Accelerating Routing Convergence Through BGP+BFD (Layer 3)
Last updated: 2024-11-05 09:46:38
Accelerating Routing Convergence Through BGP+BFD (Layer 3)
Last updated: 2024-11-05 09:46:38
This document describes how to accelerate routing convergence between customer IDC and private network by initiating BGP routing protocol on the local IDC switch and configuring bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) on Tencent Cloud direct connect gateway.
Background
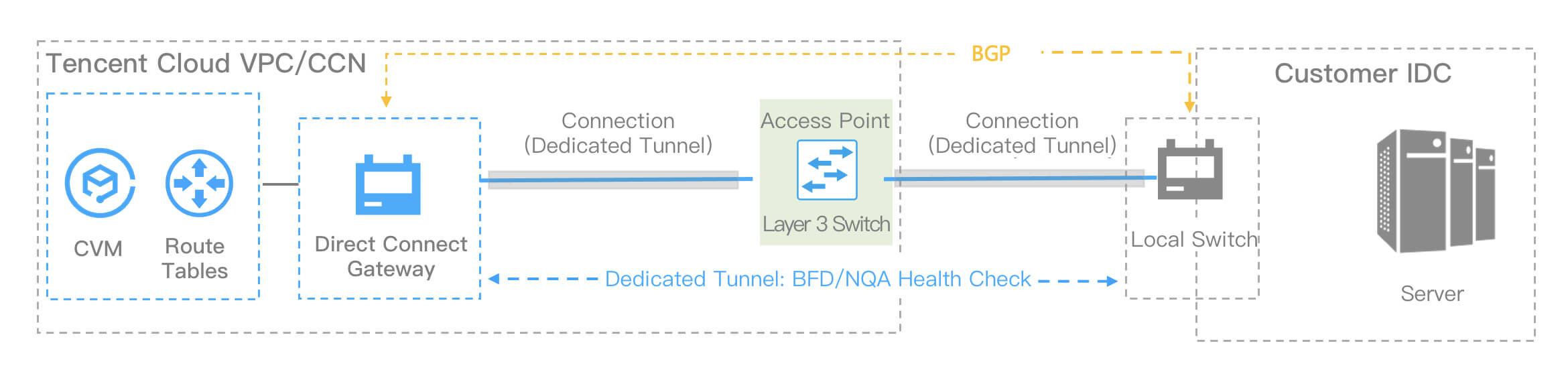
Note:
In a connection using static routes, we recommended that you use static routes and BFD/NQA to achieve route convergence.
The connection connects the IDC switch and the layer 3 network sub-interface of Tencent Cloud switch, thereby connecting IDC and Tencent Cloud network.
Implement mutual access to resources through VPC/CCN.
Implement routing convergence through BGP+BFD/NQA.
Prerequisite
You have built a VPC as instructed in Building Up an IPv4 VPC.
You have applied for a connection as instructed in Applying for Connection and completed the preparatory construction.
Configuration Guide
Step 1. Create a direct connect gateway
Step 2. Create a dedicated tunnel
The tunnels created on the connections vary depending on the access method.
The tunnels created on your own connections are exclusive dedicated tunnels, which are applicable to scenarios with requirements for high-bandwidth access and exclusive access. For more information, see Exclusive Virtual Interface.
The tunnels created on our partners' connections pre-established in Tencent are shared dedicated tunnels, which are applicable to scenarios where there is no need for high-bandwidth access and the cloudification time is short. For more information, see Shared Dedicated Tunnel.
Step 3. Configure health check
Step 4. Completing the IDC local configuration as instructed in Huawei NE Series Routers
This document takes Huawei CE switch as an example. For other local configurations, see Huawei NE Series Routers.
If you can't implement the layer 3 sub-interface connection due to special reasons, you can try layer 2 sub-interfaces. For details, see Mode 2.
(Recommended) Mode 1: Layer 3 sub-interface+BGP
# Set sub-interfaces for layer 3 connectioninterfaces<interface_number>.<sub_number>description <interface_desc>dot1q termination vid <vlan id>ip address <subinterface_ipaddress><subinterface_netmask>speed <interface_speed>duplex fullundo negotiation autocommit# Set eBGPbgp <as_number>router-id <route_id>peer <bgp_peer_address> as-number<bgp_peer_as_number>peer <bgp_peer_address> password cipher<bgp_auth_key>peer <bgp_peer_address> description<bgp_desc>ipv4-family unicastpeer <bgp_peer_address> enablecommit# Set BFD configuration of eBGPbgp <as_number>router-id <route_id>peer <bgp_peer_address> bfd min-tx-interval1000 min-rx-interval 1000 detect-multiplier 3
Mode 2: Layer 2 Vlanif interface+BGP (It is recommended to disable STP for layer 2 interfaces)
# Set portsinterfaces<interface_number>description<interface_desc>port link-typetrunkundo shutdownspeed<interface_speed>duplex fullundo negotiationautostp disable ** (****Disable****stp****STP****)**commit# Set virtual tunnelsvlan<subinterface_vlanid>description<subinterface_desc># Set logic interfacesinterface Vlanif<subinterface_vlanid>description <subinterface_desc>ip address<subinterface_ipaddress> <subinterface_netmask># Configure interface VLANinterfaces<interface_number>port trunkallow-pass vlan <subinterface_vlanid>commit# Set eBGPbgp<as_number>router-id<route_id>peer<bgp_peer_address> as-number <bgp_peer_as_number>peer<bgp_peer_address> password cipher <bgp_auth_key>peer<bgp_peer_address> description <bgp_desc>ipv4-familyunicastpeer<bgp_peer_address> enable# Set BFD configuration of eBGPbgp <as_number>router-id <route_id>peer <bgp_peer_address> bfd min-tx-interval1000 min-rx-interval 1000 detect-multiplier 3commit
How to Set Keepalive and Holdtime Parameters
After establishing a BGP connection between two peers, the two peers periodically send keepalive messages to the peer to maintain the validity of the BGP connection. If a router does not receive a keepalive message or any other type of packet from the peer within the specified holdtime, the BGP connection is considered to have been interrupted and thus the BGP connection is interrupted.
The keepalive-time and hold-time values are determined through negotiation between the two peers. The smaller hold-time value in the Open message of both peers is the final hold-time value. The smaller value between the result of the negotiated hold-time value divided by 3 and the locally configured keepalive-time value is used as the final keepalive-time value.
When the BGP connection is established, the recommended holdtime is 180 seconds (default value used by most vendors).
If the configured holdtime is less than 30 seconds, the linkage may interrupt the neighbor session in normal cases, and linkage jitter detection is required. You are advised to enable BFD to improve convergence performance.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

