Data Lake Compute
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Console Operation Introduction
- Data Development and Exploration
- Data Exploration
- Data Query Task
- Resource Management
- Engine Management
- SuperSQL Engine
- Standard Engine
- Resource Group
- Private Connection
- Storage Configuration
- Ops Management
- Insight Management
- System Management
- User and Permission Management
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Development Guide
- System Restraints
- Client Access
- JDBC Access
- Practical Tutorial
- SQL Statement
- SuperSQL Statement
- Unified Statement
- DDL Statement
- ALTER TABLE
- DML Statement
- DQL Statement
- Iceberg Table Statement
- API Documentation
- Making API Requests
- Data Table APIs
- Task APIs
- Metadata APIs
- Service Configuration APIs
- Permission Management APIs
- Data Source Connection APIs
- Data Optimization APIs
- Data Engine APIs
- General Reference
- Operation Guide on Connecting Third-Party Software to DLC
DocumentationData Lake ComputeOperation GuideConsole Operation IntroductionResource ManagementEngine ManagementStandard EngineStandard Engine Introduction
Standard Engine Introduction
Last updated: 2024-09-04 11:13:49
The Standard Engine is a type of computing resource provided by DLC that helps users quickly launch compute clusters of a certain scale. It offers comprehensive support for native syntax and behavior, enabling users who are familiar with the big data ecosystem to get started quickly and use it with ease.
Types of Standard Engine
Users can choose different Standard Engine kernels based on their needs to address various use cases. The Standard Engine is divided into the following types:
Spark: Suitable for stable and efficient offline SQL tasks, as well as native Spark streaming/batch data processing jobs.
Presto: Suitable for agile and rapid interactive query analysis.
Gateway: The Gateway is a special type of Standard Engine implemented based on native Kyuubi. The Gateway is used to connect users to the Spark/Presto computing engines and submit tasks, serving as a prerequisite for using other computing engines.
Note:
Different types of engines do not affect the unit price of engine billing. For detailed pricing information, see the Billing Overview.
Engine Elasticity
Currently, only the annual subscription Spark Standard Engine supports the configuration of pay-as-you-go for resource elasticity.
As shown in the diagram, tasks and resource groups will prioritize using the resources from the monthly or annual subscription. If a user’s submitted task exhausts the resources from this subscription, any subsequent tasks will automatically use the configured pay-as-you-go elastic resources. In the diagram, after Task 03 depletes the subscription resources, it continues to use the pay-as-you-go resources.
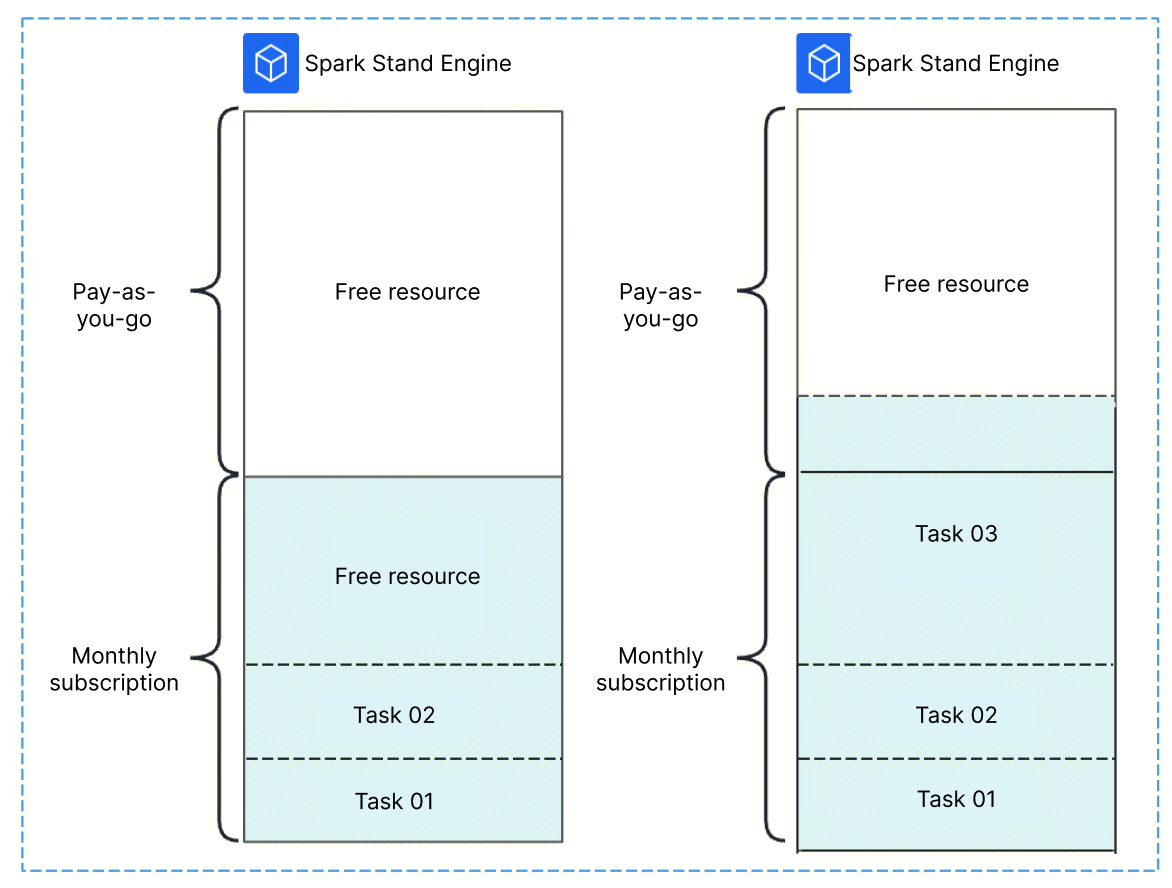
Note:
1. Pay-as-you-go elastic resources are charged based on the actual computing resources used.
2. If a task or resource group is scheduled to use pay-as-you-go resources, it will continue to use those resources even if the monthly or annual subscription resources are later freed up. The resource group will only be rescheduled to use the subscription resources after it has been restarted.
3. A single Spark Standard Engine cannot set elastic resources exceeding the amount of resources in the annual or monthly subscription. For example, a 128 CU annual or monthly subscription engine can set up to 128 CU of elastic resources. If you need to configure more elastic resources, contact us through a ticket.
Standard Engine Terminology
Terminology | Description |
Cluster Type | When purchasing a Standard Spark Engine, you can choose the cluster type. The standard type is 1 CU ≈ 1 core with 4 GB memory, and the memory type is 1 CU ≈ 1 core with 8 GB memory. Different types have different unit prices. For more details, see the Billing Overview. |
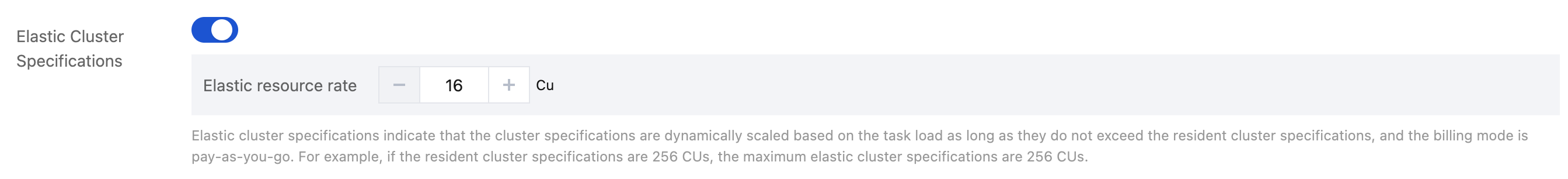
Elastic Cluster Specifications | The monthly or annual subscription Spark Engine allows users to configure elastic specifications. Once the resources from the subscription package are exhausted, the system will automatically allocate pay-as-you-go resources based on user configuration. |
Gateway Name | The name of the gateway must be globally unique. It cannot share the same name as any other gateway or compute engine. |
Engine Name | The name of the engine must be globally unique. It cannot share the same name as any other gateway or compute engine. |
Engine Type | The Standard Engine types are categorized into Presto Engine and Spark Engine. The gateway is also a special type of Standard Engine. |
Engine Status | The status of the Standard Engine varies based on the current operation of the cluster. The statuses include: Starting, Running, Ready, Paused, Pausing, Modifying, Isolated, Isolating, and Recovering. Starting: The cluster resources are being initiated. Pay-as-you-go for the engine does not occur during this time. Clusters in the starting status cannot be selected for data computation tasks. Running: The cluster is running and can be selected for data computation tasks. Ready: Similar to the running status, this status indicates that the engine is available for use. Paused: The cluster is paused and cannot be selected for data computation tasks. Pausing: The cluster is in the process of switching to the paused status. This transition may affect any running tasks, and the cluster cannot be selected for data computation during this time. Modifying: The cluster is undergoing configuration changes. During this period, it cannot be selected for data computation tasks. Isolated: The cluster has been isolated due to account arrears and cannot be selected for data computation tasks. Isolating: The cluster is in the process of being isolated due to account arrears. This transition may affect any running tasks, and the cluster cannot be selected for data computation during this time. Recovering: The process of restoring the cluster from an isolated status to a running status after the account has been recharged and is no longer in arrears. The cluster cannot be selected for data computation during this process. |
Resource Group Count | The current number of resource groups under the Standard Spark Engine. |
Used Resources / Total Resources | The quantity of resources currently used by the engine and the total available resources of the engine. The total resource count includes both the persistent resources and the elastic resources. Used resources include those occupied by the DLC deployment service system. There may be some delay in the reported data. |
Payment Type | Payment types include annual/monthly subscription and pay-as-you-go. The gateway only supports the annual/monthly subscription model. The Standard Spark and Presto engines support both annual/monthly subscription and pay-as-you-go. |
Auto-Renewal | Indicates whether the monthly or annual subscription engine will automatically renew as it approaches expiration. |
Engine Size | The total available resources of the engine, measured in CUs. For monthly or annual subscription engines, the size includes both the engine's persistent capacity and the elastic capacity billed on a pay-as-you-go basis. Note: 1. For monthly or annual subscription engines, a one-time payment is required at the time of purchase. The engine's status does not affect billing costs. 2. For pay-as-you-go engines, charges are based on the user's usage: The Standard Presto Engine incurs charges while running, but not when suspended. Some costs may be incurred during the engine's startup phase. The Standard Spark Engine does not incur charges while in a ready status. Costs are only incurred when tasks are submitted or when a resource group is started and running. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

