Prerequisites
You have a Tencent Cloud account. For more information on how to create an account, see Signing Up. You have created an ES cluster on v7.14.2. For more information on how to create a cluster, see Creating Clusters. Note:
Only autonomous indices can be created.
Developed by Tencent Cloud, the autonomous index feature is suitable for time series data use cases such as log analysis and Ops monitoring, and can achieve index lifecycle management and automatic sharding optimization, with improved read and write efficiency. This feature is naturally applicable to clusters on v7.14.2 created after June 1, 2022 and is supported for older clusters on this version after a cluster restart. To use this feature in clusters on earlier versions, upgrade them to v7.14.2 first. Directions
Step 1. Go to the "Create" page
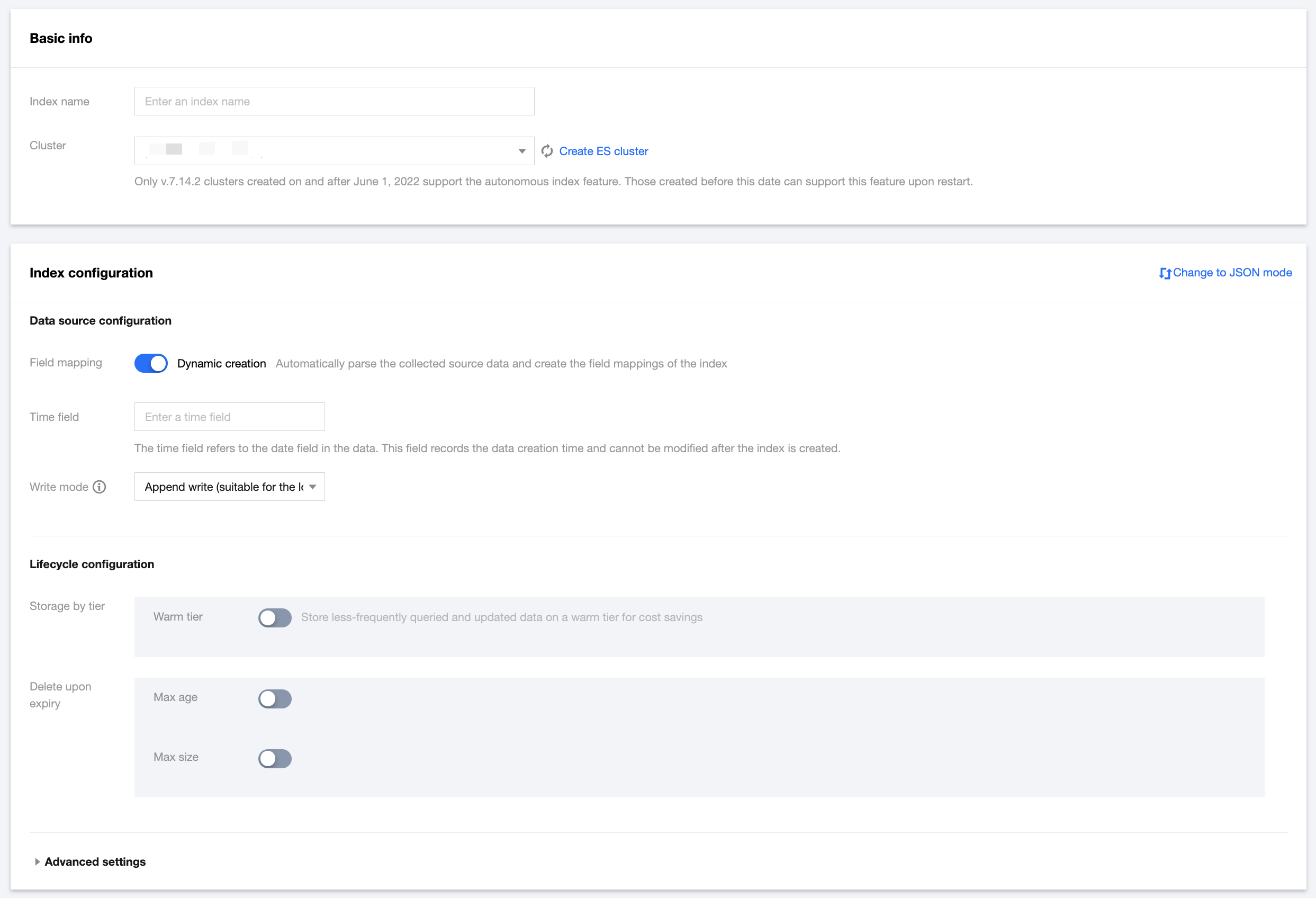
1. Log in to the ES console and click Data Management to enter the index list. 2. Click Create index to enter the Create page.
Index name: It must contain 1–255 characters, excluding Chinese characters, uppercase letters, space, and some symbols (, /, *, ?, ", <, >, |, #, :, and ,), and it cannot start with -, _, +, or .
Cluster: Cluster of the index.
Data source configuration
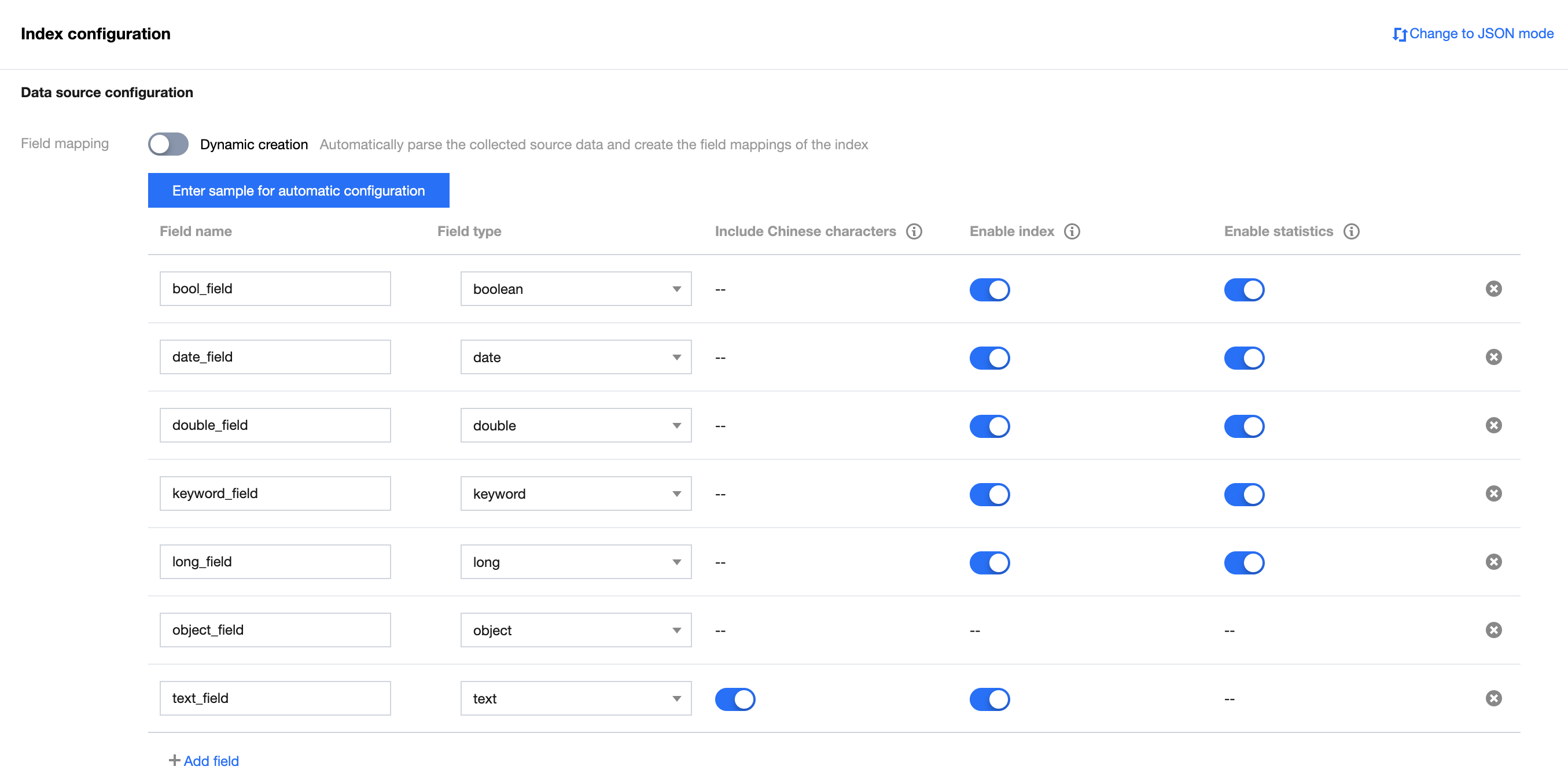
1. Field mapping
Dynamic creation: It is enabled by default. After it is enabled, the collected source data will be automatically parsed to generate the field mappings of the index.
Enter sample for automatic configuration: After disabling Dynamic creation, you can generate the field mappings of the index through the Enter sample for automatic configuration input box. After you enter a JSON-formatted data sample and click Confirm, the platform will automatically verify the data. If there is no problem, fields will be mapped to the field mapping table. The deduction rule and sample are as follows:
Deduction rule: When the field value is true or false, the mapping type is boolean; when the field value is an integer, the mapping type is long; when the field value is a floating point, the mapping type is double; when the field value is a string with 36 or fewer characters, the mapping type is keyword; when the field value is a string with more than 36 characters, the mapping type is text; when the field value is a string in date format, the mapping type is date; when the field value supports nesting, the mapping type is object.Enter the following JSON-formatted data sample in the Enter sample for automatic configuration input box:
{
"bool_field": true,
"date_field": "2022/01/26 00:00:00",
"double_field": 3.14,
"keyword_field": "This is a line of text that does not require word segmentation",
"long_field": 126,
"object_field": {
"sub_field": 2022
},
"text_field": "This is a line of text that requires word segmentation. Text with more than 36 characters will be identified as requiring word segmentation and defined as the text type"
}
The parsing result is as shown below:
Field mapping splits the original data into multiple segments by field (i.e., key:value) for indexing and search as follows:
|
Field name | Name of the field in the written data |
| Field data type. Valid values: boolean, keyword, long, double, date, text. More field types are supported in the JSON mode. For more information, see Field data types. |
Include Chinese characters | This feature can be enabled if the field contains Chinese characters and you want to search for Chinese characters, but it will increase the index size. After this feature is enabled, the ik_max_word analyzer will be applied to the text field by default. |
| Enabling this feature allows for creating an index for this field for search. |
| Enabling this option allows for statistical analysis of field values, but it increases the index size. |
2. Time field
The time field refers to the date field in the data. This field records the data creation time and cannot be modified after the index is created.
Enable index and Enable statistics are enabled by default for the time field and cannot be disabled.
After dynamic creation is disabled, the time field will map the date fields in the table, and you can select one from the drop-down list as the time field.
3. Write mode
Data is written to the index. This mode cannot be changed after the index is created successfully. Currently, two write modes are supported:
Append write (suitable for the log case): Data will be written to the latest backing index.
Shard-based write by time (suitable for the monitoring case): Data will be written in the backing index of the corresponding time period based on the time field.
Lifecycle configuration
1. Storage by tier
Storage by tier indicates that you can store indices on nodes with different attributes based on their access frequency. For example, you can store less-frequently queried and updated data on a warm tier for cost savings.The time it takes to migrate an index to a tier is calculated from the index rolling update start.
2. Deletion upon expiry
The Delete upon expiry option supports deleting historical data based on the Max age and Max size.
Max age: If the write mode is Append write, the backing index will be deleted when the specified value is reached after the index creation time. If the write mode is Shard-based write by time, the backing index will be deleted when the specified value is reached after the time when no more data is written to the index.
Max size: When the size of the autonomous index reaches the specified value, a historical backing index will be deleted based on the applicable condition. If the write mode is Append write, the oldest backing index will be deleted, starting from the index creation time. If the write mode is Shard-based write by time, the oldest backing index will be deleted, starting from the time when no more data is written to the index.
Advanced settings
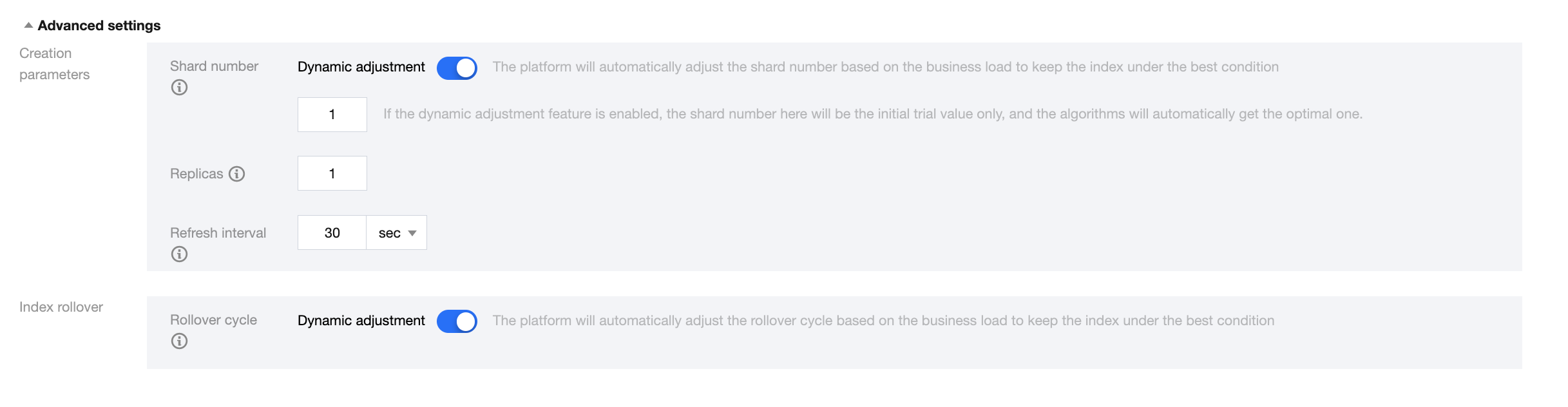
1. Creation parameters
Shard number: A shard is a partition of data stored in the index. If Dynamic adjustment is enabled, the shard quantity is only used as the initial value for the backing index and will be automatically adjusted to the optimal value by algorithms.
Shard quantity dynamic adjustment: The platform will automatically adjust the shard quantity based on the business load to keep the index under the best condition. The adjusted shard quantity will apply to backing indices that are rolled over subsequently but not to existing backing indices.
Replicas: The number of replica shards of each primary shard.
Refresh interval: The interval required for data to be searchable after it is written in the index.
2. Index rollover
Rollover cycle: From the creation date, roll the index over once in each specified cycle.
Rollover cycle dynamic adjustment: The platform will automatically adjust the rollover cycle based on the business load to keep the index under the best condition.
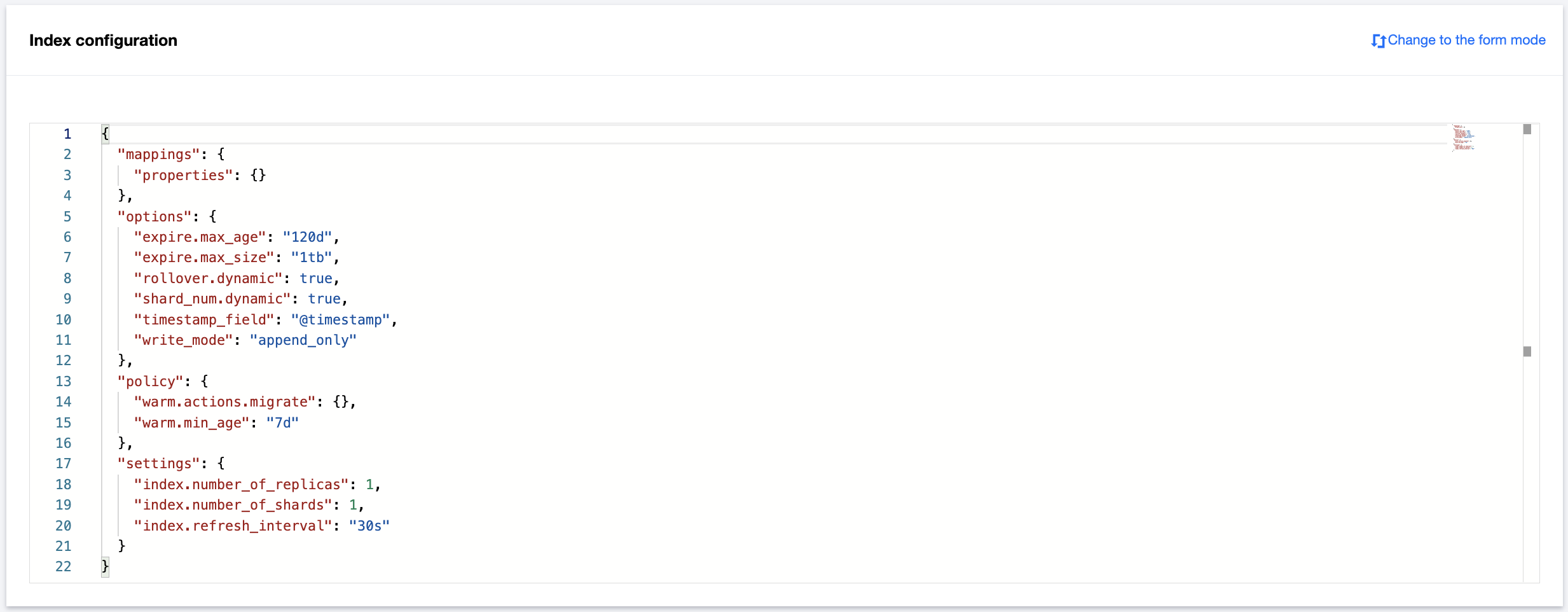
JSON mode
1. Feature description
Currently, you can switch to the JSON mode by clicking Change to JSON mode in the top-right corner of Index configuration to create an index. After a successful switch, the configuration information will be automatically synced to the UI in the corresponding mode.
2. Description of common parameters
The autonomous index feature provides options and policies to help you quickly configure rolling update and lifecycle management. It is compatible with the native syntax of Elasticsearch settings and mappings. Common parameters are as described below:
|
settings | index.number_of_shards | Number of primary shards | It is of the numeric type and must be an integer greater than or equal to 1. |
| index.number_of_replicas | Number of replicas | It is of the numeric type and must be an integer greater than or equal to 0. |
| index.refresh_interval | Refresh interval | It is of the string type. The unit can be set to `d` (day), `h` (hour), `m` (minute), `s` (second), `ms` (millisecond). `micros` (microsecond), or `nanos` (nanosecond). For example, `30s` indicates to set the refresh interval to 30 seconds. |
mappings | field | Field name | It is of the string type, cannot contain Chinese characters, and must be unique. |
| type | Field type | It is of the string type and can be set to `boolean`, `keyword`, `long`, `double`, `date`, or `text`. For more information, see Field data types |
| analyzer | Analyzer | It is of the string type and can be an analyzer in the ES cluster, such as `ik_max_word`. |
| index | Index status | It is of the boolean type and can be set to `true` or `false`. |
| doc_values | Statistics status | It is of the boolean type and can be set to `true` or `false`. |
options | pre_create.enable | Index precreation | It is of the boolean type and can be set to `true` (default) or `false`. Note that if it is disabled when the write mode is **Append write**, backing indices will not be rolled over based on the specified rollover cycle. |
| rollover.dynamic | Rollover cycle dynamic adjustment | It is of the boolean type and can be set to `true` or `false`. |
| rollover.max_age | Rollover cycle | It is of the string type. The unit can be set to `d` (day) or `h` (hour). For example, `1d` indicates to set the rollover cycle to one day. |
| shard_num.dynamic | Shard quantity dynamic adjustment | It is of the boolean type and can be set to `true` or `false`. |
| write_mode | Write mode | It is of the string type. `append_only` indicates `Append write`, and `time_partition` indicates `Shard-based write by time`. |
| expire.max_age | Max age for deletion upon expiry | It is of the string type. The unit can be set to `d` (day) or `h` (hour). For example, `1d` indicates to set the max age to one day. |
| expire.max_size | Max size for deletion upon expiry | It is of the string type. The unit can be set to `PB`, `TB`, `GB`, `MB`, `KB` or `B`. For example, `1TB` indicates to set the max size to 1 TB. |
policy | warm.actions.migrate | Index migration settings for the warm phase | |
| warm.min_age | Storage period before migration to the warm tier | It is of the string type. The unit can be set to `d` (day) or `h` (hour). For example, `1d` indicates to migrate the index to the warm tier one day after the start of the index rolling update. |
| cold.actions.migrate | Index migration settings for the cold phase | |
| cold.min_age | Storage period before migration to the cold tier | It is of the string type. The unit can be set to `d` (day) or `h` (hour). For example, `1d` indicates to migrate the index to the cold tier one day after the start of the index rolling update. |
Creation completion
Click Confirm. After the index is created successfully, you will be redirected to the index list in which the index is included.
Subsequent Operations
Index search and analysis
Data management allows you to redirect to the index search and analysis page. For more information, see Index Search and Analysis. Data management allows you to view the index information and manage backing indices in the console. For more information, see Basic Index Information. Index monitoring
Data management provides a rich set of index monitoring metrics to help you view the real-time data of indices during use. For more information, see Index Monitoring. Index configuration management
Data management enables you to flexibly modify the index configuration information in the console in response to business changes. After successful modification, lifecycle configurations will apply to all backing indices, and configurations of other items will take effect only in those rolled over later and will not update existing ones. For more information, see Index Configuration Management.