TencentDB for MongoDB
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Features
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Access Management
- Instance Management
- Node Management
- Network Configuration
- Backup and Rollback
- Data Rollback
- Data Security
- SSL Authentication
- Database Management
- Disaster Recovery/Read-Only Instances
- Parameter Configuration
- Data Migration Guide
- Creating a DTS Migration Task
- Fix for Verification Failure
- Consistency Check After Migration
- Practical Tutorial
- Ops and Development Guide
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- Making API Requests
- Backup APIs
- Instance APIs
- Account APIs
- Task APIs
- Other APIs
- Instance Connection
- Product Performance
- Service Agreement
DocumentationTencentDB for MongoDBOperation GuideBackup and RollbackRestoring to Self-built Database
Restoring to Self-built Database
Last updated: 2024-01-15 14:40:06
Restoring a Physical Backup to a Self-Built Database
A replica set instance has only one copy of data, while each shard of a sharded cluster has one copy of data. Restore your data based on your business needs. This document describes how to restore a single copy of data.
Restoring data to a single node
1. Copy the data to an empty data directory in the self-built database, such as /data/27017/.
cp -r * /data/27017/
2. Restart mongod and check the data. Below is a command sample:
./mongod --dbpath /data/27017 --port 27017 --logpath /var/log/mongodb/27017.log --fork
Restoring data to a replica set
As a physical backup retains the configuration of the original instance by default, the original configuration needs to be removed first; otherwise, the data may become inaccessible.
1. Restore the data to a single-node self-built database and then restart the node in the form of replica set. Below is a command sample:
./mongod --replSet mymongo --dbpath /data/27017 --port 27017 --logpath /var/log/mongodb/27017.log --fork
2. Log in to the node and remove the replica set configuration of the original instance by running the following command:
rs.slaveOk()use localdb.system.replset.remove({})
3. Restart the node, add a node to the replica set, initialize it, and check the data. The node added to the replica set should have been started with no data contained. Below is a command sample:
rs.initiate({"_id":"mymongo","members":[{"_id":0,"host":"127.0.0.1:27017"},{"_id":1, "host":"127.0.0.1:27018"},{"_id":2, "host":"127.0.0.1:27019"}]})
Notes:
Data cannot be restored to a sharded cluster. As the route of physical backup is missing in a sharded cluster, mongos can only read the data of the primary shard even if the data of each shard is restored to the self-built replica set (each shard of the sharded cluster).
Restoring a Logical Backup to a Self-Built Database
To avoid any impact on data check after the data is restored to a self-built database, the self-built database must be empty.
For v3.6, you need to delete the
config directory manually and then run the mongorestore command to restore the data of each shard.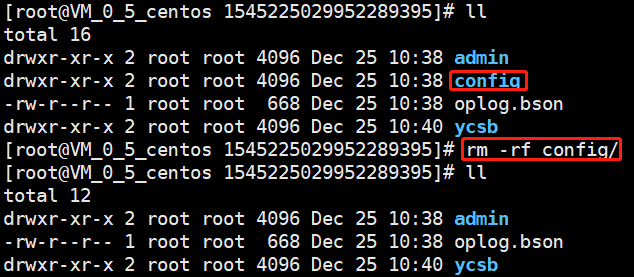
For v3.2, you need to merge all the files in individual collections manually before restoring the data. Below is a file merge operation sample:
The
c_10 collection is in the ycsb directory in the database and contains data files from c_10.bson.gz.chunk-64 to c_10.bson.gz.chunk-127. The merge command is cat c_10.bson.gz.chunk-* > ./c_10.bson.gz.Notes:
Chunk distinction will appear in some scenarios on v3.2.
Run the
mongorestore command to restore the data, where the -h parameter specifies the self-built database address, --dir specifies the directory of the data file, and --gzip must be specified to decompress the backup file. The command is as follows:./mongorestore --gzip --drop -h127.0.0.1:27017 --dir ./1544517027220146694
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

