Cloud Load Balancer
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Product Comparison
- Purchase Guide
- CLB Resource Package
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- CLB Instance
- CLB Listener
- Real Server
- Health Check
- Certificate Management
- Log Management
- Monitoring and Alarm
- Cloud Access Management
- Practical Tutorial
- Obtaining Real Client IPs
- Ops Guide
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- Instance APIs
- Listener APIs
- Backend Service APIs
- Target Group APIs
- Redirection APIs
- Other APIs
- Classic CLB APIs
- Making API Requests
- Load Balancing APIs
- CLB API 2017
- Making API Requests
- Request Structure
- Returned Results
- General APIs
- Classic CLB APIs
- APIs for CLB Instances
- APIs for Listeners
- CLB Real Server APIs
- APIs for Health Check
- FAQs
- Troubleshooting Health Check Issues
DocumentationCloud Load BalancerOperation GuideCLB ListenerSNI Support for Binding Multiple Certificates to a CLB Instance
SNI Support for Binding Multiple Certificates to a CLB Instance
Last updated: 2024-10-10 16:46:13
SNI Support for Binding Multiple Certificates to a CLB Instance
Last updated: 2024-10-10 16:46:13
Server Name Indication (SNI) is designed to solve the problem that one server can only use one certificate so as to improve SSL/TLS extensions of the server and the client. If a server supports SNI, it means that the server can be bound to multiple certificates. To use SNI for the client, the domain name to connect to should be specified before SSL/TLS connections to the server are established, and then the server will return an appropriate certificate based on the domain name.
Use Cases
A layer-7 HTTPS CLB listener supports SNI, i.e., binding multiple certificates, which can be used by different domain names in the listening rules. For example, in the same
HTTPS:443 listener of a CLB instance, you can use certificate 1 and certificate 2 for *.test.com and *.example.com respectively to forward requests from these domain names to two different sets of servers.Prerequisites
Note:
Classic CLB does not support forwarding based on domain name and URL; therefore, it does not support SNI.
Directions
1. Log in to the CLB console.
2. Configure an HTTPS listener and enable SNI.
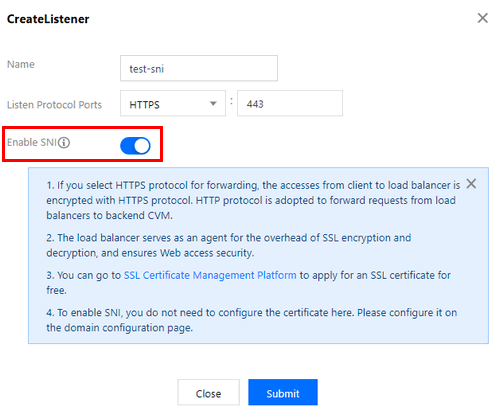
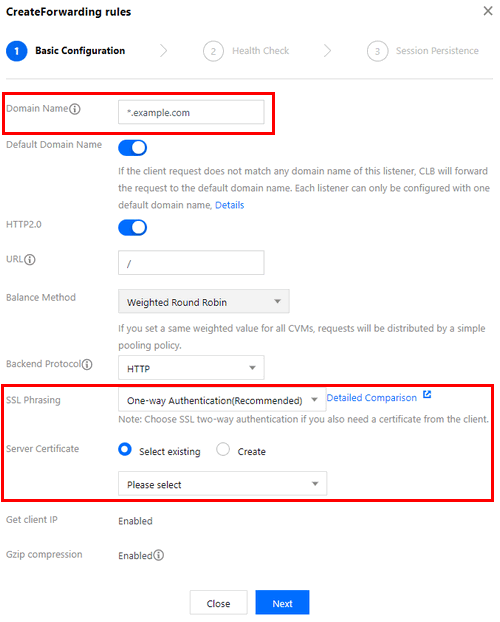
3. When adding a forwarding rule to the listener, configure different server certificates for different domain names. Then, click Next and configure health check and session persistence.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

