Creating Disaster Recovery Instance
Last updated: 2025-02-06 17:46:06
Overview
For scenarios with strong requirements for business continuity and data reliability, or due to regulatory needs, you can create one or more disaster recovery instances across regions based on the current instance’s cluster architecture and storage engine. If the region where the current instance is located loses communication due to power, network, or other force majeure factors in any AZ, and the HA system fails, the disaster recovery instance can be promoted to the primary instance. This allows cross-region disaster recovery, ensuring the continuity of data services.
Must-Knows
Due to data synchronization delay, the real-time synchronization of disaster recovery instances may not be guaranteed. The synchronization delay between each disaster recovery instance and the primary instance can be viewed in the console.
During the lifecycle of a disaster recovery instance, it is read-only and cannot be used for data writing or updates.
When the source instance of the disaster recovery instance is terminated, or the disaster recovery instance is manually promoted, it becomes a regular instance with full read/write capabilities, quickly supporting business needs.
Version Information
The current replica set instances of versions 4.0, 4.2, 4.4, 5.0, and 6.0 all support creating read-only instances. Sharded instances support this feature only in version 4.0 and later.
Prerequisite
The current instance is running normally.
The region, AZ, and network for the disaster recovery instance have been planned.
The storage specifications and the number of disaster recovery instances have been estimated.
The billing mode has been selected based on the business scenario, and the necessary budget for the disaster recovery instance has been planned.
Creating a Disaster Recovery Instance
1. Log in to the MongoDB console.
2. In the left sidebar, choose NoSQL Database > MongoDB.
3. In the MongoDB dropdown list, select either Replica Set Instance or Shard Instance. The process for replica sets and sharded clusters is similar.
4. At the top of the instance list page, select the region.
5. In the instance list, find the target instance for which you want to create a disaster recovery instance.
You can use the search box in the top-right corner of the instance list to find the target instance by entering the instance ID, instance name, private IP address, or tag key.
If the instance is not found in the instance list, go to the left sidebar and choose Recycle Bin to check if the instance has been isolated due to expired payments. For more details, see Recycle Bin.
6. Click the target instance ID to enter the Instance Details page.
7. Select the RO/DR tab, then go to the DR instance page, and click Create .
8. On the TencentDB for MongoDB DR Instance purchase page, confirm the Primary Instance Info and select the required configuration.
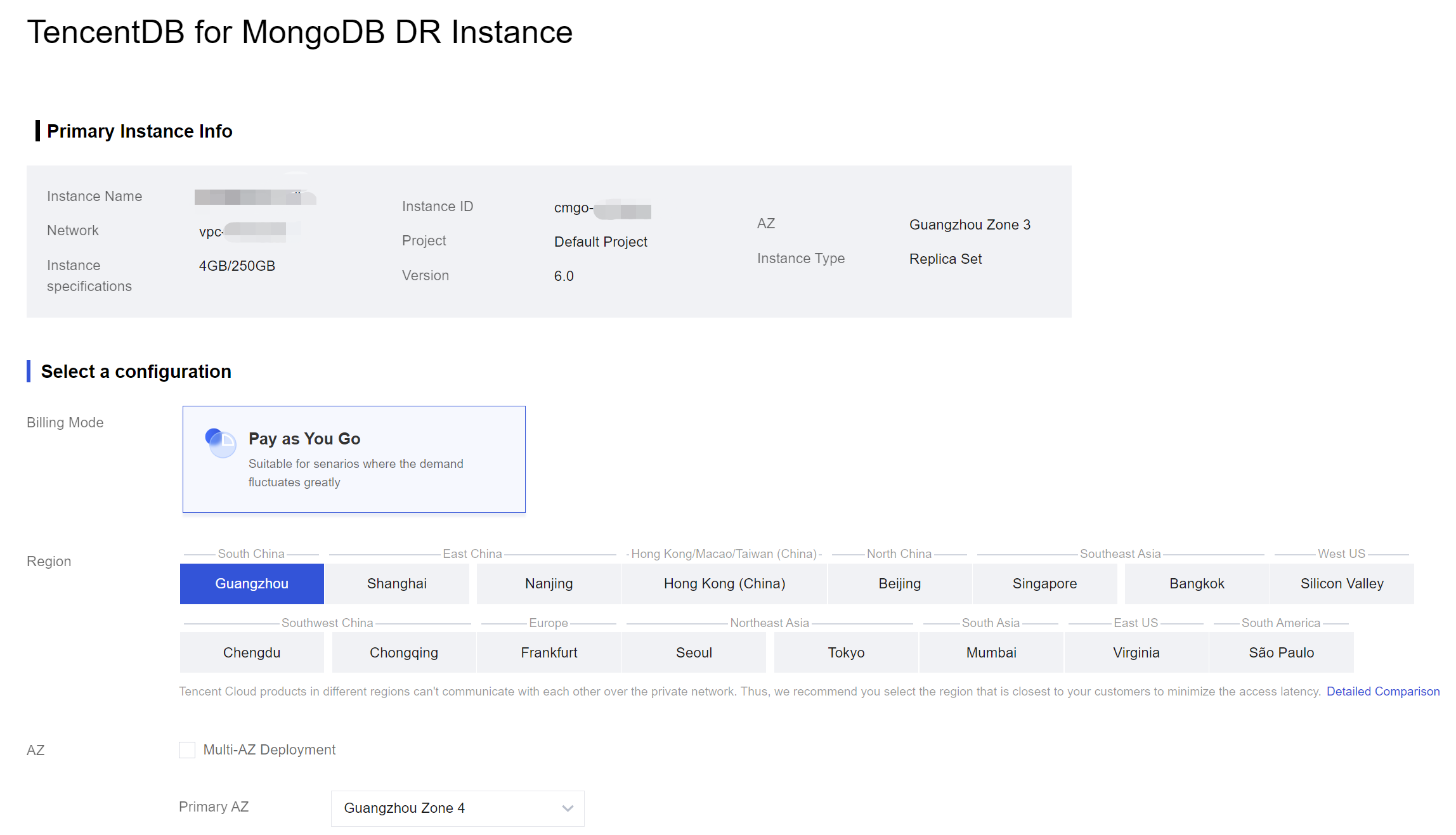
See the table below to configure the instance specifications based on your actual needs.
Parameter Name | Description |
Billing mode | Supports both monthly subscription and pay-as-you-go billing. For details on choosing a billing method, see Billing Overview. |
Region | Select the region where the disaster recovery instance is located. |
AZ | Choose whether to enable multi-AZ deployment, based on the actual high availability business needs. |
Database version | The database version is fixed to match the source instance and cannot be changed. |
Architecture type | The architecture type is fixed to match the source instance and cannot be changed. For more details on architecture types, see System Architecture. |
Storage engine | The default storage engine is WiredTiger. |
Mongod specifications | Select the computing specifications of the database instance from the dropdown list. The disaster recovery instance’s CPU cores and memory capacity should be equal to or greater than those of the source instance. The higher the specifications, the higher the IOPS. For more details on supported specifications, see Product Specification. After creating the instance, you can adjust the instance’s computing specifications. For more details, see Adjust Instance Configuration. |
Mongod shard count | This parameter is displayed when the architecture type is set to Sharded Cluster. It is used to configure the number of shards in the sharded cluster, with a valid range of [1, 20]. The number of shards in the disaster recovery instance should be equal to or greater than that of the source instance. Each shard is a replica set, and increasing the number of shards can expand the storage capacity of the cluster. Select based on your needs. After creating the instance, you can adjust the number of Mongod shards. For detailed steps, see Adjust Instance Configuration. |
Disk capacity | Select the storage capacity of the database instance using the slider. The disaster recovery instance’s disk capacity should be equal to or greater than that of the source instance. The value range of disk capacity varies depending on the Mongod specifications. See Product Specifications. The system by default allocates 10% of the selected storage capacity for Oplog. The size of the Oplog can be adjusted in the console’s instance list. For detailed directions, see Adjust Oplog Capacity. After creating the instance, you can adjust the disk capacity. For detailed directions, see Adjust Instance Configuration. |
Number of primary and secondary nodes | This parameter is displayed when the architecture type is set to Replica Set. The default is 3 nodes (1 primary and 2 secondary), with 3 storage nodes forming the 1 primary and 2 secondary architecture. Customizing the number of replica nodes is currently not supported. You can select from the dropdown list to choose 5 nodes (1 primary and 4 secondary) or 7 nodes (1 primary and 6 secondary). After creating the disaster recovery instance, you can increase the number of secondary nodes. For detailed directions, see Add New Secondary Node. |
Number of primary and secondary nodes per shard | This parameter is displayed when the architecture type is set to Sharded Cluster. It is used to configure the number of nodes per shard in the cluster. The system default is 3 nodes (1 primary and 2 secondary), meaning each shard follows a 1 primary and 2 secondary architecture. You can choose from the dropdown list to select 5 nodes (1 primary and 4 secondary) or 7 nodes (1 primary and 6 secondary), but customizing the number of nodes is not currently supported. After creating the disaster recovery instance, you can increase the number of secondary nodes per shard. For detailed directions, see Add New Secondary Node. |
Number of read-only nodes | Configure the number of read-only nodes, supporting no read-only nodes or 1 to 5 read-only nodes. Only versions 4.0 and 4.2 support configuring the number of read-only nodes; version 3.6 does not support this feature. After creating the disaster recovery instance, you can increase the number of read-only nodes. For detailed directions, see Add New Read-Only Node. |
Configuration notes | The maximum number of connections for the instance is calculated based on the configured Mongod specifications, helping you predict whether the current specifications meet your expectations. |
Mongos specifications | This parameter is displayed when the architecture type is set to Sharded Cluster. It is used to configure the specifications for Mongos. After the Mongod specifications are configured, Mongos will be automatically assigned default specifications. For example, if Mongod is configured with 2 cores and 4 GB, the default configuration for Mongos will be 1 core and 2 GB. Increasing the Mongos specifications will incur additional fees. For more details on pricing, see Product Pricing. The maximum number of connections for a sharded cluster is determined by the specifications and number of Mongos nodes. You can view the maximum number of connections in the configuration notes. After creating the instance, you can change the configuration of the Mongos nodes. For detailed directions, see Change Mongos Node Configuration Specifications. |
Number of Mongos | This parameter is displayed when the architecture type is set to Sharded Cluster. It is used to configure the number of Mongos nodes. If the instance is deployed in the same AZ, the valid range for Mongos nodes is [3, 32]. If multi-AZ deployment is enabled, and the instance is deployed across different AZs, the valid range for Mongos nodes is [6, 32]. Increasing the number of Mongos nodes will incur additional fees. For billing details, see Product Pricing. After creating the instance, you can adjust the number of Mongos nodes. For detailed directions, see Add new Mongos nodes. |
Network type | Only VPC is supported. |
IPv4 network | Select the specific VPC and its subnet. It is recommended to choose the same VPC within the same region as that of your cloud server. The VPC has a region attribute (e.g., Guangzhou), while the subnet has an AZ attribute (e.g., Guangzhou Zone 1). A VPC can be divided into one or more subnets, and subnets within the same VPC have internal communication by default, whereas different VPCs (regardless of being in the same region) are isolated by default. After purchasing the instance, you can switch the VPC. For detailed directions, see Switch Instance Network. You can also click Create VPC and Create Subnet to recreate the required network environment. For more details, see Create VPC. |
IPv6 network | Check whether to enable IPv6 access. Currently, it is not supported. |
Security group | Set security group rules for the instance to control incoming traffic to the database. You can select an existing security group from the dropdown, or click Customize Security Group to set new inbound security group rules. For more details, see Configure Security Group. |
Assign project | Assign the instance to the appropriate project. You can manage instances based on the assigned project. |
Tag | Set tags for the instance. You can categorize and manage instances based on tags. Click Add to select a tag key and tag value. |
Instance name | Set the name for the instance. Choose a name that is easy to identify. It supports Chinese, English, or numbers with a length of fewer than 60 characters, as well as hyphens (-) and underscores (_). |
Quantity purchased | A maximum of 3 disaster recovery instances can be created for a single instance. |
Total fees | For pay-as-you-go billing, the hourly fee is displayed. Click billing details for more information and see Product Pricing. |
9. Once you have confirmed the parameter configuration is correct, click Buy Now to complete the purchase. After the purchase success prompt is prompted, click Go to Console. In the instance list, once the instance status shows Running, it is ready for use.
Viewing Disaster Recovery Instance
1. Log in to the MongoDB console.
2. In the dropdown list under MongoDB in the left sidebar, choose either Replica Set Instance or Shard Instance. The process for replica sets and sharded instances is similar.
3. At the top of the instance list page, select the region.
4. In the instance list, find the source instance to which the disaster recovery instance belongs.
You can use the search box in the top-right corner of the instance list to search for the target instance by entering the instance ID, instance name, private IP address, or tag key.
If the instance is not found in the instance list, choose Recycle Bin from the left sidebar to check whether the instance has been isolated due to expired fees. For more details, see Recycle Bin.
5. In the Instance ID/Name column of the source instance, click Instance ID to enter the Instance Details page.
6. Click the RO/DR tab, and then select the DR Instance tab.
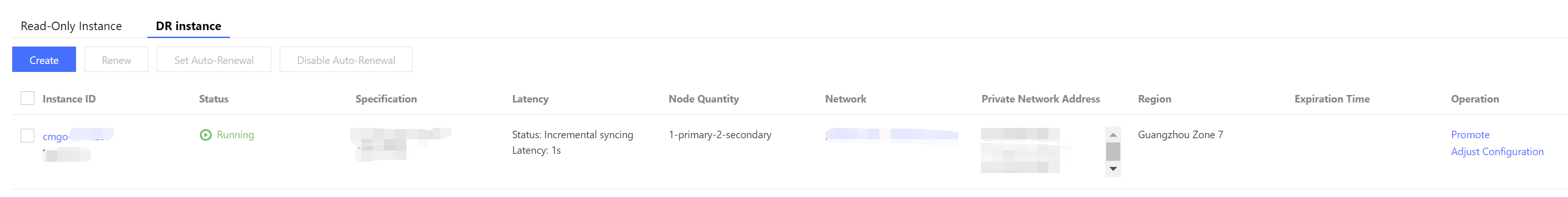
7. In the disaster recovery instance list, view all disaster recovery instances under the source instance.
Parameter | Description |
Instance ID | The disaster recovery instance ID and its name. Click the instance ID in blue to navigate to the disaster recovery instance details page. For more details, see View Instance Details. |
Status | The current running status of the instance. The normal status is Running. |
Specifications | Instance specification information, including memory and disk capacity. |
Latency | The synchronization status and latency of the disaster recovery instance based on the source instance. |
Number of nodes | The number of primary and secondary nodes in the disaster recovery instance. |
Network | The name of the VPC to which the disaster recovery instance belongs. |
Private IP address | The private IPV4 address assigned by the VPC. To access the database, you need to configure the private IP address and port information. For detailed directions, see Connecting Instances. |
Region | Information about the region and AZ. |
Expiration time | For monthly subscription billing, the specific expiration time of the instance is displayed. For pay-as-you-go billing, this field is blank. |
Operations | Click Modify Configuration to adjust the specifications of the disaster recovery instance. When adjusting the specifications of the source instance, be sure to upgrade the disaster recovery instance as well; otherwise, data loss may occur. |
Promoting Disaster Recovery Instance to Primary Instance
1. Log in to the MongoDB console.
2. In the dropdown list under MongoDB in the left sidebar, choose either Replica Set Instance or Shard Instance. The process for replica sets and sharded instances is similar.
3. At the top of the instance list page, select the region.
4. In the instance list, find the source instance to which the disaster recovery instance belongs.
You can use the search box in the top-right corner of the instance list to search for the target instance by entering the instance ID, instance name, private IP address, or tag key.
If the instance is not found in the instance list, choose Recycle Bin from the left sidebar to check whether the instance has been isolated due to expired fees. For more details, see Recycle Bin.
5. In the Instance ID/Name column of the source instance, click Instance ID to enter the Instance Details page.
6. Click the RO/DR tab, and then select the DR instance tab.
7. In the disaster recovery instance list, find the instance you want to promote.
8. In the Operation column, click Promote. In the Promote DR Instance dialog box, confirm the prompt information, and click OK.
9. The disaster recovery instance will immediately be converted to a regular instance and removed from the disaster recovery instance list.
Related API
API | Description |
Query the list of MongoDB instances. | |
Modify the instance name. | |
Adjust the MongoDB instance configuration. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

