群属性保存的麦位信息private void pickSeat(String userId, int seatIndex) {// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的麦位信息SeatInfo localInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(seatIndex);SeatInfo seatInfo = new SeatInfo();seatInfo.status = SeatInfo.STATUS_USED;seatInfo.mute = localInfo.mute;seatInfo.userId = userId;// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(seatInfo, SeatInfo.class);HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("seat" + seatIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,抱麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,触发 onGroupAttributeChanged 回调}});}// 听众端收到群属性变更回调,匹配自身信息成功后开始推流V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupAttributeChanged(String groupID, Map<String, String> groupAttributeMap) {// 上一次本地保存的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> oldSeatInfoList = mSeatInfoList;// 最新从 groupAttributeMap 中解析的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> newSeatInfoList = getSeatListFromAttr(groupAttributeMap, seatSize);// 遍历全量麦位信息列表,对比新旧麦位信息for (int i = 0; i < seatSize; i++) {SeatInfo oldInfo = oldSeatInfoList.get(i);SeatInfo newInfo = newSeatInfoList.get(i);if (oldInfo.status != newInfo.status && newInfo.status == SeatInfo.STATUS_USED) {if (newInfo.userId.equals(mUserId)) {// 匹配自身信息成功,切换 TRTC 角色并开始推流mTRTCCloud.switchRole(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAnchor);mTRTCCloud.startLocalAudio(TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_AUDIO_QUALITY_DEFAULT);} else {// 更新本地麦位列表,渲染本地麦位视图}}}}});
3. 主动下麦。
连麦听众可以通过修改群属性的方式重置麦位信息,其他用户会收到群属性变更回调,更新本地麦位信息。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;private void leaveSeat(int seatIndex) {// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的麦位信息SeatInfo localInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(seatIndex);SeatInfo seatInfo = new SeatInfo();seatInfo.status = SeatInfo.STATUS_UNUSED;seatInfo.mute = localInfo.mute;seatInfo.userId = "";// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(seatInfo, SeatInfo.class);HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("seat" + seatIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,下麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,切换 TRTC 角色并停止推流mTRTCCloud.switchRole(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAudience);mTRTCCloud.stopLocalAudio();}});}
4. 踢人下麦。
主播踢人下麦,直接修改群属性保存的麦位信息,对应连麦听众收到群属性变更回调后匹配 userId 成功即可切换 RTC Engine 角色并停止推流。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;// 主播端调用该接口修改群属性保存的麦位信息private void kickSeat(int seatIndex) {// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的麦位信息SeatInfo localInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(seatIndex);SeatInfo seatInfo = new SeatInfo();seatInfo.status = SeatInfo.STATUS_UNUSED;seatInfo.mute = localInfo.mute;seatInfo.userId = "";// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(seatInfo, SeatInfo.class);HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("seat" + seatIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,踢麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,触发 onGroupAttributeChanged 回调}});}// 连麦听众端收到群属性变更回调,匹配自身信息成功后停止推流V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupAttributeChanged(String groupID, Map<String, String> groupAttributeMap) {// 上一次本地保存的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> oldSeatInfoList = mSeatInfoList;// 最新从 groupAttributeMap 中解析的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> newSeatInfoList = getSeatListFromAttr(groupAttributeMap, seatSize);// 遍历全量麦位信息列表,对比新旧麦位信息for (int i = 0; i < seatSize; i++) {SeatInfo oldInfo = oldSeatInfoList.get(i);SeatInfo newInfo = newSeatInfoList.get(i);if (oldInfo.status != newInfo.status && newInfo.status == SeatInfo.STATUS_UNUSED) {if (oldInfo.userId.equals(mUserId)) {// 匹配自身信息成功,切换 TRTC 角色并停止推流mTRTCCloud.switchRole(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAudience);mTRTCCloud.stopLocalAudio();} else {// 更新本地麦位列表,渲染本地麦位视图}}}}});
5. 麦位禁音。
主播禁音/解禁某个麦位,直接修改群属性保存的麦位信息,对应连麦听众收到群属性变更回调后匹配 userId 成功即可暂停/恢复本地推流。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;// 主播端调用该接口修改群属性保存的麦位信息private void muteSeat(int seatIndex, boolean mute) {// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的麦位信息SeatInfo localInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(seatIndex);SeatInfo seatInfo = new SeatInfo();seatInfo.status = localInfo.status;seatInfo.mute = mute;seatInfo.userId = localInfo.userId;// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(seatInfo, SeatInfo.class);HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("seat" + seatIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,禁麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,触发 onGroupAttributeChanged 回调}});}// 连麦听众端收到群属性变更回调,匹配自身信息成功后暂停/恢复推流V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupAttributeChanged(String groupID, Map<String, String> groupAttributeMap) {// 上一次本地保存的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> oldSeatInfoList = mSeatInfoList;// 最新从 groupAttributeMap 中解析的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> newSeatInfoList = getSeatListFromAttr(groupAttributeMap, seatSize);// 遍历全量麦位信息列表,对比新旧麦位信息for (int i = 0; i < seatSize; i++) {SeatInfo oldInfo = oldSeatInfoList.get(i);SeatInfo newInfo = newSeatInfoList.get(i);if (oldInfo.mute != newInfo.mute) {if (oldInfo.userId.equals(mUserId)) {// 匹配自身信息成功,暂停/恢复本地推流mTRTCCloud.muteLocalAudio(newInfo.mute);} else {// 更新本地麦位列表,渲染本地麦位视图}}}}});
6. 麦位锁定。
主播锁定/解锁某个麦位,直接修改群属性保存的麦位信息,听众收到群属性变更回调后更新对应麦位视图。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;// 主播端调用该接口修改群属性保存的麦位信息private void lockSeat(int seatIndex, boolean isLock) {// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的麦位信息SeatInfo localInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(seatIndex);SeatInfo seatInfo = new SeatInfo();seatInfo.status = isLock ? SeatInfo.STATUS_LOCKED : SeatInfo.STATUS_UNUSED;seatInfo.mute = localInfo.mute;seatInfo.userId = "";// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(seatInfo, SeatInfo.class);HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("seat" + seatIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,锁麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,触发 onGroupAttributeChanged 回调}});}// 听众端收到群属性变更回调,更新对应麦位视图V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupAttributeChanged(String groupID, Map<String, String> groupAttributeMap) {// 上一次本地保存的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> oldSeatInfoList = mSeatInfoList;// 最新从 groupAttributeMap 中解析的全量麦位信息列表final List<SeatInfo> newSeatInfoList = getSeatListFromAttr(groupAttributeMap, seatSize);// 遍历全量麦位信息列表,对比新旧麦位信息for (int i = 0; i < seatSize; i++) {SeatInfo oldInfo = oldSeatInfoList.get(i);SeatInfo newInfo = newSeatInfoList.get(i);if (oldInfo.status == SeatInfo.STATUS_LOCKED && newInfo.status == SeatInfo.STATUS_UNUSED) {// 解锁麦位} else if (oldInfo.status != newInfo.status && newInfo.status == SeatInfo.STATUS_LOCKED) {// 锁定麦位}}}});
7. 麦位移动。
麦上主播移动麦位,需要分别修改群属性保存的源和目标麦位信息,听众收到群属性变更回调后更新对应麦位视图。
// 本地保存的全量麦位信息列表private List<SeatInfo> mSeatInfoList;// 麦上主播调用该接口修改群属性保存的麦位信息private void moveSeat(int dstIndex) {// 根据 userId 获取源麦位编号int srcIndex = -1;for (int i = 0; i < mSeatInfoList.size(); i++) {SeatInfo seatInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(i);if (seatInfo != null && mUserId.equals(seatInfo.userId)) {srcIndex = i;break;}}// 根据麦位编号获取对应麦位信息SeatInfo srcSeatInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(srcIndex);SeatInfo dstSeatInfo = mSeatInfoList.get(dstIndex);// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的源麦位信息SeatInfo srcChangeInfo = new SeatInfo();srcChangeInfo.status = SeatInfo.STATUS_UNUSED;srcChangeInfo.mute = srcSeatInfo.mute;srcChangeInfo.userId = "";// 创建麦位信息实例,存储修改后的目标麦位信息SeatInfo dstChangeInfo = new SeatInfo();dstChangeInfo.status = SeatInfo.STATUS_USED;dstChangeInfo.mute = dstSeatInfo.mute;dstChangeInfo.userId = mUserId;// 将麦位信息对象序列化为 JSON 格式Gson gson = new Gson();HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();String json = gson.toJson(srcChangeInfo, SeatInfo.class);map.put("seat" + srcIndex, json);json = gson.toJson(dstChangeInfo, SeatInfo.class);map.put("seat" + dstIndex, json);// 设置群属性,已有该群属性则更新其 value 值,没有该群属性则添加该属性V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().setGroupAttributes(groupId, map, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 修改群属性失败,移麦失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 修改群属性成功,移麦成功}});}
步骤六:音频管理
时序图

1. 订阅模式。
RTC Engine SDK 默认为自动订阅音频流逻辑,用户进房会自动开始播放远端用户的声音。如有手动订阅音频流的需求,需要额外调用
muteRemoteAudio(userId, mute) 来订阅和播放远端用户音频流。// 自动订阅模式(默认)mTRTCCloud.setDefaultStreamRecvMode(true, true);// 手动订阅模式(自定义)mTRTCCloud.setDefaultStreamRecvMode(false, false);
注意:
设置订阅模式
setDefaultStreamRecvMode 必须在进房 enterRoom 之前调用才会生效。2. 采集与发布。
// 开启本地音频的采集和发布mTRTCCloud.startLocalAudio(TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_AUDIO_QUALITY_DEFAULT)// 停止本地音频的采集和发布mTRTCCloud.stopLocalAudio();
说明:
startLocalAudio 会申请麦克风使用权限,stopLocalAudio 会释放麦克风使用权限。3. 闭麦与开麦。
// 暂停发布本地音频流(闭麦)mTRTCCloud.muteLocalAudio(true);// 恢复发布本地音频流(开麦)mTRTCCloud.muteLocalAudio(false);// 暂停订阅和播放某远端用户的音频流mTRTCCloud.muteRemoteAudio(userId, true);// 恢复订阅和播放某远端用户的音频流mTRTCCloud.muteRemoteAudio(userId, false);// 暂停订阅和播放所有远端用户的音频流mTRTCCloud.muteAllRemoteAudio(true);// 恢复订阅和播放所有远端用户的音频流mTRTCCloud.muteAllRemoteAudio(false);
说明:
相比之下,
muteLocalAudio 只需要在软件层面对数据流进行暂停或者放行即可,因此效率更高更平滑,也更适合需要频繁开闭麦的场景。4.
音质及音量类型
。音质设置
// 本地音频采集和发布时设置音质mTRTCCloud.startLocalAudio(TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_AUDIO_QUALITY_DEFAULT);// 音频推流过程中动态设置音质mTRTCCloud.setAudioQuality(TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_AUDIO_QUALITY_DEFAULT);
说明:
音量类型设置
RTC Engine 每档音质都对应有默认的音量类型,如需强制指定音量类型可以使用如下接口。
// 设置音量类型mTRTCCloud.setSystemVolumeType(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCSystemVolumeTypeAuto);
说明:
音频路由设置
手机等移动端设备上通常有扬声器和听筒两个播放位置,如需强制指定音频路由可以使用如下接口。
// 设置音频路由mTRTCCloud.setAudioRoute(TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_AUDIO_ROUTE_SPEAKER);
说明:
高级功能
弹幕消息互动
语聊直播间通常会有文本形式的弹幕消息互动,这里可以通过 Chat 的发送及接收群聊普通文本消息来实现。
// 发送公屏弹幕消息V2TIMManager.getInstance().sendGroupTextMessage(text, groupID, V2TIMMessage.V2TIM_PRIORITY_NORMAL, new V2TIMValueCallback<V2TIMMessage>() {@Overridepublic void onError(int i, String s) {// 发送弹幕消息失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess(V2TIMMessage v2TIMMessage) {// 发送弹幕消息成功}});// 接收公屏弹幕消息V2TIMManager.getInstance().addSimpleMsgListener(new V2TIMSimpleMsgListener() {@Overridepublic void onRecvGroupTextMessage(String msgID, String groupID, V2TIMGroupMemberInfo sender, String text) {Log.i(TAG, sender.getNickName + ": " + text);}});
音量大小回调
RTC Engine 可以按照固定频率回调麦上主播的音量大小,通常用于展示音波音浪,提示正在发言的主播。
// 启用音量大小回调,建议在进房成功后即开启// interval: 回调间隔(ms); enable_vad: 是否开启人声检测mTRTCCloud.enableAudioVolumeEvaluation(int interval, boolean enable_vad);private class TRTCCloudImplListener extends TRTCCloudListener {public void onUserVoiceVolume(ArrayList<TRTCCloudDef.TRTCVolumeInfo> userVolumes, int totalVolume) {super.onUserVoiceVolume(userVolumes, totalVolume);// userVolumes 用于承载所有正在说话的用户的音量大小,包括本地用户和远端推流用户// totalVolume 用于反馈远端推流用户中的最大音量值...// 根据音量大小在 UI 上做出相应的音浪展示...}}
注意:
人声检测仅反馈本地人声检测结果,且自身角色必须为主播,方便提示用户开麦。
userVolumes 为一个数组,对于数组中的每一个元素,当 userId 为自己时表示本地麦克风采集的音量大小,其他代表远端用户的音量大小。音乐及音效播放
播放背景音乐及音效是语聊房场景中的高频需求,下面将对常用的背景音乐相关接口的使用及注意事项进行说明。
1. 开始/停止/暂停/恢复播放。
// 获取用于对背景音乐、短音效和人声特效进行设置的管理类TXAudioEffectManager mTXAudioEffectManager = mTRTCCloud.getAudioEffectManager();TXAudioEffectManager.AudioMusicParam param = new TXAudioEffectManager.AudioMusicParam(musicID, musicPath);// 是否将音乐发布到远端(否则仅本地播放)param.publish = true;// 播放的是否为短音效文件param.isShortFile = false;// 开始播放背景音乐mTXAudioEffectManager.startPlayMusic(param);// 停止播放背景音乐mTXAudioEffectManager.stopPlayMusic(musicID);// 暂停播放背景音乐mTXAudioEffectManager.pausePlayMusic(musicID);// 恢复播放背景音乐mTXAudioEffectManager.resumePlayMusic(musicID);
注意:
RTC Engine 支持同时播放多首音乐,通过 musicID 唯一标识,若您想要同一时刻只播放一首音乐,需要注意在开始播放前停止播放其他音乐,或者可以使用同一个 musicID 来播放不同的音乐,这样 SDK 会先停止播放旧的音乐,再播放新的音乐。
RTC Engine 支持播放本地和网络音频文件,通过
musicPath 传入本地绝对路径 或 URL 地址,支持 MP3/AAC/M4A/WAV 格式。2. 调节音乐及人声音量占比。
// 设置某一首背景音乐的本地播放音量的大小mTXAudioEffectManager.setMusicPlayoutVolume(musicID, volume);// 设置某一首背景音乐的远端播放音量的大小mTXAudioEffectManager.setMusicPublishVolume(musicID, volume);// 设置所有背景音乐的本地音量和远端音量的大小mTXAudioEffectManager.setAllMusicVolume(volume);// 设置人声采集音量的大小mTXAudioEffectManager.setVoiceCaptureVolume(volume);
注意:
音量值 volume 正常取值范围为0-100,默认值为60,最大可设为150,但有爆音风险。
如果出现背景音乐压制人声的情况,可适当调低音乐播放音量,调高人声采集音量。
闭麦不禁背景音乐:使用
setVoiceCaptureVolume(0) 替代 muteLocalAudio(true)。3. 设置音乐播放的事件回调。
mTXAudioEffectManager.setMusicObserver(mCurPlayMusicId, new TXAudioEffectManager.TXMusicPlayObserver() {@Override// 背景音乐开始播放public void onStart(int id, int errCode) {// -4001: 路径打开失败// -4002: 解码失败// -4003: URL地址无效// -4004: 播放未停止if (errCode < 0) {// 播放失败后重新播放前需要先停止播放当前音乐mTXAudioEffectManager.stopPlayMusic(id);}}@Override// 背景音乐的播放进度public void onPlayProgress(int id, long curPtsMs, long durationMs) {// curPtsMS 当前播放时长(毫秒)// durationMs 当前音乐总时长(毫秒)}@Override// 背景音乐已经播放完毕public void onComplete(int id, int errCode) {// 播放中途因弱网导致的播放失败也会抛出此回调,此时 errCode < 0// 中途暂停播放或停止播放不会触发 onComplete 回调}});
注意:
请在播放背景音乐之前使用该接口设置播放事件回调,以便感知背景音乐的播放进度;
如果 MusicId 无需重复使用,可在播放完毕后执行
setMusicObserver(musicId, null) 彻底释放 Observer。4. 循环播放背景音乐及音效
方案一:使用
AudioMusicParam 中的 loopCount 参数设置循环播放次数。取值范围为0 - 任意正整数,默认值:0。0 表示播放音乐一次;1 表示播放音乐两次;以此类推。
private void startPlayMusic(int id, String path, int loopCount) {TXAudioEffectManager.AudioMusicParam param = new TXAudioEffectManager.AudioMusicParam(id, path);// 是否将音乐发布到远端param.publish = true;// 播放的是否为短音效文件param.isShortFile = true;// 设定循环播放次数,负数表示无限循环param.loopCount = loopCount < 0 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : loopCount;mTRTCCloud.getAudioEffectManager().startPlayMusic(param);}
注意:
方案一每次循环播放完毕并不会触发
onComplete 回调,只有等设置的循环次数全部播放完毕才会触发该回调。方案二:通过“背景音乐已经播放完毕”的事件回调
onComplete 来实现循环播放,通常用于列表循环或单曲循环。// 标识是否循环播放的成员变量private boolean loopPlay;private void startPlayMusic(int id, String path) {TXAudioEffectManager.AudioMusicParam param = new TXAudioEffectManager.AudioMusicParam(id, path);mTXAudioEffectManager.setMusicObserver(id, new MusicPlayObserver(id, path));mTXAudioEffectManager.startPlayMusic(param);}private class MusicPlayObserver implements TXAudioEffectManager.TXMusicPlayObserver {private final int mId;private final String mPath;public MusicPlayObserver(int id, String path) {mId = id;mPath = path;}@Overridepublic void onStart(int i, int i1) {}@Overridepublic void onPlayProgress(int i, long l, long l1) {}@Overridepublic void onComplete(int i, int i1) {mTXAudioEffectManager.stopPlayMusic(i);if (i1 >= 0 && loopPlay) {// 这里可替换循环列表音乐的 ID、PathstartPlayMusic(mId, mPath);}}}
混流转推及回推
1. 混流回推 RTC Engine 房间。
private void startPublishMediaToRoom(String roomId, String userId) {// 创建 TRTCPublishTarget 对象TRTCCloudDef.TRTCPublishTarget target = new TRTCCloudDef.TRTCPublishTarget();// 混流后回推到房间target.mode = TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_PublishMixStream_ToRoom;target.mixStreamIdentity.strRoomId = roomId;// 混流机器人的 userid,不能和房间内其他用户的 userid 重复target.mixStreamIdentity.userId = userId + MIX_ROBOT;// 设置转码后的音频流的编码参数(可自定义)TRTCCloudDef.TRTCStreamEncoderParam trtcStreamEncoderParam = new TRTCCloudDef.TRTCStreamEncoderParam();trtcStreamEncoderParam.audioEncodedChannelNum = 2;trtcStreamEncoderParam.audioEncodedKbps = 64;trtcStreamEncoderParam.audioEncodedCodecType = 2;trtcStreamEncoderParam.audioEncodedSampleRate = 48000;// 设置转码后的视频流的编码参数(纯音频混流可忽略)trtcStreamEncoderParam.videoEncodedFPS = 15;trtcStreamEncoderParam.videoEncodedGOP = 3;trtcStreamEncoderParam.videoEncodedKbps = 30;trtcStreamEncoderParam.videoEncodedWidth = 64;trtcStreamEncoderParam.videoEncodedHeight = 64;// 设置音频混流参数TRTCCloudDef.TRTCStreamMixingConfig trtcStreamMixingConfig = new TRTCCloudDef.TRTCStreamMixingConfig();// 默认情况下填空值即可,代表会混合房间中的所有音频trtcStreamMixingConfig.audioMixUserList = null;// 配置视频混流模板(纯音频混流可忽略)TRTCCloudDef.TRTCVideoLayout videoLayout = new TRTCCloudDef.TRTCVideoLayout();trtcStreamMixingConfig.videoLayoutList.add(videoLayout);// 开始混流回推mTRTCCloud.startPublishMediaStream(target, trtcStreamEncoderParam, trtcStreamMixingConfig);}
2. 事件回调及更新停止任务。
任务结果事件回调。
private class TRTCCloudImplListener extends TRTCCloudListener {@Overridepublic void onStartPublishMediaStream(String taskId, int code, String message, Bundle extraInfo) {// taskId: 当请求成功时,TRTC 后台会在回调中提供给您这项任务的 taskId,后续您可以通过该 taskId 结合 updatePublishMediaStream 和 stopPublishMediaStream 进行更新和停止// code: 回调结果,0 表示成功,其余值表示失败}@Overridepublic void onUpdatePublishMediaStream(String taskId, int code, String message, Bundle extraInfo) {// 您调用媒体流发布接口 (updatePublishMediaStream) 时传入的 taskId,会通过此回调再带回给您,用于标识该回调属于哪一次更新请求// code: 回调结果,0 表示成功,其余值表示失败}@Overridepublic void onStopPublishMediaStream(String taskId, int code, String message, Bundle extraInfo) {// 您调用停止发布媒体流 (stopPublishMediaStream) 时传入的 taskId,会通过此回调再带回给您,用于标识该回调属于哪一次停止请求// code: 回调结果,0 表示成功,其余值表示失败}}
更新发布媒体流。
该接口会向 RTC Engine 服务器发送指令,更新通过
startPublishMediaStream 启动的媒体流。// taskId: 通过 onStartPublishMediaStream 回调的任务 ID// target: 例如增删发布的 CDN URL// params: 建议保持媒体流编码输出参数一致,避免播放侧断流// config: 更新参与混流转码的用户列表,例如跨房 PKmTRTCCloud.updatePublishMediaStream(taskId, target, trtcStreamEncoderParam, trtcStreamMixingConfig);
注意:
同一个任务不支持纯音频、音视频、纯视频之间的切换。
停止发布媒体流
该接口会向 RTC Engine 服务器发送指令,停止通过
startPublishMediaStream 启动的媒体流。// taskId: 通过 onStartPublishMediaStream 回调的任务 IDmTRTCCloud.stopPublishMediaStream(taskId);
注意:
若 taskId 填空字符串,将会停止该用户所有通过
startPublishMediaStream 启动的媒体流,如果您只启动了一个媒体流或者想停止所有通过您启动的媒体流,推荐使用这种方式。网络质量实时回调
可以通过监听
onNetworkQuality 来实时统计本地及远端用户的网络质量,该回调每隔2秒抛出一次。private class TRTCCloudImplListener extends TRTCCloudListener {@Overridepublic void onNetworkQuality(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCQuality localQuality,ArrayList<TRTCCloudDef.TRTCQuality> remoteQuality) {// localQuality userId 为空,代表本地用户网络质量评估结果// remoteQuality 代表远端用户网络质量评估结果,其结果受远端和本地共同影响switch (localQuality.quality) {case TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_QUALITY_Excellent:Log.i(TAG, "当前网络非常好");break;case TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_QUALITY_Good:Log.i(TAG, "当前网络比较好");break;case TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_QUALITY_Poor:Log.i(TAG, "当前网络一般");break;case TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_QUALITY_Bad:Log.i(TAG, "当前网络较差");break;case TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_QUALITY_Vbad:Log.i(TAG, "当前网络很差");break;case TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_QUALITY_Down:Log.i(TAG, "当前网络不满足 TRTC 最低要求");break;default:Log.i(TAG, "未定义");break;}}}
高级权限控制
RTC Engine 高级权限控制可用于对不同房间设置不同进入权限,例如高级 VIP 房;也可用于控制听众上麦权限,例如处理幽灵麦。
步骤三:进房校验&上麦校验 PrivateMapKey。
进房校验
TRTCCloudDef.TRTCParams mTRTCParams = new TRTCCloudDef.TRTCParams();mTRTCParams.sdkAppId = SDKAPPID;mTRTCParams.userId = mUserId;mTRTCParams.strRoomId = mRoomId;// 从业务后台获取到的 UserSigmTRTCParams.userSig = getUserSig();// 从业务后台获取到的 PrivateMapKeymTRTCParams.privateMapKey = getPrivateMapKey();mTRTCParams.role = TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAudience;mTRTCCloud.enterRoom(mTRTCParams, TRTCCloudDef.TRTC_APP_SCENE_VOICE_CHATROOM);
上麦校验
// 从业务后台获取到最新的 PrivateMapKey 传入切换角色接口mTRTCCloud.switchRole(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCRoleAnchor, getPrivateMapKey());
异常处理
异常错误处理
UserSig 相关
枚举 | 取值 | 描述 |
ERR_TRTC_INVALID_USER_SIG | -3320 | 进房参数 UserSig 不正确,请检查 TRTCParams.userSig 是否为空。 |
ERR_TRTC_USER_SIG_CHECK_FAILED | -100018 | UserSig 校验失败,请检查参数 TRTCParams.userSig 是否填写正确或已经过期。 |
进退房相关
进房失败请先检查进房参数是否正确,且进退房接口必须成对调用,即便进房失败也需要调用退房接口。
枚举 | 取值 | 描述 |
ERR_TRTC_CONNECT_SERVER_TIMEOUT | -3308 | 请求进房超时,请检查是否断网或者是否开启 VPN,您也可以切换4G进行测试。 |
ERR_TRTC_INVALID_SDK_APPID | -3317 | 进房参数 sdkAppId 错误,请检查 TRTCParams.sdkAppId 是否为空 |
ERR_TRTC_INVALID_ROOM_ID | -3318 | 进房参数 roomId 错误,请检查 TRTCParams.roomId 或 TRTCParams.strRoomId 是否为空,注意 roomId 和 strRoomId 不可混用。 |
ERR_TRTC_INVALID_USER_ID | -3319 | 进房参数 userId 不正确,请检查 TRTCParams.userId 是否为空。 |
ERR_TRTC_ENTER_ROOM_REFUSED | -3340 | 进房请求被拒绝,请检查是否连续调用 enterRoom 进入相同 ID 的房间。 |
设备相关
可监听设备相关错误,在出现相关错误时 UI 提示用户。
枚举 | 取值 | 描述 |
ERR_MIC_START_FAIL | -1302 | 打开麦克风失败,例如在 Windows 或 Mac 设备,麦克风的配置程序(驱动程序)异常,禁用后重新启用设备,或者重启机器,或者更新配置程序。 |
ERR_SPEAKER_START_FAIL | -1321 | 打开扬声器失败,例如在 Windows 或 Mac 设备,扬声器的配置程序(驱动程序)异常,禁用后重新启用设备,或者重启机器,或者更新配置程序。 |
ERR_MIC_OCCUPY | -1319 | 麦克风正在被占用中,例如移动设备正在通话时,打开麦克风会失败。 |
异常退出处理
1. 断网感知与超时退房。
可以通过以下回调监听 RTC Engine 断网和重连事件通知。
收到
onConnectionLost 回调后可在本地麦位 UI 展示断网标识提醒用户,同时本地启动一个计时器,当超过设定时间阈值后仍然没有收到 onConnectionRecovery 回调,即网络持续处于断连状态,此时可本地启动下麦和退房流程,同时弹窗提醒用户已退出房间并销毁页面。若断网超过90秒(默认)会触发超时退房,RTC Engine 服务端会将该用户踢出房间,如果该用户为主播角色,则房间内其他用户会收到 onRemoteUserLeaveRoom 回调。private class TRTCCloudImplListener extends TRTCCloudListener {@Overridepublic void onConnectionLost() {// SDK 与云端的连接已经断开}@Overridepublic void onTryToReconnect() {// SDK 正在尝试重新连接到云端}@Overridepublic void onConnectionRecovery() {// SDK 与云端的连接已经恢复}}
2. 离线状态下自动下麦。
Chat 用户的普通状态分为在线(ONLINE)、离线(OFFLINE)、未登录(UNLOGGED),其中离线状态通常是由于用户强杀进程或网络异常中断导致的。您可以通过主播订阅连麦听众用户状态来检测离线连麦听众,从而将其踢下麦。
// 主播订阅连麦听众用户状态V2TIMManager.getInstance().subscribeUserStatus(userList, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 订阅用户状态成功}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 订阅用户状态失败}});// 主播取消订阅下麦听众用户状态V2TIMManager.getInstance().unsubscribeUserStatus(userList, new V2TIMCallback() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess() {// 取消订阅用户状态成功}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String message) {// 取消订阅用户状态失败}});// 用户状态变更通知与处理V2TIMManager.getInstance().addIMSDKListener(new V2TIMSDKListener() {@Overridepublic void onUserStatusChanged(List<V2TIMUserStatus> userStatusList) {for (V2TIMUserStatus userStatus : userStatusList) {final String userId = userStatus.getUserID();int status = userStatus.getStatusType();if (status == V2TIMUserStatus.V2TIM_USER_STATUS_OFFLINE) {// 离线状态执行踢麦kickSeat(getSeatIndexFromUserId(userId));}}}});
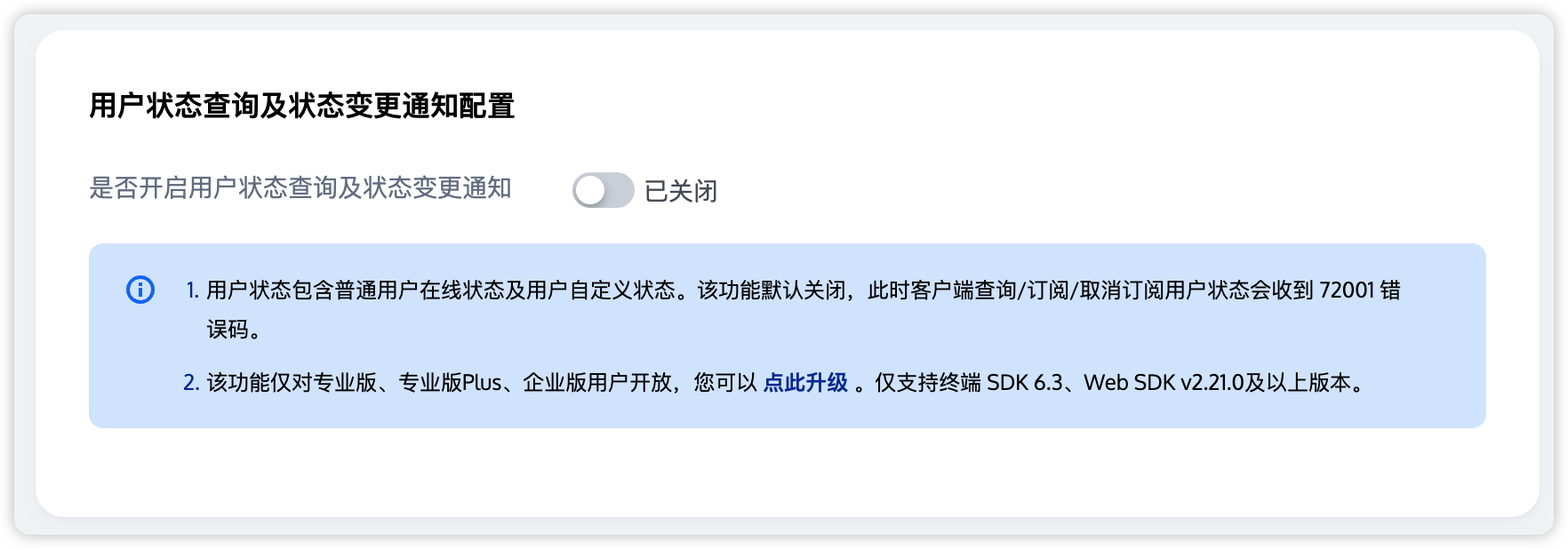
注意:
订阅用户状态需要升级到专业版套餐,详情请参见 基础服务详情。
订阅用户状态需要提前在 Chat 控制台 开启 用户状态查询及状态变更通知配置,如果未开启则调用
subscribeUserStatus 会报错。服务端踢人及解散房间
1. 服务端踢人。
首先调用 RTC Engine 服务端踢人接口 RemoveUser(整型房间号)或 RemoveUserByStrRoomId(字符串房间号)将目标用户踢出 RTC Engine 房间,输入示例如下:
https://trtc.tencentcloudapi.com/?Action=RemoveUser&SdkAppId=1400000001&RoomId=1234&UserIds.0=test1&UserIds.1=test2&<公共请求参数>
执行踢人成功后,目标用户在客户端会收到
onExitRoom() 回调,且 reason 值为1。此时您可以在该回调中处理下麦、退出 Chat 群组等操作。// 离开 TRTC 房间事件回调@Overridepublic void onExitRoom(int reason) {if (reason == 0) {Log.d(TAG, "主动调用 exitRoom 退出房间");} else {// reason 1: 被服务器踢出当前房间// reason 2: 当前房间被整个解散Log.d(TAG, "被服务器踢出房间,或当前房间被解散");// 下麦leaveSeat(seatIndex);// 退出 IM 群组quitGroup(groupID, new V2TIMCallback() {});}}
2. 服务端解散房间。
https://xxxxxx/v4/group_open_http_svc/destroy_group?sdkappid=88888888&identifier=admin&usersig=xxx&random=99999999&contenttype=json
执行解散群组成功后,目标群组内的全部成员在客户端均会收到
onGroupDismissed() 回调。此时您可以在该回调中处理退出 TRTC 房间等操作。// 群组被解散回调V2TIMManager.getInstance().addGroupListener(new V2TIMGroupListener() {@Overridepublic void onGroupDismissed(String groupID, V2TIMGroupMemberInfo opUser) {// 退出 TRTC 房间mTRTCCloud.stopLocalAudio();mTRTCCloud.exitRoom();}});
说明:
当房间内所有用户调用
exitRoom() 完成退房后,RTC Engine 房间会自动解散。当然,您也可以调用服务端接口 DismissRoom(整型房间号)或 DismissRoomByStrRoomId(字符串房间号)强制解散 RTC Engine 房间。进房查看直播间历史消息
使用 AVChatRoom 默认不存储直播间历史消息,当新用户进入直播间后,只能看到进入直播间后用户发送的消息。为了优化新进群用户的体验,可在控制台配置直播群用户拉取进群前消息条数,如图:
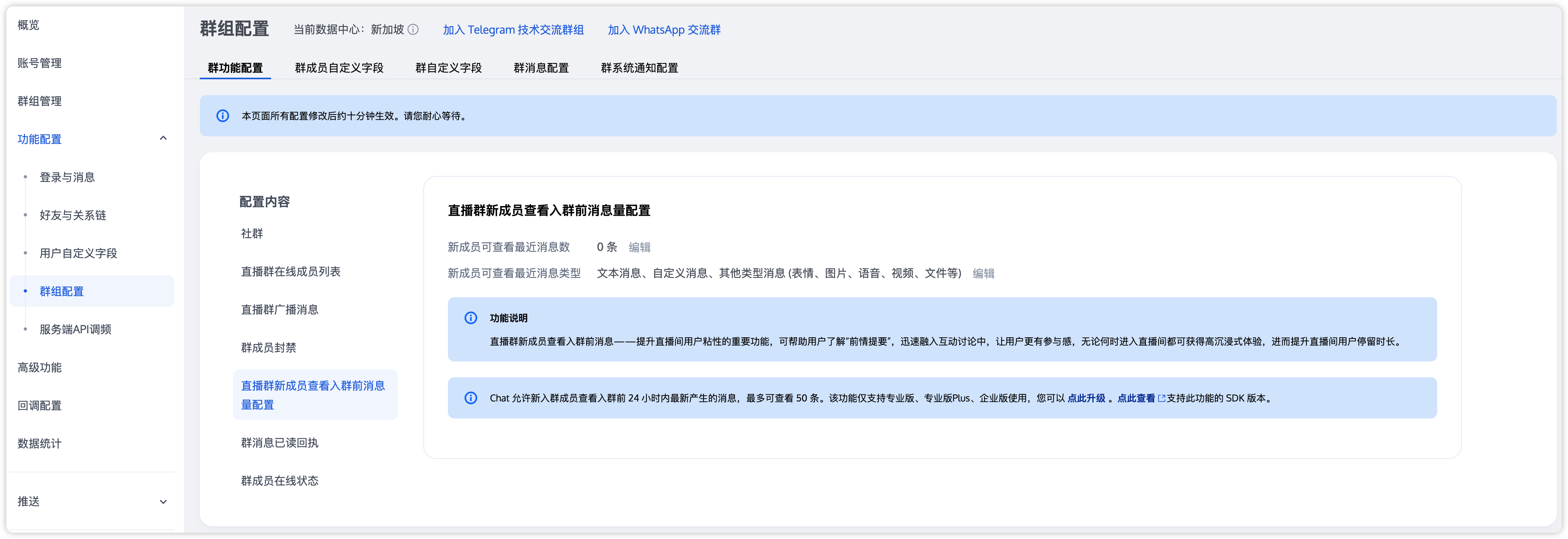
直播群用户拉取进群前历史消息与拉取其他群历史消息一样,代码示例:
V2TIMMessageListGetOption option = new V2TIMMessageListGetOption();option.setGetType(V2TIMMessageListGetOption.V2TIM_GET_CLOUD_OLDER_MSG); // 拉取云端的更老的消息option.setGetTimeBegin(1640966400); // 从 2022-01-01 00:00:00 开始option.setGetTimePeriod(1 * 24 * 60 * 60); // 拉取一整天的消息option.setCount(Integer.MAX_VALUE); // 返回时间范围内所有的消息option.setGroupID(#you group id#); // 拉取群聊消息V2TIMManager.getMessageManager().getHistoryMessageList(option, new V2TIMValueCallback<List<V2TIMMessage>>() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess(List<V2TIMMessage> v2TIMMessages) {Log.i("imsdk", "success");}@Overridepublic void onError(int code, String desc) {Log.i("imsdk", "failure, code:" + code + ", desc:" + desc);}});
注意:
此功能仅限进阶版用户才可开通,且仅支持拉群24小时内最多20条历史消息。
进房感知麦上主播静音状态
方案一:进房时默认所有主播为静音状态,然后根据
onUserAudioAvailable(userId, true) 回调解除对应主播禁音状态。private class TRTCCloudImplListener extends TRTCCloudListener {@Overridepublic void onUserAudioAvailable(String userId, boolean available) {if (available) {// 解除对应主播的禁音状态}}}
方案二:把主播的静音状态存储在 RTC Engine 群属性中,听众进房获取全量群属性,解析麦上主播禁音状态。
V2TIMManager.getGroupManager().getGroupAttributes(groupID, null, new V2TIMValueCallback<Map<String, String>>() {@Overridepublic void onError(int i, String s) {// 获取群属性失败}@Overridepublic void onSuccess(Map<String, String> attrMap) {// 获取群属性成功,假设存储主播禁音状态的 key 为 muteStatusString muteStatus = attrMap.get("muteStatus");// 解析 muteStatus,获取每个麦上主播的禁音状态}});
蓝牙耳机的音频输入输出问题
手机已经成功连接蓝牙耳机,但 RTC Engine 应用的音频输入或输出仍然使用手机麦克风或扬声器。
1. 如果音频输出正常使用蓝牙耳机,只有音频输入仍旧使用手机麦克风,此时请检查音量类型的设置。只有通话音量模式下支持通过蓝牙耳机上的麦克风进行拾音,详情请参阅 音频管理 - 音质及音量类型。
mTRTCCloud.setSystemVolumeType(TRTCCloudDef.TRTCSystemVolumeTypeVOIP);
2. 如果音频的输入及输出均无法使用蓝牙耳机,此时请检查 App 权限中是否配置了蓝牙权限。对于 Android 设备,Android 12 以下系统需至少配置
BLUETOOTH 权限,Android 12 及以上系统需至少配置 BLUETOOTH_CONNECT 权限且需在代码中动态申请权限。在 AndroidManifest.xml 中配置蓝牙权限,为了兼容 Android 12 以下系统,建议声明方式如下:
<!--普通权限:基础蓝牙连接权限--><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" android:maxSdkVersion="30"/><!--普通权限:蓝牙管理、扫描权限--><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" android:maxSdkVersion="30" /><!--运行时权限:Android 12 蓝牙权限 查找蓝牙设备--><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_SCAN" /><!--运行时权限:Android 12 蓝牙权限 使当前设备可被其他蓝牙设备检测到--><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADVERTISE" /><!--运行时权限:Android 12 蓝牙权限 与已配对的蓝牙设备通信或者获取当前手机蓝牙是否打开--><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT" />
对于 Android 12 及以上系统新增的蓝牙细分权限,动态申请方法如下:
private List<String> permissionList = new ArrayList<>();protected void initPermission() {// 判断 Android SDK 版本,大于等于 Android 12if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S) {// 根据需求添加需要动态申请的权限permissionList.add(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH_SCAN);permissionList.add(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADVERTISE);permissionList.add(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT);}if (permissionList.size() != 0) {// 动态申请权限ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, permissionList.toArray(new String[0]), REQ_PERMISSION_CODE);}}
音乐播放支持的资源路径问题
使用 RTC Engine SDK API
startPlayMusic 播放背景音乐,其中音乐资源路径参数 path 不支持传入 Android 开发中的 assets/raw 等用来存储应用资源文件目录下的文件路径,因为这些目录下的文件会被打包到 APK 中,安装之后不会被解压到手机的文件系统中。目前只支持传入网络资源 URL、安卓设备外部存储及应用私有目录下资源文件的绝对路径。您可以通过将 assets 目录下的资源文件提前拷贝到设备外部存储或应用私有目录下的方法规避这一问题,示例代码如下:
public static void copyAssetsToFile(Context context, String name) {// 应用程序自身目录下的 files 目录String savePath = ContextCompat.getExternalFilesDirs(context, null)[0].getAbsolutePath();// 应用程序自身目录下的 cache 目录// String savePath = getApplication().getExternalCacheDir().getAbsolutePath();// 应用程序私有存储目录下的 files 目录// String savePath = getApplication().getFilesDir().getAbsolutePath();String filename = savePath + "/" + name;File dir = new File(savePath);// 如果目录不存在,创建这个目录if (!dir.exists()) {dir.mkdir();}try {if (!(new File(filename)).exists()) {InputStream is = context.getResources().getAssets().open(name);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filename);byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int count = 0;while ((count = is.read(buffer)) > 0) {fos.write(buffer, 0, count);}fos.close();is.close();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
应用私有存储 files 目录路径:
/data/user/0/<package_name>/files/<file_name>应用外部存储 files 目录路径:
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/<package_name>/files/<file_name>应用外部存储 cache 目录路径:
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/<package_name>/cache/<file_name>注意:
如果您传入的路径为非应用程序自身特定目录下的其他外部存储路径,在 Android 10及以上设备上可能面临拒绝访问资源,这是因为 Google 引入了新的存储管理系统,分区存储。可以通过在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中的 <application> 标签内添加以下代码暂时规避:
android:requestLegacyExternalStorage="true"。该属性只在 targetSdkVersion 为29(Android 10)的应用上生效,更高版本 targetSdkVersion 的应用仍建议您使用应用的私有或外部存储路径。RTC Engine SDK 11.5 及以上版本 Content Provider 组件的 Content URI 来播放 Android 设备上的本地音乐资源。
Android 11 及 HarmonyOS 3.0 以上系统,如果无法访问外部存储目录下的资源文件,需要申请
MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 权限:首先,需要在您的应用的 AndroidManifest 文件中添加以下条目。
<manifest ...><!-- This is the permission itself --><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /><application ...>...</application></manifest>
然后,在您的应用需要使用到这个权限的地方引导用户手动授权。
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.R) {if (!Environment.isExternalStorageManager()) {Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_MANAGE_APP_ALL_FILES_ACCESS_PERMISSION);Uri uri = Uri.fromParts("package", getPackageName(), null);intent.setData(uri);startActivity(intent);}} else {// For Android versions less than Android 11, you can use the old permissions modelActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE}, REQUEST_CODE);}
文档反馈

