This document shows the success story of the use of SCF in online education made available by IMWeb, which boasts the following achievements:
Affiliated to Tencent, the IMWeb team is a leading professional frontend team in China.
Focusing on the frontend field for many years, it has been taking charge of businesses with hundreds of millions of daily access requests such as QQ profiles, QQ sign-up, and QQ groups.
Currently, it focuses on the online education field and is dedicated to developing three major products: Tencent Class, Tencent Penguin Tutoring and ABCmouse.
Technical Attempts
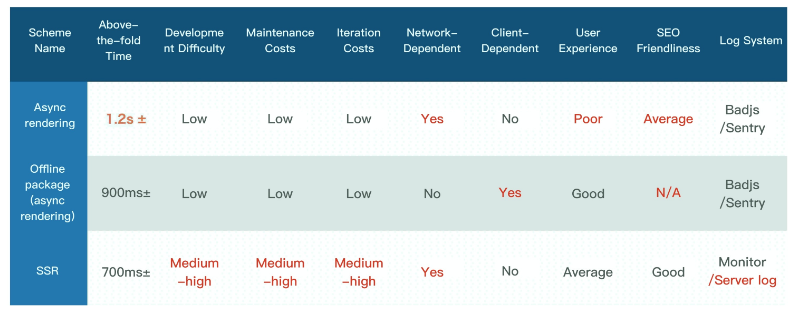
IMWeb has made various technological attempts in the traditional web application area, such as traditional offline package and PWA offline application. However, each technology stack has its own strengths and weaknesses. The multi-dimensional comparison between the team's current technical schemes is as shown below:
The comparison unveils that server-side rendering (SSR) has outstanding performance with regard to above-the-fold rendering and SEO. Based on the result, the team favors the SSR scheme for the following reasons:
SSR application performance
The following performance optimization issues are highlighted:
Processing of a large amount of CPU-intensive computation: SSR used in React-like applications works by calling the renderToString method of React on the server to render the React component as HTML strings. For complicated SSR applications, this process may involve a large amount of CPU-intensive computation, which is not a field of expertise of Node.
Improvement in above-the-fold rendering performance: As offline packages depend on the environment (application), a complete solution for caching relevant pages is required in a traditional web environment in order to improve the above-the-fold rendering performance.
SSR Ops costs
Service availability: As most frontend engineers may not be good at service Ops, service availability is also an important concern in technical scheme selection.
Based on the issues mentioned above, the considerations can be summarized as follows:
How to design a method that boasts all the strengths of the three schemes available?
Offline features independent of client environment.
Short above-the-fold time and great SEO experience.
Low Ops cost and easier troubleshooting
Is the scheme general and replicable?
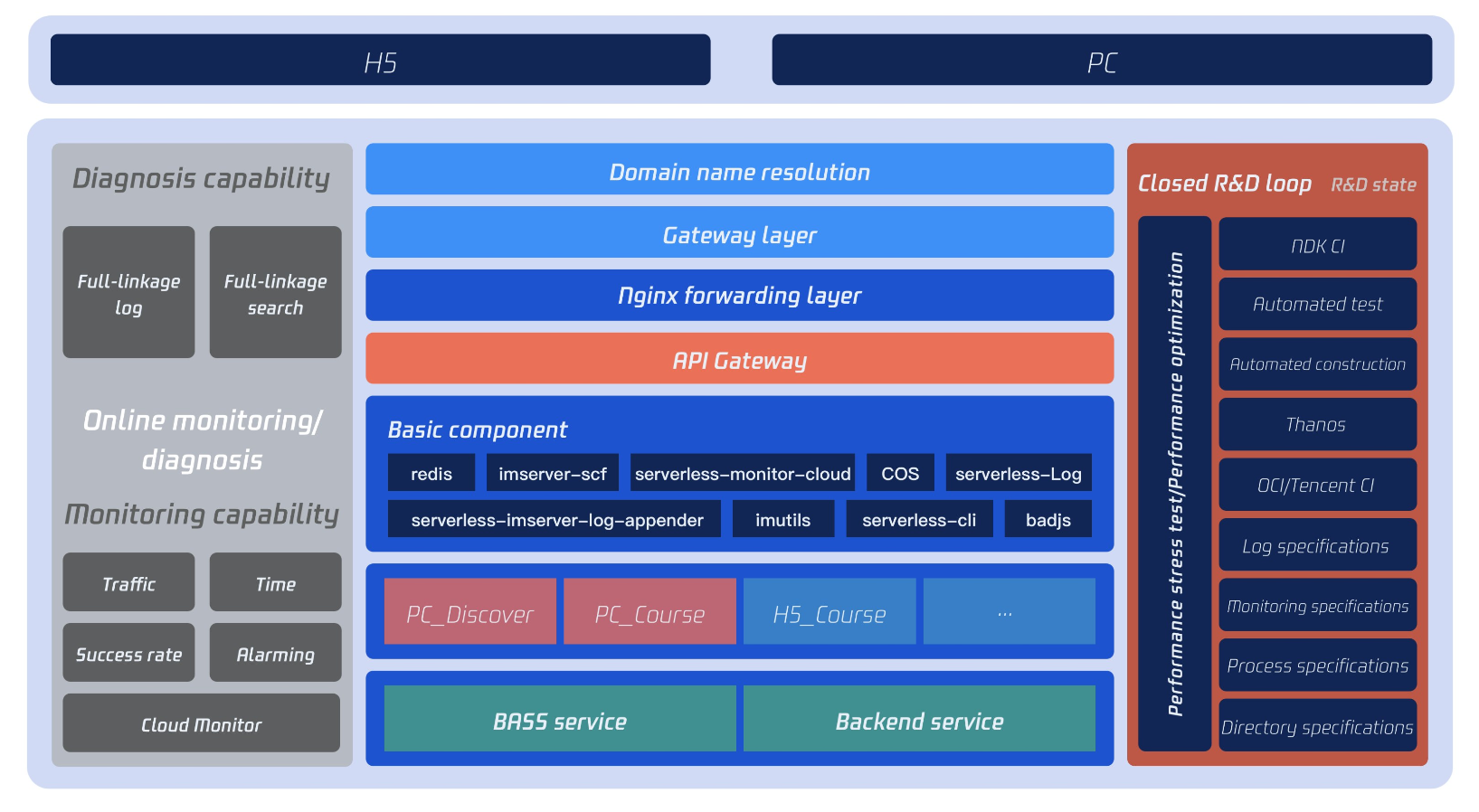
Overview of SSR Architecture Scheme by IMWeb
The SSR technical architecture used by the team is as shown below:
The following sections describe the team's existing schemes in terms of code organization, performance optimization, and runtime context.
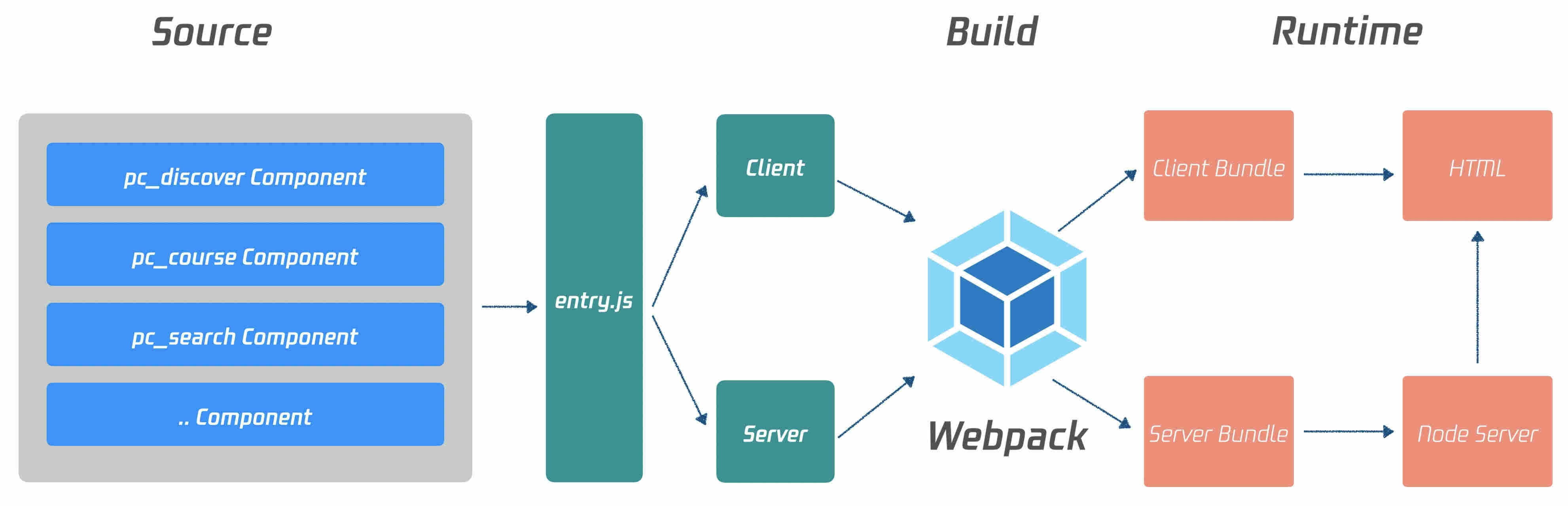
Code organization
A heterogeneous mode is used in both the PC and HTML5 projects to construct SSR applications as shown below:
In heterogeneous mode, business developers can focus more on the business features without being distracted by runtime problems; however, they also need to pay attention to the following:
Correctly use constants such as window and document in traditional browsers.
Ensure that the HTTP data request library can support both the server and client.
Reasonably use the lifecycle of React applications.
Inject environment variables to differentiate between current runtime environments.
Performance optimization
Separating dynamic/static API data
Page rendering usually depends on backend data, which can be divided into dynamic data and static data:
Static data: Data that rarely changes in a page, such as course title and description in Penguin Tutoring.
Dynamic data: Data related to user login status in a page, such as whether a course has been purchased and current course discount.
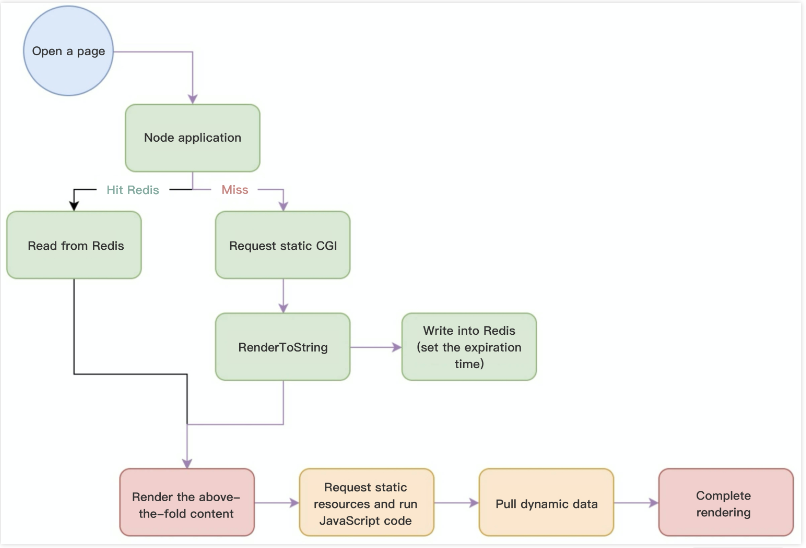
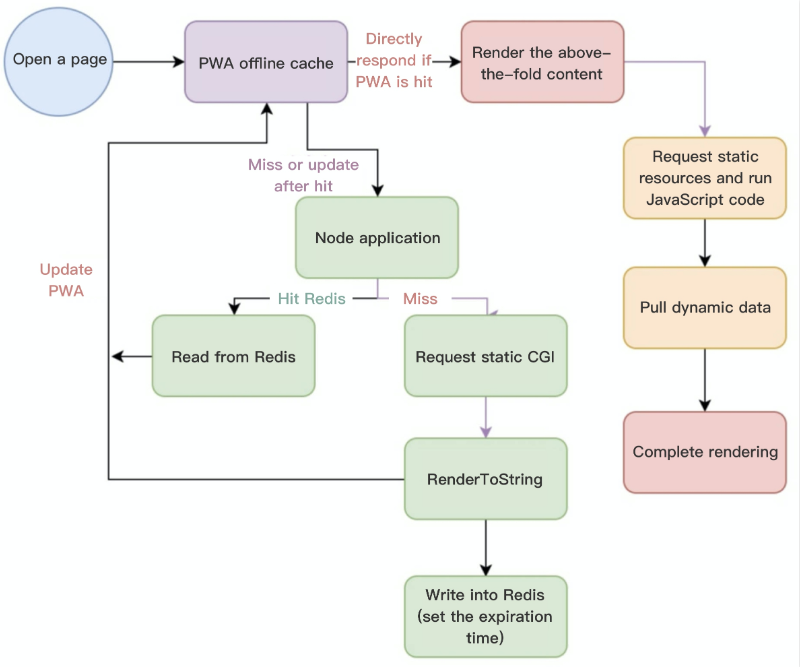
By separating dynamic/static data for APIs, the static data can be used for caching thanks to its low latency sensitivity. After static data is used to render the page on the server, the dynamic data will be used to perform secondary rendering on the server. The main logic is as shown below:
Redis is used to cache the page rendered with static data, which not only accelerates SSR rendering but also improves the QPS of a single server (renderToString is a CPU-intensive operation in a certain sense).
Using PWA in browser for offline caching
On the client, PWA can be used to cache static data-based HTML SSR pages offline so as to further improve the above-the-fold rendering performance. The main logic is as shown below: Runtime context
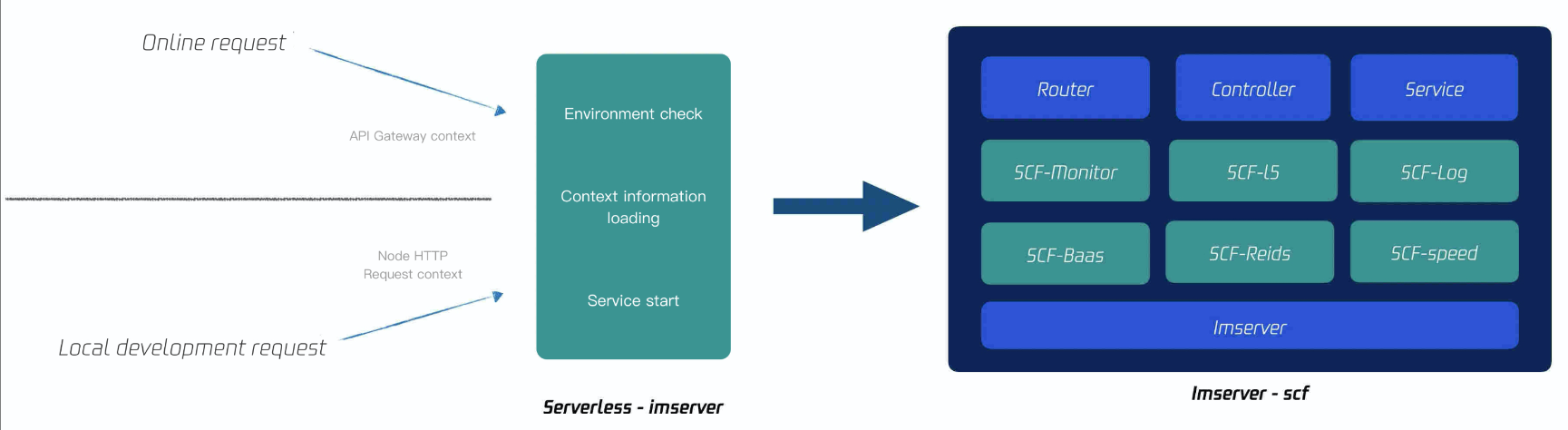
Because of the high Ops complexity and maintenance costs of backend applications, Serverless (Tencent Cloud SCF) is used to deploy SSR applications. Thanks to the inherent advantages of the Serverless architecture mode, the team does not need to concern over issues such as service Ops and scaling.
As shown above, in essence, an SSR application is a Node application, and SCF invocation is an event. Therefore, the following method is used to ensure compatibility with the two modes:
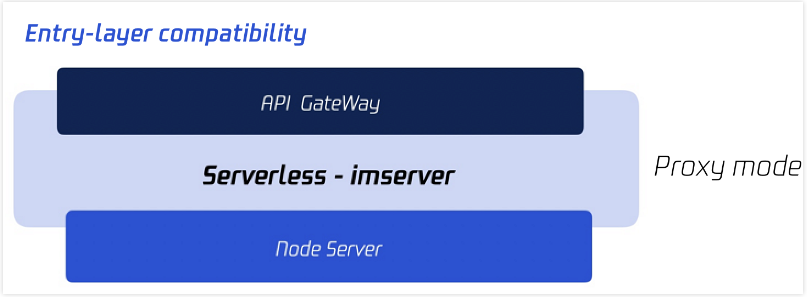
Based on the various standardized APIs provided by Tencent Cloud Serverless Cloud Framework, Serverless-based encapsulation is added to Tencent Cloud's proprietary Node framework (imserver). In addition, compatibility with the elements from Event to Koa Request Context has been added to the entry as shown below: Problems in SSR Technical Scheme Implementation
Problem 1. SCF function division
As a business has multiple pages implemented through SSR, if SCF is used to implement SSR, it is required to determine whether the business features should be combined to one SCF function (at the business level) or divided into multiple functions (at the page level). The latter is recommended for the following advantages:
SCF functions are independent from each other. If the function of page A fails to be invoked, the function of business B will not be affected.
The function package size can be reduced. A smaller package size also shortens the function's cold start.
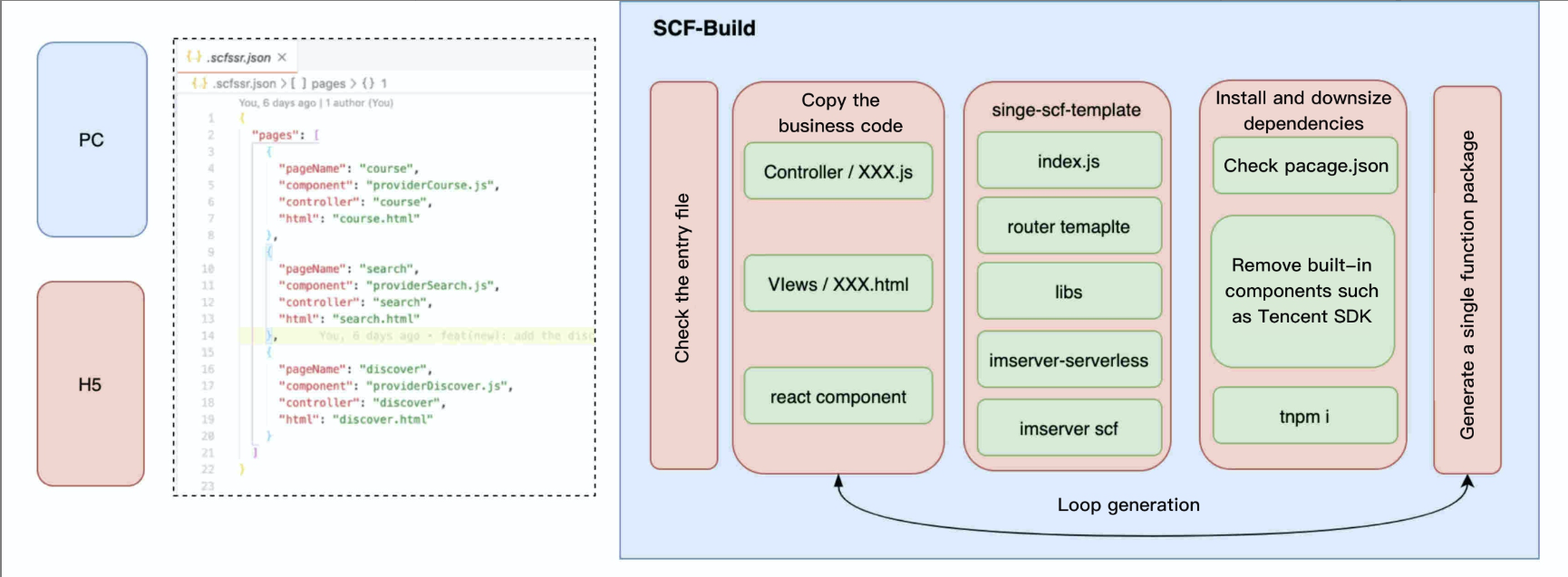
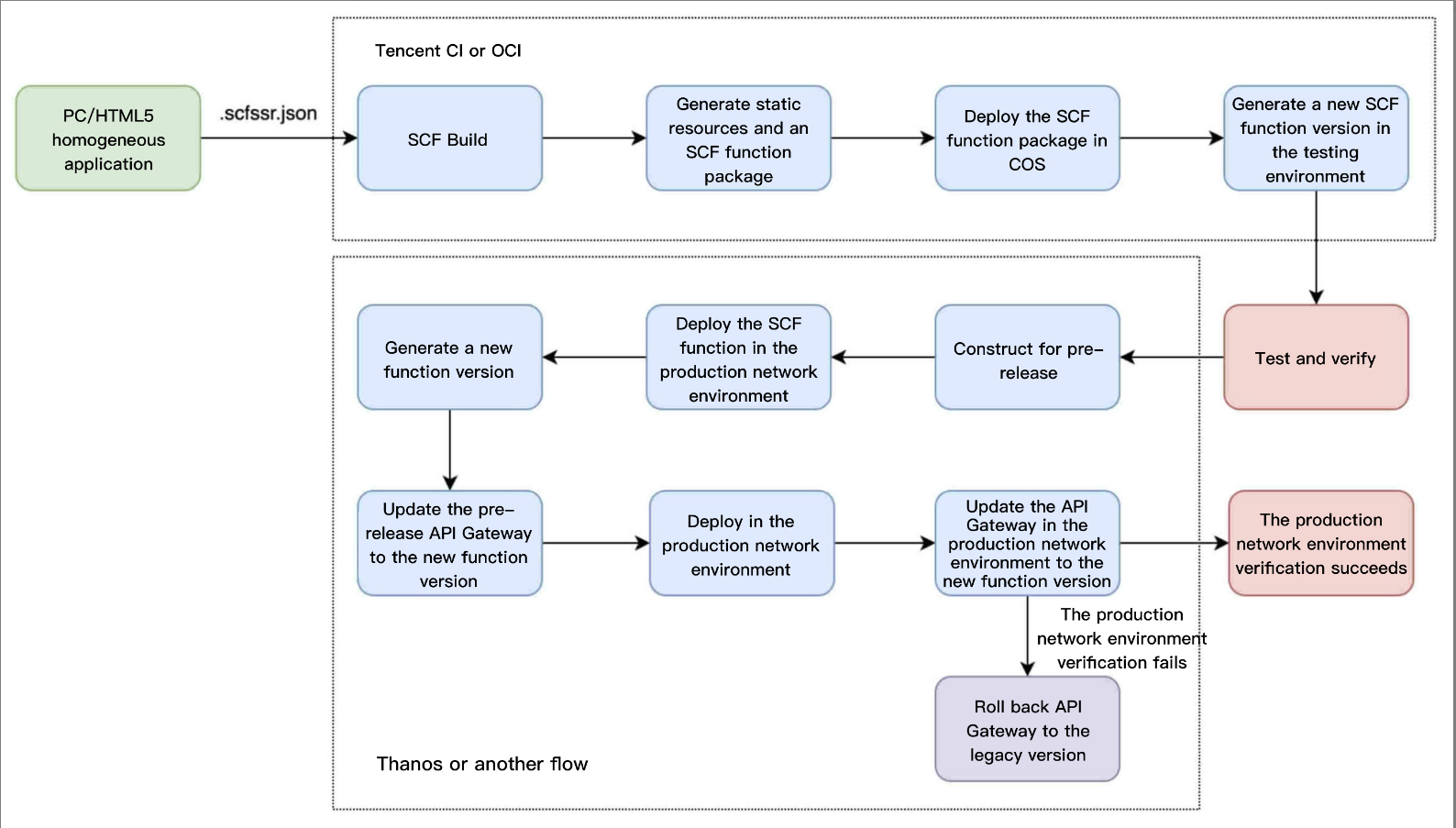
Here, as the current project has implemented automated construction of SCF functions, the corresponding function will be automatically generated with the .scfssr.json configuration file, which will have no impact on the current development. Only multiple functions will be generated during the construction, minimizing the application maintenance and development costs.
In addition, based on the SCF function construction process, the code of a single function can be made simpler. Based on the analysis of the dependencies in package.json, built-in toolkits can be removed from the function container, and import analysis will be performed on the third-party packages depended on by the function to remove redundancy as shown below: Problem 2. SCF function release optimization
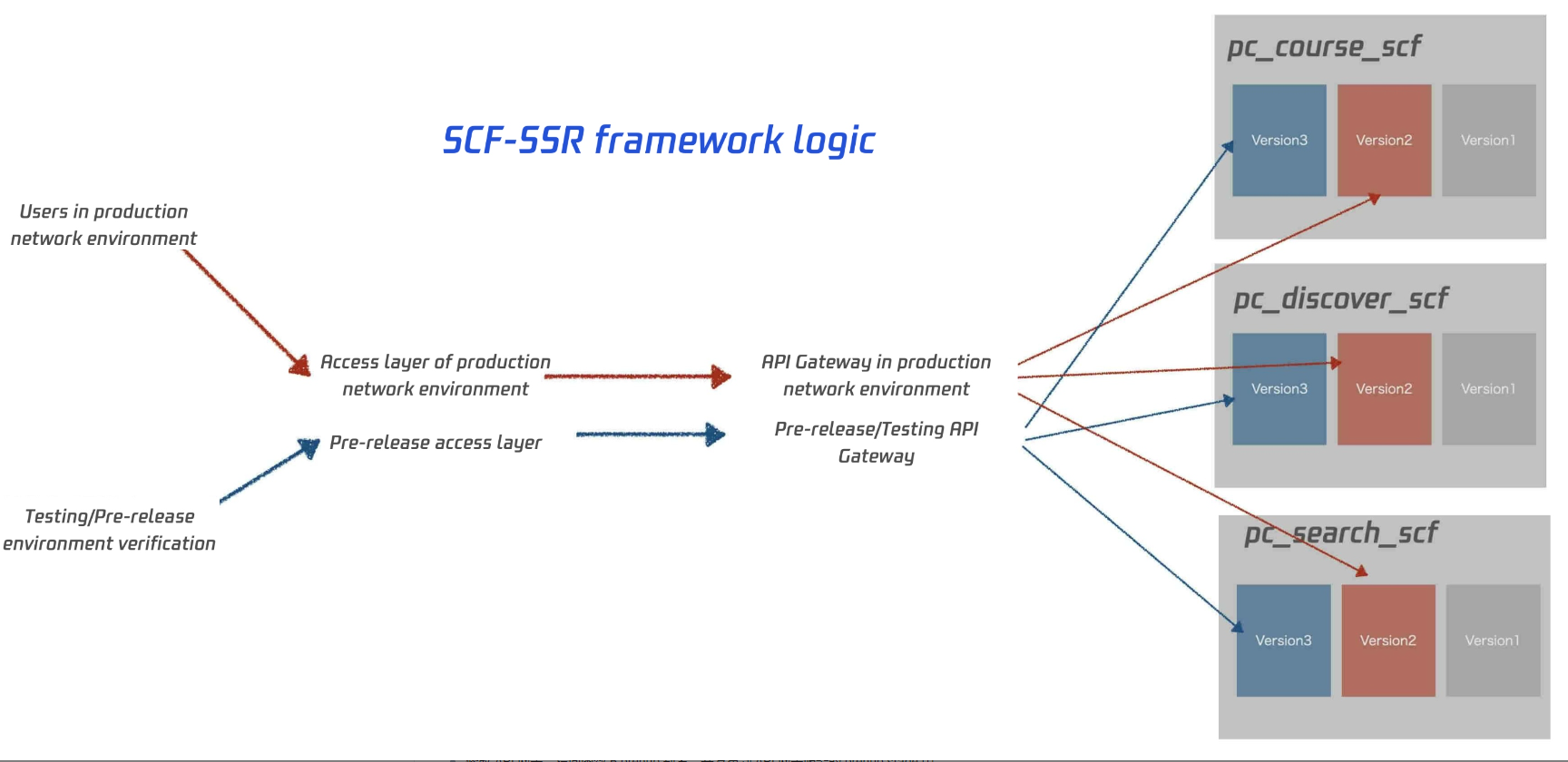
The logic of SCF-based multi-function SSR scheme is as shown below. When there is a version update, the release process and steps will become relatively complicated.
One-Time initialization in configuration
Create the release and prehub aliases in the function and point them to the $LATEST version.
Create service A in API Gateway and configure API Gateway to point it to the release alias of function B and publish it into the release stage of the API Gateway service.
Modify API Gateway to point it to the prehub alias of function B and publish it into the prehub stage of the API Gateway service.
Modify API Gateway to point it to the default traffic of function B and publish it into the dev stage of the API Gateway service.
At this point, API Gateway configuration is completed, and there will be no need to modify and publish the configuration again in API Gateway.
Continuous development, testing, and release
Continuously develop the function and publish the versions 1, 2, 3 at a time.
To develop and test the latest version, configure the $DEFAULT alias to point it to the $LATEST version. Continuous development and modification can be performed based on this version, and new versions can be published after modification.
The prehub alias can be configured to point to version 3 for test and trial in the pre-release environment.
Version 2 has been tried out in the pre-release layer and can be launched. Switch the release alias from version 1 to version 2.
View the canary release process through monitoring information and logs and check whether the traffic of versions 2/1 increases/decreases normally, errors of each version during the release, and overall errors.
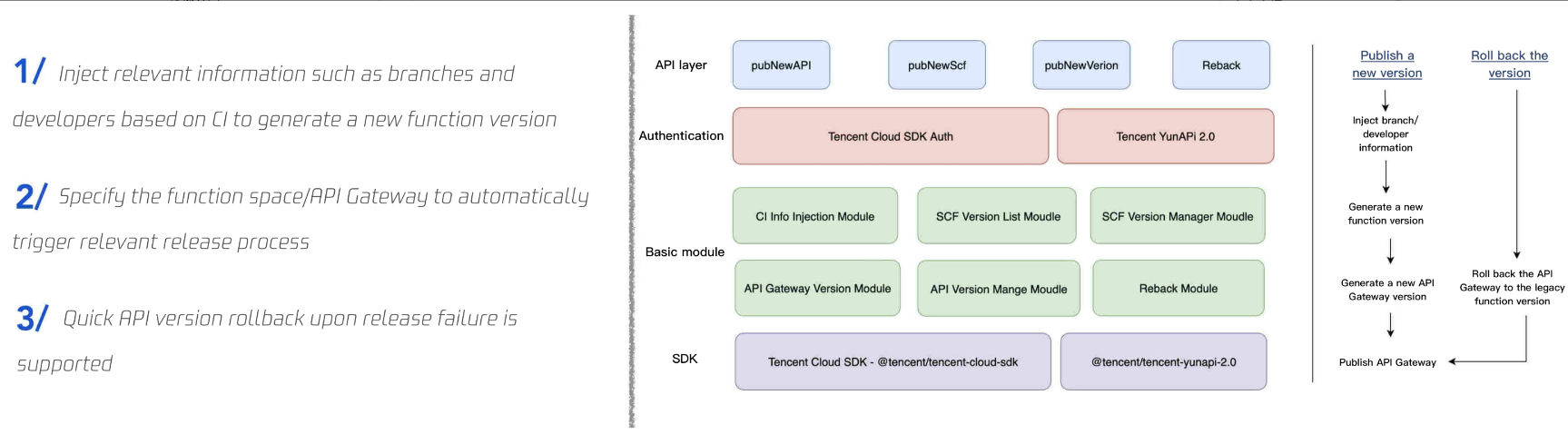
To optimize the SCF function release process, a quick SCF function release tool developed based on the Node SDK of Tencent Cloud Serverless is provided as shown below:
A complete lifecycle of an SCF SSR application is as shown below: Tencent Cloud Serverless SSR Scheme Strengths and Subsequent Planning
The SCF-based SSR scheme can greatly reduce the service Ops costs. Based on the Tencent Cloud Serverless log system, all individual SSR application requests can have complete linkage on the log platform, which greatly speeds up problem locating and troubleshooting.
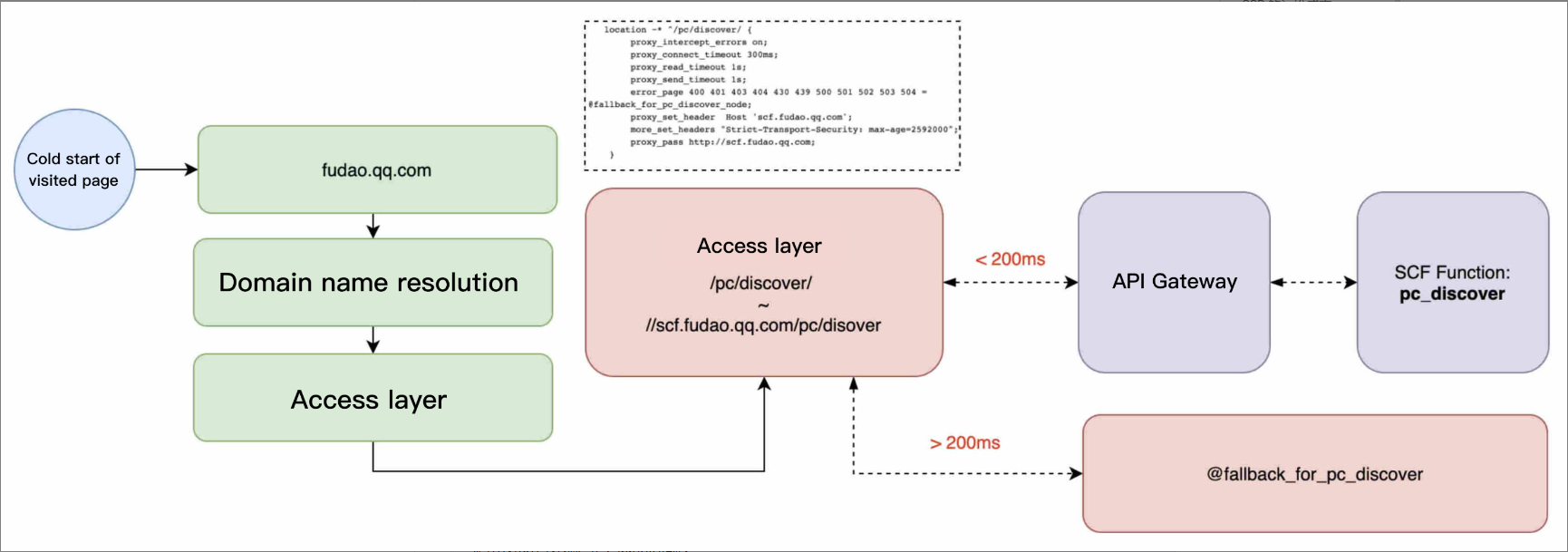
The Serverless architecture mode has a long cold start time, and technical improvements have been made in SCF accordingly, such as pre-start container. The actual business can also be optimized; for example, downgrade optimization can be made on the service at the access layer. The optimization is as shown below:
Subsequent optimization can be made from various aspects such as beta test and multi-dimensional downgrade.
Suggestions on Use of SSR Technology
To have a better user experience, we recommend that you perform SSR optimization on core businesses and use Serverless for business deployment and Ops. Serverless reduces your workload of server Ops and scaling, enabling you to improve your team productivity.
After SSR is used, we recommend that you further improve the DevOps process of your business and streamline the entire R&D process, so that development, testing, and deployment can be conducted more efficiently.
We recommend that you use the business access layer for service downgrade so as to improve the SSR application availability.