- Release Notes and Announcements
- User Guide
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Resource Management
- Permission Management
- Log Collection
- Collection Overview
- Collecting Logs in Self-Built Kubernetes Cluster
- Collecting Syslog
- Collection by LogListener
- Collecting Text Log
- Uploading Log over Kafka
- Uploading Logs via Anonymous Write
- Uploading Logs via Logback Appender
- Uploading Logs via Log4j Appender
- Uploading Log via SDK
- Uploading Log via API
- Importing Data
- Tencent Cloud Service Log Access
- Metric Collection
- Log Storage
- Metric Storage
- Search and Analysis (Log Topic)
- Syntax and Rules
- Statistical Analysis (SQL)
- Quick Analysis
- SQL Syntax
- SQL Functions
- String Function
- Date and Time Functions
- IP Geographic Function
- URL Function
- Mathematical Calculation Functions
- Mathematical Statistical Function
- General Aggregate Function
- Geospatial Function
- Binary String Function
- Estimation Function
- Type Conversion Function
- Logical Function
- Operators
- Bitwise Operation
- Regular Expression Function
- Lambda Function
- Conditional Expressions
- Array Functions
- Interval-Valued Comparison and Periodicity-Valued Comparison Functions
- JSON Functions
- Window Functions
- Sampling Analysis
- Configuring Indexes
- Reindexing
- Context Search and Analysis
- Downloading Log
- Search and Analysis (Metric Topic)
- Dashboard
- Data Processing documents
- Data Processing
- Creating Processing Task
- Viewing Data Processing Details
- Data Processing Functions
- Function Overview
- Key-Value Extraction Functions
- Enrichment Functions
- Flow Control
- Row Processing Functions
- Field Processing Functions
- Value Structuring Functions
- Regular Expression Processing Functions
- Time Value Processing Functions
- String Processing Functions
- Type Conversion Functions
- Logical and Mathematical Functions
- Encoding and Decoding Functions
- IP Parsing Functions
- Processing Cases
- Scheduled SQL Analysis
- SCF
- Data Processing
- Shipping and Consumption
- Monitoring Alarm
- Historical Documentation
- Practical Tutorial
- Developer Guide
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Topic Management APIs
- Log Set Management APIs
- Index APIs
- Topic Partition APIs
- Machine Group APIs
- Collection Configuration APIs
- Log APIs
- Metric APIs
- Alarm Policy APIs
- Data Processing APIs
- Kafka Protocol Consumption APIs
- CKafka Shipping Task APIs
- Kafka Data Subscription APIs
- COS Shipping Task APIs
- SCF Delivery Task APIs
- Scheduled SQL Analysis APIs
- COS Data Import Task APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- CLS Service Level Agreement
- CLS Policy
- Contact Us
- Glossary
- Release Notes and Announcements
- User Guide
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Resource Management
- Permission Management
- Log Collection
- Collection Overview
- Collecting Logs in Self-Built Kubernetes Cluster
- Collecting Syslog
- Collection by LogListener
- Collecting Text Log
- Uploading Log over Kafka
- Uploading Logs via Anonymous Write
- Uploading Logs via Logback Appender
- Uploading Logs via Log4j Appender
- Uploading Log via SDK
- Uploading Log via API
- Importing Data
- Tencent Cloud Service Log Access
- Metric Collection
- Log Storage
- Metric Storage
- Search and Analysis (Log Topic)
- Syntax and Rules
- Statistical Analysis (SQL)
- Quick Analysis
- SQL Syntax
- SQL Functions
- String Function
- Date and Time Functions
- IP Geographic Function
- URL Function
- Mathematical Calculation Functions
- Mathematical Statistical Function
- General Aggregate Function
- Geospatial Function
- Binary String Function
- Estimation Function
- Type Conversion Function
- Logical Function
- Operators
- Bitwise Operation
- Regular Expression Function
- Lambda Function
- Conditional Expressions
- Array Functions
- Interval-Valued Comparison and Periodicity-Valued Comparison Functions
- JSON Functions
- Window Functions
- Sampling Analysis
- Configuring Indexes
- Reindexing
- Context Search and Analysis
- Downloading Log
- Search and Analysis (Metric Topic)
- Dashboard
- Data Processing documents
- Data Processing
- Creating Processing Task
- Viewing Data Processing Details
- Data Processing Functions
- Function Overview
- Key-Value Extraction Functions
- Enrichment Functions
- Flow Control
- Row Processing Functions
- Field Processing Functions
- Value Structuring Functions
- Regular Expression Processing Functions
- Time Value Processing Functions
- String Processing Functions
- Type Conversion Functions
- Logical and Mathematical Functions
- Encoding and Decoding Functions
- IP Parsing Functions
- Processing Cases
- Scheduled SQL Analysis
- SCF
- Data Processing
- Shipping and Consumption
- Monitoring Alarm
- Historical Documentation
- Practical Tutorial
- Developer Guide
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Topic Management APIs
- Log Set Management APIs
- Index APIs
- Topic Partition APIs
- Machine Group APIs
- Collection Configuration APIs
- Log APIs
- Metric APIs
- Alarm Policy APIs
- Data Processing APIs
- Kafka Protocol Consumption APIs
- CKafka Shipping Task APIs
- Kafka Data Subscription APIs
- COS Shipping Task APIs
- SCF Delivery Task APIs
- Scheduled SQL Analysis APIs
- COS Data Import Task APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- CLS Service Level Agreement
- CLS Policy
- Contact Us
- Glossary
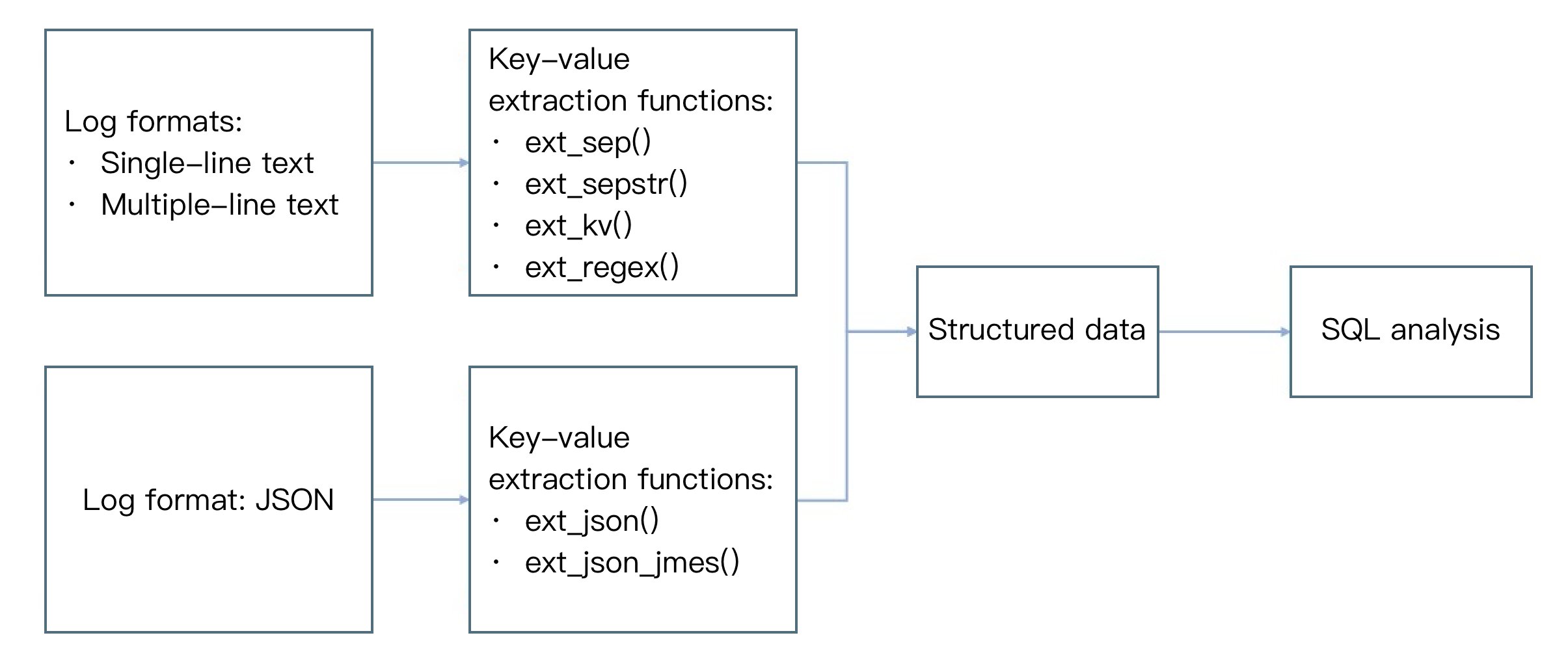
Overview
The figure below shows the common use cases of key-value extraction functions. After key-value extraction, logs are processed into structured data, which can be used for SQL analysis.

Function ext_sep()
Function definition
This function is used to extract field value content based on a separator (single character).
Syntax description
ext_sep("Source field name", "Target field 1,Target field 2,Target field...", sep="Separator", quote="Non-segmentation part"", restrict=False, mode="overwrite")
Field description
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field to extract | string | Yes | - | Name of an existing field in the user log |
output | A single field name or multiple new field names concatenated with commas | string | Yes | - | - |
sep | Separator | string | No | , | Any single character |
quote | Characters that enclose the value | string | No | - | - |
restrict | Handling mode when the number of extracted values is inconsistent with the number of target fields entered by the user: True: ignore the extraction function and do not perform any extraction processing. False: try to match the first few fields | bool | No | False | - |
mode | Write mode of the new field | string | No | overwrite | - |
Sample
Example 1. Extract values from logs by using a comma as the separatorRaw log:
{"content": "hello Go,hello Java,hello python"}
Processing rule:
// Use a comma as the separator to divide the `content` field into three parts, corresponding to the `f1`, `f2`, and `f3` fields separately.ext_sep("content", "f1, f2, f3", sep=",", quote="", restrict=False, mode="overwrite")// Delete the `content` field.fields_drop("content")
Processing result:
{"f1":"hello Go","f2":"hello Java","f3":"hello python"}
Example 2. Process the
content string as a whole by using quoteRaw log:{"content": " Go,%hello ,Java%,python"}
Processing rule:
ext_sep("content", "f1, f2", quote="%", restrict=False)
Processing result:
// Though `%hello ,Java%` does contain a comma, it does not participate in separator extraction as a whole.{"content":" Go,%hello ,Java%,python","f1":" Go","f2":"hello ,Java"}
Example 3:
restrict=True indicates the number of divided values is different from the target fields, the function is not executed.Raw log:{"content": "1,2,3"}
Processing rule:
ext_sep("content", "f1, f2", restrict=True)
Processing result:
{"content":"1,2,3"}
Function ext_sepstr()
Function definition
This function is used to extract field value content based on multiple characters (string).
Syntax description
ext_sepstr("Source field name","Target field 1,Target field 2,Target field...", sep="abc", restrict=False, mode="overwrite")
Field description
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field to extract | string | Yes | - | Name of an existing field in the user log |
output | A single field name or multiple new field names concatenated with commas | string | Yes | - | - |
sep | Separator (string) | string | No | , | - |
restrict | Handling mode when the number of extracted values is inconsistent with the number of target fields entered by the user: True: ignore the extraction function and do not perform any extraction processing. False: try to match the first few fields | bool | No | False | - |
mode | Write mode of the new field | string | No | overwrite | - |
Sample
Raw log:
{"message":"1##2##3"}
Processing rule:
// Use "##" as the separator to extract key-values.ext_sepstr("message", "f1,f2,f3,f4", sep="##")
Processing result:
// If the number of target fields is greater than the number of divided values, `""` is returned for the excessive fields.{"f1":"1","f2":"2","message":"1##2##3","f3":"3","f4":""}
Function ext_json()
Function definition
This function is used to extract field values from JSON data.
Syntax description
ext_json("Source field name",prefix="",suffix="",format="full",exclude_node="JSON nodes not to expand")
Field description
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field to extract | string | Yes | - | - |
prefix | Prefix of the new field | string | No | - | - |
suffix | Suffix of the new field | string | No | - | - |
format | full: The field name format is in full path format (parent + sep + prefix + key + suffix).simple: non-full path format (prefix + key + suffix) | string | No | simple | - |
sep | Concatenation character, used to concatenate node names | string | No | # | - |
depth | Depth to which the function expands the source field, beyond which nodes will not be expanded any more | number | No | 100 | 1-500 |
expand_array | Whether to expand an array node | bool | No | False | - |
include_node | Allowlist of node names that match the specified regular expression | string | No | - | - |
exclude_node | Blocklist of node names that match the specified regular expression | string | No | - | - |
include_path | Allowlist of node paths that match the specified regular expression | string | No | - | - |
exclude_path | Allowlist of node paths that match the specified regular expression | string | No | - | - |
retain | Retains some special symbols without escaping them, such as \\n and \\t. | string | No | - | - |
escape | Whether to escape data. Default value: True. If special symbols are contained, escaping cannot be performed. | bool | No | True | - |
Sample
Example 1. Extract the key-values of all nodes and construct new fields based on the extracted values. The example log is multi-level nesting, but the extraction does not distinguish hierarchy.Raw log:
{"data": "{ \\"k1\\": 100, \\"k2\\": { \\"k3\\": 200, \\"k4\\": { \\"k5\\": 300}}}"}
Processing rule:
ext_json("data")
Processing result:
{"data":"{ \\"k1\\": 100, \\"k2\\": { \\"k3\\": 200, \\"k4\\": { \\"k5\\": 300}}}","k1":"100","k3":"200","k5":"300"}
Example 2. Perform extraction excluding
sub_field1
Raw log: {"content": "{\\"sub_field1\\":1,\\"sub_field2\\":\\"2\\"}"}
Processing rule:
// `exclude_node=subfield1` indicates not to extract the node.ext_json("content", format="full", exclude_node="sub_field1")
Processing result:
{"sub_field2":"2","content":"{\\"sub_field1\\":1,\\"sub_field2\\":\\"2\\"}"}
Example 3. Add
prefix to subnodesRaw log:{"content": "{\\"sub_field1\\":{\\"sub_sub_field3\\":1},\\"sub_field2\\":\\"2\\"}"}
Processing rule 1:
// When `sub_field2` is extracted, the prefix `udf\\_` is automatically added to it, making it `udf\\_\\_sub\\_field2`.ext_json("content", prefix="udf_", format="simple")
Processing result 1:
{"content":"{\\"sub_field1\\":{\\"sub_sub_field3\\":1},\\"sub_field2\\":\\"2\\"}","udf_sub_field2":"2","udf_sub_sub_field3":"1"}
Processing rule 2:
// `format=full` indicates to retain the hierarchy of the extracted field name. When `sub_field2` is extracted, the name of its parent node is automatically to it, making it `#content#__sub_field2`.ext_json("content", prefix="__", format="full")
Processing result 2:
{"#content#__sub_field2":"2","#content#sub_field1#__sub_sub_field3":"1","content":"{\\"sub_field1\\":{\\"sub_sub_field3\\":1},\\"sub_field2\\":\\"2\\"}"}
Example 4. Support special symbols
Raw log 1:
{"content": "{\\"sub_field1\\":1,\\"sub_field2\\":\\"\\\\n2\\"}"}
Processing rule 1:
ext_json("content",retain="\\n")
Processing result 1:
{"sub_field2":"\\\\n2","content":"{\\"sub_field1\\":1,\\"sub_field2\\":\\"\\\\n2\\"}","sub_field1":"1"}
Raw log 2:
{"content": "{\\"sub_field1\\":1,\\"sub_field2\\":\\"\\\\n2\\\\t\\"}"}
Processing rule 2:
ext_json("content",retain="\\n,\\t")
Processing result 2:
{"sub_field2":"\\\\n2\\\\t","content":"{\\"sub_field1\\":1,\\"sub_field2\\":\\"\\\\n2\\\\t\\"}","sub_field1":"1"}
Example 5. Specify whether to escape
Raw log:
{"message":"{\\"ip\\":\\"183.6.104.157\\",\\"params\\":\\"[{\\\\\\"tokenType\\\\\\":\\\\\\"RESERVED30\\\\\\",\\\\\\"otherTokenInfo\\\\\\":{\\\\\\"unionId\\\\\\":\\\\\\"123\\\\\\"},\\\\\\"unionId\\\\\\":\\\\\\"adv\\\\\\"}]\\"}"}
Processing rule:
ext_json("message", escape=False)fields_drop("message")
Processing result:
{"ip":"183.6.104.157", "params":"[{\\"tokenType\\":\\"RESERVED30\\",\\"otherTokenInfo\\":{\\"unionId\\":\\"123\\"},\\"unionId\\":\\"adv\\"}]"}
Function ext_json_jmes()
Function definition
This function is used to extract field values from JSON data.
Syntax description
ext_json_jmes("Source field name", jmes= "JSON extraction expression", output="Target field", ignore_null=True, mode="overwrite")
Field description
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field to extract | string | Yes | - | - |
jmes | string | Yes | - | - | |
output | Output field name. Only a single field is supported. | string | Yes | - | - |
ignore_null | Whether to ignore a node whose value is null. The default value is True, ignoring fields whose value is null. Otherwise, an empty string is returned. | bool | No | True | - |
mode | Write mode of the new field. Default value: overwrite | string | No | overwrite | - |
Sample
Example 1. Extract only one node from multi-layer JSON data
Raw log:
{"content": "{\\"a\\":{\\"b\\":{\\"c\\":{\\"d\\":\\"value\\"}}}}"}
Processing rule:
// `jmes="a.b.c.d"` means to extract the value of `a.b.c.d`.ext_json_jmes("content", jmes="a.b.c.d", output="target")
Processing result:
{"content":"{\\"a\\":{\\"b\\":{\\"c\\":{\\"d\\":\\"value\\"}}}}","target":"value"}
Example 2Raw log:
{"content": "{\\"a\\":{\\"b\\":{\\"c\\":{\\"d\\":\\"value\\"}}}}"}
Processing rule:
// `jmes="a.b.c.d"` means to extract the value of `a.b.c`.ext_json_jmes("content", jmes="a.b.c", output="target")
Processing result:
{"content":"{\\"a\\":{\\"b\\":{\\"c\\":{\\"d\\":\\"value\\"}}}}","target":"{\\"d\\":\\"value\\"}"}
Function ext_regex()
Function definition
This function is used to extract the value of a field by using a regular expression.
Syntax description
ext_regex("Source field name", regex="Regular expression", output="Target field 1,Target field 2,Target field.......", mode="overwrite")
Field description looking for b
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field to extract | string | Yes | - | - |
regex | Regular expression. If the expression contains a special character, escaping is required. Otherwise, syntax error is reported. | string | Yes | - | - |
output | A single field name or multiple new field names concatenated with commas | string | No | - | - |
mode | Write mode of the new field. Default value: overwrite | string | No | overwrite | - |
Sample
Example 1. Match digitsRaw log:
{"content": "1234abcd5678"}
Processing rule:
ext_regex("content", regex="\\d+", output="target1,target2")
Processing result:
{"target2":"5678","content":"1234abcd5678","target1":"1234"}
Example 2. The regular expression contains named capturing group, and some field values are automatically filled
Raw log:
{"content": "1234abcd"}
Processing rule:
ext_regex("content", regex="(?<target1>\\d+)(.*)", output="target2")
Processing result:
{"target2":"abcd","content":"1234abcd","target1":"1234"}
Function ext_kv()
Function definition
This function is used to extract key-value pairs by using two levels of separators.
Syntax description
ext_kv("Source field name", pair_sep=r"\\s", kv_sep="=", prefix="", suffix="", mode="fill-auto")
Field description
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field to extract | string | Yes | - | - |
pair_sep | Level-1 separator, separating multiple key-value pairs | string | Yes | - | - |
kv_sep | Level-2 separator, separating keys and values | string | Yes | - | - |
prefix | Prefix of the new field | string | No | - | - |
suffix | Suffix of the new field | string | No | - | - |
mode | Write mode of the new field. Default value: overwrite | string | No | - | - |
Sample
The raw log contains two levels of separators: "|" and "=".
Raw log:
{"content": "a=1|b=2|c=3"}
Processing rule:
ext_kv("content", pair_sep="|", kv_sep="=")
Processing result:
{"a":"1","b":"2","c":"3","content":"a=1|b=2|c=3"}
Function ext_first_notnull()
Function definition
This function is used to return the first non-null and non-empty result value.
Syntax description
ext_first_notnull(value 1, value 2, ...)
Field description
Parameter | Description | Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
Variable parameter list | Parameters or expressions that participate in the calculation | string | Yes | - | - |
Sample
Raw log:
{"data1": null, "data2": "", "data3": "first not null"}
Processing rule:
fields_set("result", ext_first_notnull(v("data1"), v("data2"), v("data3")))
Processing result:
{"result":"first not null","data3":"first not null","data2":"","data1":"null"}
Function ext_grok
Function definition
This function is used to extract the matched result value according to the Grok syntax.
Syntax description
ext_grok(Field value, grok="", extend="")
Field description
Parameter | Description | Type | Required | Default Value | Value Range |
field | Field value | string | Yes | - | - |
grok | Expression | string | Yes | - | - |
extend | Custom Grok expression | string | Yes | - | - |
Sample
Example 1
Raw log:
{"content":"2019 June 24 \\"I am iron man\\""}
Processing rule:
ext_grok("content", grok="%{YEAR:year} %{MONTH:month} %{MONTHDAY:day} %{QUOTEDSTRING:motto}")fields_drop("content")
Processing result:
{"day":"24", "month":"June", "motto":"I am iron man", "year":"2019"}
Example 2
Raw log:
{"content":"Beijing-1104,Beijing-Beijing"}
Processing rule:
ext_grok("content", grok="%{ID1:user_id1},%{ID2:user_id2}",extend="ID1=%{WORD}-%{INT},ID2=%{WORD}-%{WORD}")fields_drop("content")
Processing result:
{"user_id1":"Beijing-1104", "user_id2":"Beijing-Beijing"}

 예
예
 아니오
아니오
문제 해결에 도움이 되었나요?