The Python code mode extends the expression mode to support more complex syntax and more powerful features. It is more difficult to use and requires a basic knowledge of Python programming.
Use of IDE
Directions
- Hover over any Dataway textbox, and the mode selection buttons will pop up automatically. Click Code to enter the code mode.
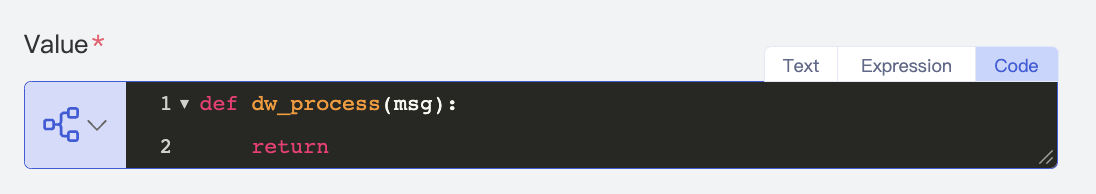
- Click the textbox, and the code editor will pop up. The Python script editor is selected by default, where you can edit a Python script.

- After editing the script, click Confirm.
Feature description
The editor provides various IDE-like features, including syntax check, formatting, script debugging, autocomplete, and code highlighting.
- Syntax check
The Python script editor can check the syntax of the Python script in real time and display conspicuous prompts on the left of the script editing window and below the incorrect code. When you hover over an error prompt, the detailed error message will be displayed.
You can modify the Python script based on the syntax prompts. Only code that passes the syntax check can be saved successfully.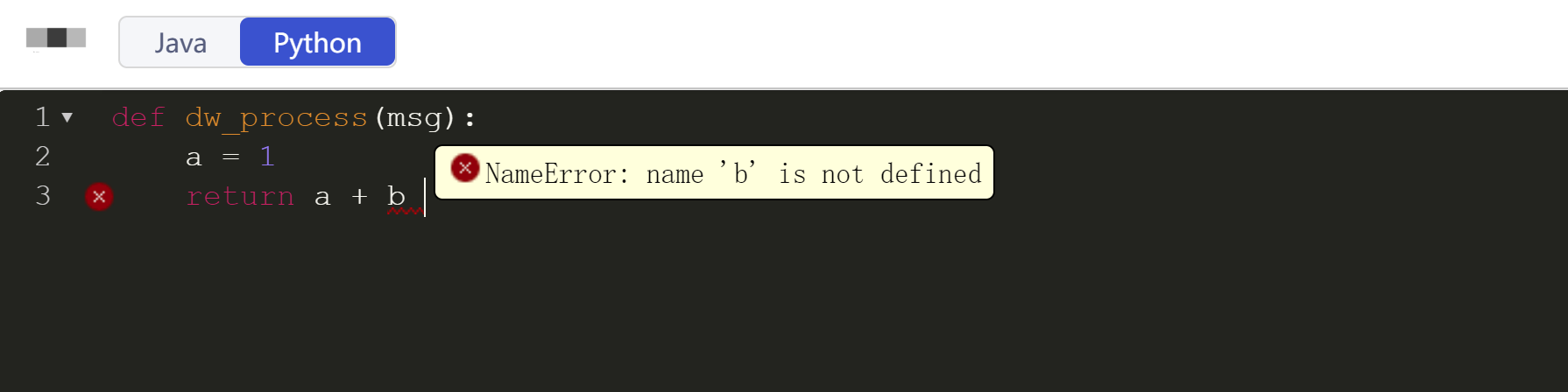
- Formatting
The Python script editor offers a formatting feature button. You can click the formatting icon in the top-right corner to quickly format the Python script, making the code simpler and more standard. After you click the formatting icon in the top-right corner, the formatted code is as shown below:
After you click the formatting icon in the top-right corner, the formatted code is as shown below:

- Script debugging
The Python script editor offers a debugging feature button. You can click the Debug icon in the top-right corner to debug the Python script online as instructed in Script debugging.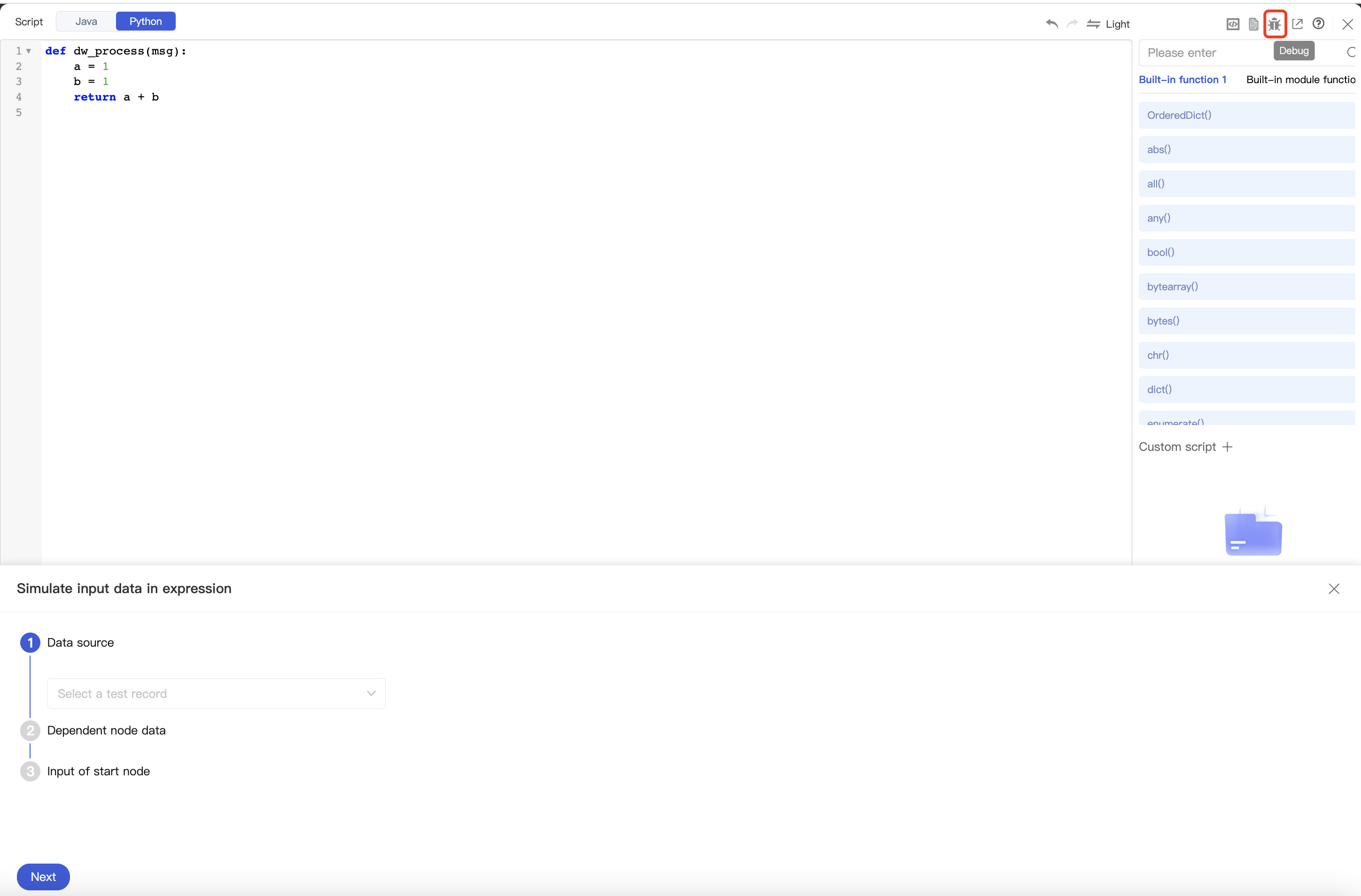
- Autocomplete
When you input content in the textbox, the Python script editor will automatically display the syntax prompts based on the current context below the cursor. Generally, syntax prompts include built-in functions, keywords, and third-party modules.
- Reference on the flow data panel
In code mode, you can reference data on the flow data panel. For more information, see Flow Data Panel.
- Code highlighting
The Python script editor highlights the Dataway code and completes parentheses and brackets by default.
Script Structure
A complete script in Python code mode must be in compliance with Python 3 syntax and contain the entry function definition def dw_process(msg), such as:
def dw_process(msg):
sq = func(3)
val = {
'square': sq,
'data': msg.payload['realData'] + 1
}
return Entity.from_value(val, mime_type='application/json')
def func(x):
return x*x
The dw_process entry function only accepts a parameter msg, which represents the message that Dataway needs to process currently. The returned value of the function is also the returned value of the script.
Enter the above expression in the Set Payload component. If the input message of the component is in JSON structure {"realData": 123}, the calculation output result of the Python script will be as follows:
{
"square": 9,
"data": 124
}
Basic Dataway Syntax Description
The Python code mode is implemented based on Python 3 syntax. This section describes the basic syntax of the Python code mode.
Keyword
The Python code mode supports the following keywords. As reserved words in Python code mode, keywords won't be treated as any identifier name.
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| True | Boolean value. True indicates true, which is opposite to False. |
| True | Boolean value. False indicates false, which is opposite to True. |
| None | Null. |
| and | Logical AND. |
| or | Logical OR. |
| not | Logical NOT. |
| as | Creates an alias. |
| assert | Uses an assertion to test an expression. |
| break | Stops a loop statement. |
| continue | Jumps out of the current loop. |
| def | Defines a function. |
| if/else/elif | Forms a conditional statement. |
| for | Forms a loop statement. |
| global | Declares a global variable. |
| in | Checks whether a value is present in an object. |
| is | Checks whether two variables refer to the same object. |
| lambda | Creates an anonymous function. A function can be implemented in a single line. |
| nonlocal | Declares a nonlocal variable in a nested function. This keyword can modify variables defined externally. |
| pass | Null statement, which can be used as a placeholder. |
| raise | Throws an exception. |
| return | Returns the value of a function. |
Line and indentation
The Python code mode identifies code blocks based on indentation. Different numbers of indentation spaces indicate different code levels. The number of indentation spaces at the same level must be the same.
Operator
The Python code mode supports the following common operators, including arithmetic, comparison, assignment, logical, and bitwise operators. Suppose variable a is 5 and b is 3, the examples are as listed below:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Assignment. | c = 3 |
| + | Addition. | a + b = 3 |
| - | Subtraction. | a - b = 2 |
| * | Multiplication. | a * b = 15 |
| / | Division. | 15 / a = b |
| % | Modulus, which returns the remainder of a division. | 16 % b = 1 |
| ** | Exponentiation. | a ** b = 125 |
| // | Returns the greatest integer less than or equal to the specified value. | a // b = 1 |
| += | Addition assignment. | c += a is equivalent to c = c + a. |
| -= | Subtraction assignment. | c -= a is equivalent to c = c - a. |
| *= | Multiplication assignment. | c *= a is equivalent to c = c * a. |
| /= | Division assignment. | c /= a is equivalent to c = c / a. |
| == | Checks whether two values are equal. | a == b returns False. |
| != | Checks whether two values are not equal. | a != b returns True. |
| > | Checks whether a value is greater than another. | a > b returns True. |
| < | Checks whether a value is less than another. | a < b returns False. |
| >= | Checks whether a value is greater than or equal to another. | a >= b returns True. |
| <= | Checks whether a value is less than or equal to another. | a <= b returns False. |
| & | Bitwise AND. | a & b = 1(0101 & 0011 = 0001). |
| | | Bitwise OR. | a | b = 7 (0101 & 0011 = 0111). |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR. | a ^ b = 6 (0101 ^ 0011 = 0110). |
| ~ | Bitwise negation. | ~a = -6. |
| << | Left shift. | a << 3 = 20 (0000 0101 << 3 = 0001 0100). |
| << | Right shift. | a >> 1 = 2 (0101 >> 1 = 0010). |
Conditional and loop control statements
- The Python code mode uses
if,elif, andelsestatements for conditional control. For example, the value ofais checked to return different strings:def dw_process(msg): a = 100 if a < 10: return 'a is lower than 10' elif a <= 100 and a >= 10: return 'a is between 10 and 100' else: return 'a is bigger than 100'
The execution result of the Dataway expression is a is between 10 and 100.
- The Python code mode uses the
forloop for loop control. For example, aforloop is used to get the product of elements ina:def dw_process(msg): a = [1, 2, 3, 4] num = 1 for i in a: num *= i return num
The execution result of the Dataway expression is 24.
Function definition
In Python code mode, you can use the def keyword to define a function as follows: the def keyword is followed by a function name and parameter name list, the function definition line ends with a colon :, the next line is indented by default, and the entire function ends with a return statement; if no return statement is used, None will be returned.
After defining a function, you can call and execute it in another function. In Python code mode, the default entry function dw_process doesn't need to be declared manually. To customize a function, directly define it below the dw_process entry function. For example, a function test() is defined to calculate the sum of the list elements and is called in the dw_process function, and a return statement is used at the end to return the result:
def dw_process(msg):
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
return add_list(a)
def add_list(alist):
sum = 0
for i in reversed(alist):
sum += i
return sum
The final output result is 10.
Module call
The Python code mode has various built-in third-party modules, including time, json, math, base64, hmac, random, hashlib, Crypto, socket, struct, decimal, and datetime. When using a module, you can directly reference the module name without using the import keyword. For the specific function description, see Expression Mode Appendix. For example, a JSON string is received and converted into a dictionary:
def dw_process(msg):
jsonStr = '{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}'
jsonDict = json.loads(jsonStr) # Convert into a `dict` object
num = 1
for k, v in jsonDict.items(): # Traverse the `dict` object
num += math.pow(v, 2)
return num
The final output result is 15.0.
Comment
In Python code mode, single-line comments start with #, and you can use multiple # symbols, ''', or """ for multi-line comments. For example, execute the following code:
# Dataway comment
'''
Dataway comment
Dataway comment
'''
"""
Dataway comment
Dataway comment
"""
def dw_process(msg):
return 'Dataway Hello World!'
The output result is:
Dataway Hello World!
Note:The Python code mode provides the syntax check feature to check the syntax in real time and prompt errors when you write code. For the detailed syntax description, see The Python Language Reference.
dw_process Entry Function
dw_process is the main entry function in Python code mode, which acts like the main function in C or C++.
dw_process only accepts a parameter of the Message type, and its returned value is the output value of the script in Python code mode.
As a stage in the data processing process in iPaaS, the dw_process function currently supports core types for its returned value.
For more information on the data types and returned value in Python code mode, see Data Type System.
Data Type System
| Type | Description | Unique to Dataway | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| str | String, i.e., native str type in Python. |
No | "abc" |
| None | None in Python. |
No | None |
| bool | Boolean, i.e., native bool type in Python. |
No | True/False |
| float | Float, i.e., native float type in Python. |
No | 123.123 |
| int | Integer, i.e., native int type in Python. |
No | 123 |
| bytes | Byte array, i.e., bytes type in Python. |
No | b'this_is_a_bytes' |
| set | Set, i.e., set type in Python. |
No | {1,2,3} |
| list | List (a sequence container), i.e., native list type in Python. |
No | [1,2,3] |
| dict | Dictionary (a key-value pair container), i.e., native dict type in Python. |
No | {1:1, 'key': 'value'} |
| Entity | Entity data in iPaaS, which represents a binary object and is accessed as an Entity object in Dataway. It contains information such as blob, mime_type, and encoding. |
Yes | payload in a message constructed by the HTTP Listener component, such as msg.payload |
| MultiMap | Multi-value map. Like xml but unlike dict, this type supports duplicate key values. |
Yes | Object obtained after data in application/www-form-urlencoded format is parsed |
| FormDataParts | Array + list data structure, which is similar to orderDict in Python. |
Yes | Object obtained after data in multipart/form-data format is parsed |
| Message | Message in iPaaS, which is accessed as a Message object in Dataway. |
Yes | msg parameter in the dw_process entry function |
Note:
- The above types can be used in the Python code mode, but the data type of the returned value of the
dw_processfunction must be a core type.- If the output value of a Dataway expression is the final result returned by the flow, the types supported for the returned value will also be subject to the flow components. If an HTTP Listener component is used as the first component in the flow, the final
payloadvalue must be ofEntitytype.
Script Debugging
The Python code mode supports script debugging to help troubleshoot problems and verify the result. With this feature, you can manually define the input parameter msg and click Test to directly view the script execution result, debugging log, and error message.
- Enter an expression in the script textbox.
In Dataway debugging mode, you can use theprint()function in the expression to print the information to be observed. The printed message will be displayed on the UI after the script is executed.
- Click the Debug icon in the top-right corner of the script editing window. In the simulated data configuration pop-up window, you can set the payload, attributes, and variables of
msg. After completing the configuration, click Start test, and the system will automatically assemble amsgparameter and pass it to thedw_processfunction as the script input.
After the
dw_processfunction is executed, the execution result and printed debugging log will pop up at the bottom of the editing window. If errors occur during execution, error messages will be displayed.Output: It displays the execution result of the Dataway expression.
Error: It displays the script execution error message. If no errors occur, a green tick will be displayed.
Other Support
The Python code mode provides various built-in functions and third-party modules for you to choose as needed to quickly implement predefined features. For more information, see Python Appendix.

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?