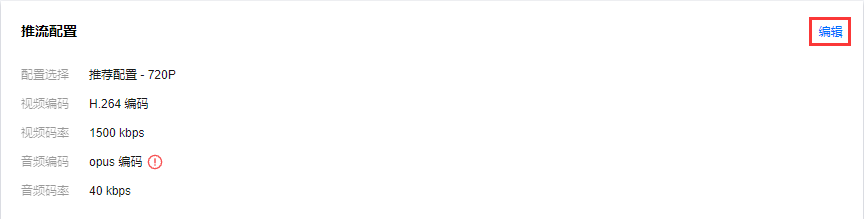腾讯云为您提供 Web 推流功能,支持摄像头采集、屏幕分享采集和本地文件采集三种采集方式进行直播。可实现快速生成推流地址,在线推流测试直播功能。
前提条件
您的设备已安装摄像头,并浏览器支持 Flash 插件调用摄像头权限。
单路推流
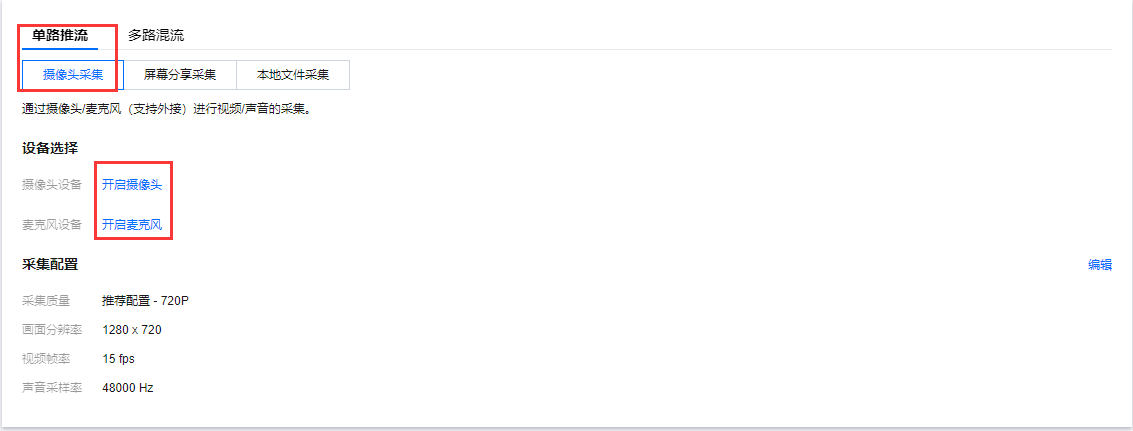
1. 登录云直播控制台,选择 Web推流。单击单路推流。 2. 选择采集方式。您可选择摄像头采集、屏幕分享采集和本地文件采集三种采集方式进行直播。
摄像头采集是通过摄像头/麦克风(支持外接)进行视频/声音的采集。单击 开启摄像头/ 开启麦克风,首次开启需授予浏览器使用摄像头和麦克风权限。
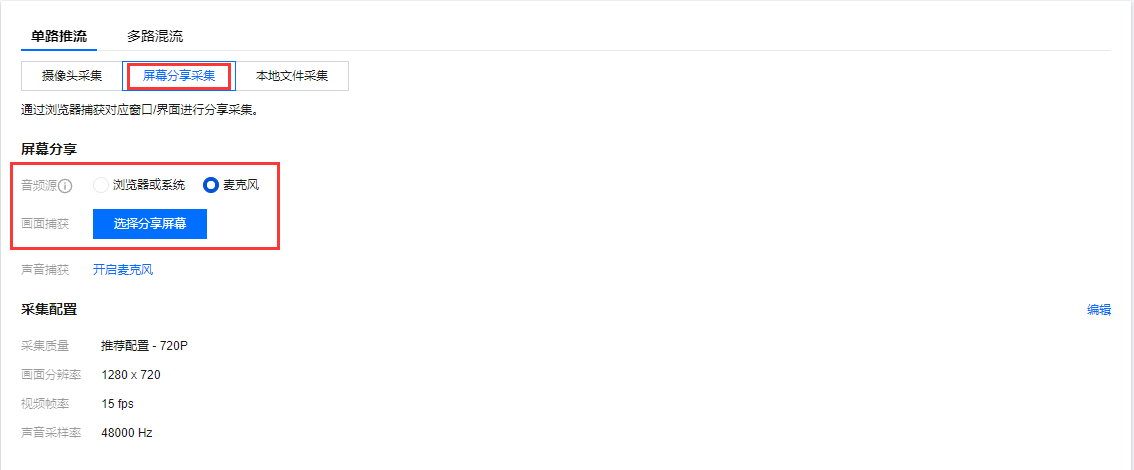
屏幕分享采集是通过浏览器捕获对应窗口/界面进行分享采集。单击 选择屏幕分享 选择分享的内容,可为整个屏幕/某个窗口/浏览器标签页。
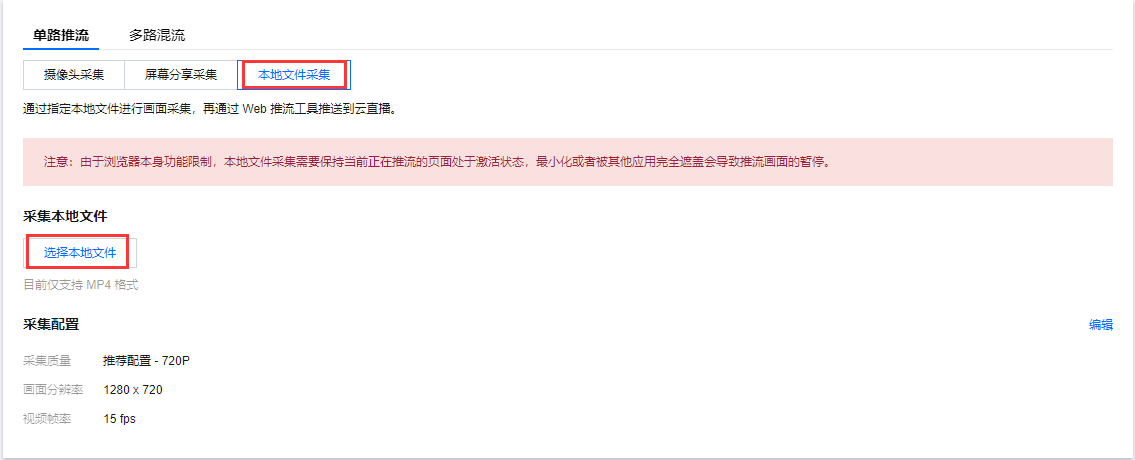
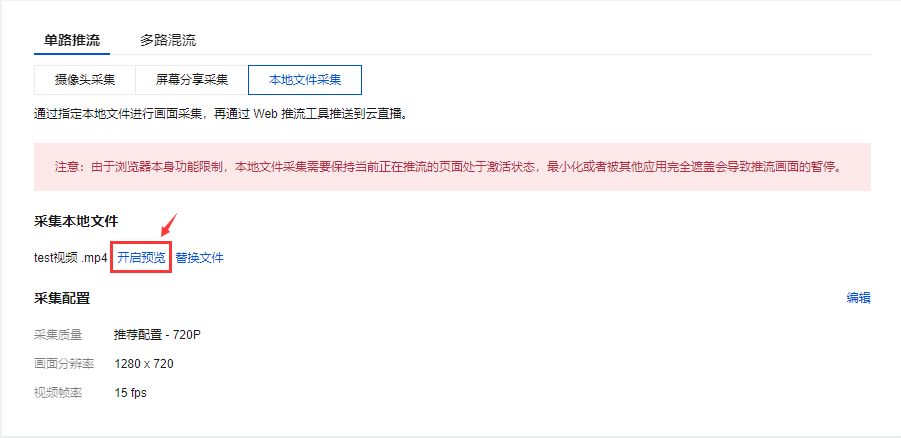
本地文件采集是通过指定本地文件进行画面采集,再通过 Web 推流工具推送到云直播。单击 选择本地文件 选择需要推流的内容,目前仅支持 MP4 格式文件。
注意:
在开启预览或选定分享屏幕内容后,不可切换采集方式,需关闭预览或取消分享屏幕后才可切换采集方式。
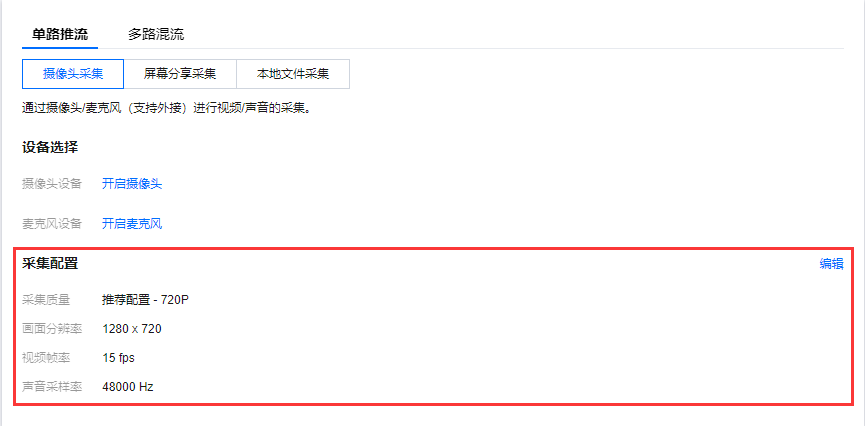
3. 采集配置。设置采集配置,默认为推荐配置(不同分辨率有不同推荐配置),可在右上角单击编辑进入自定义编辑配置。(摄像头采集和屏幕分享采集额外增加声音采样率的设置选项,本地文件采集只有分辨率和视频帧率的设置选项。)
4. 推流配置。设置推流配置,默认为推荐配置(不同分辨率有不同视频码率的推荐配置,音频码率不支持修改),可在右上角单击编辑进入自定义编辑配置,可自定义修改视频码率和音频码率。
说明:
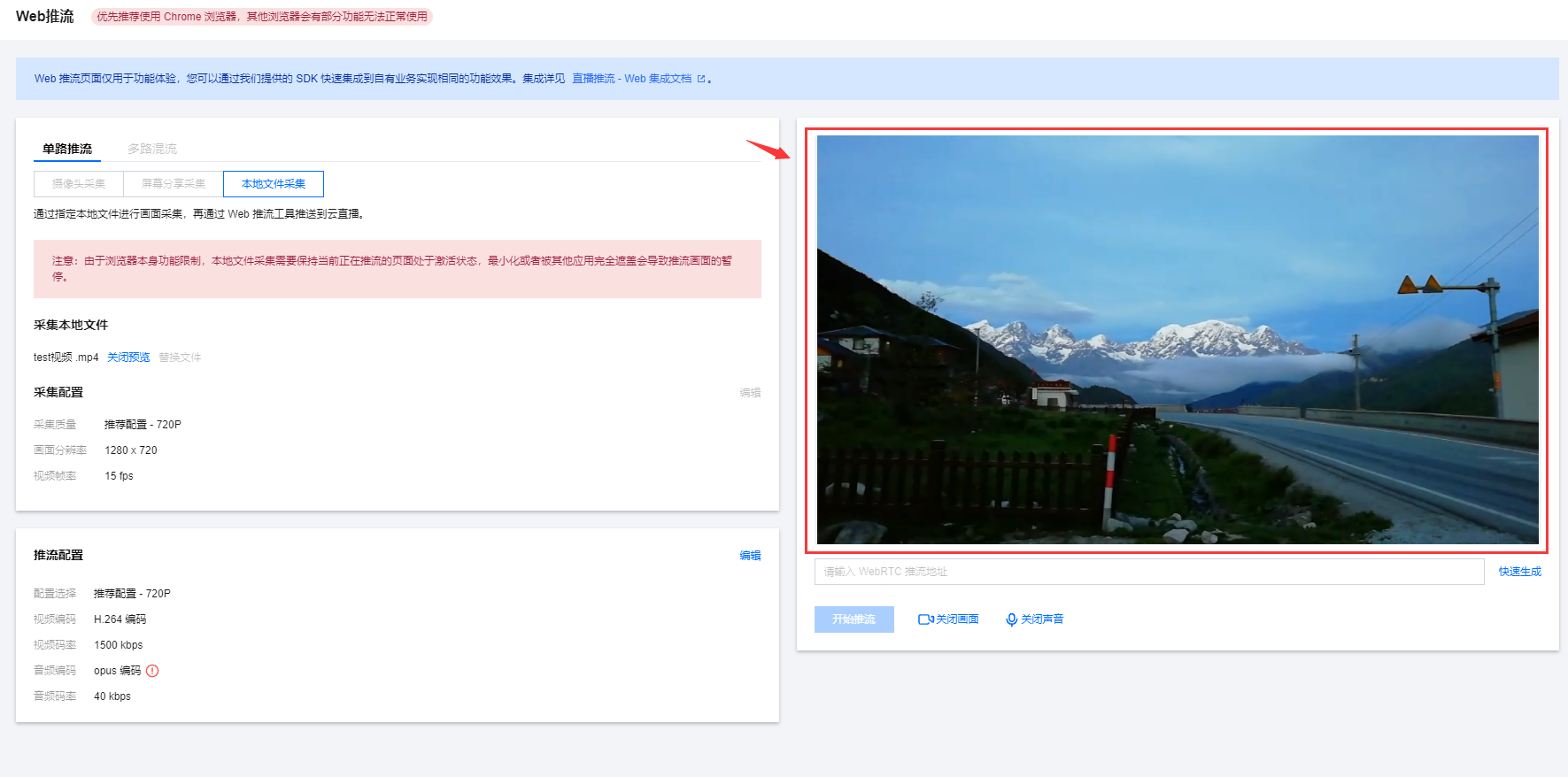
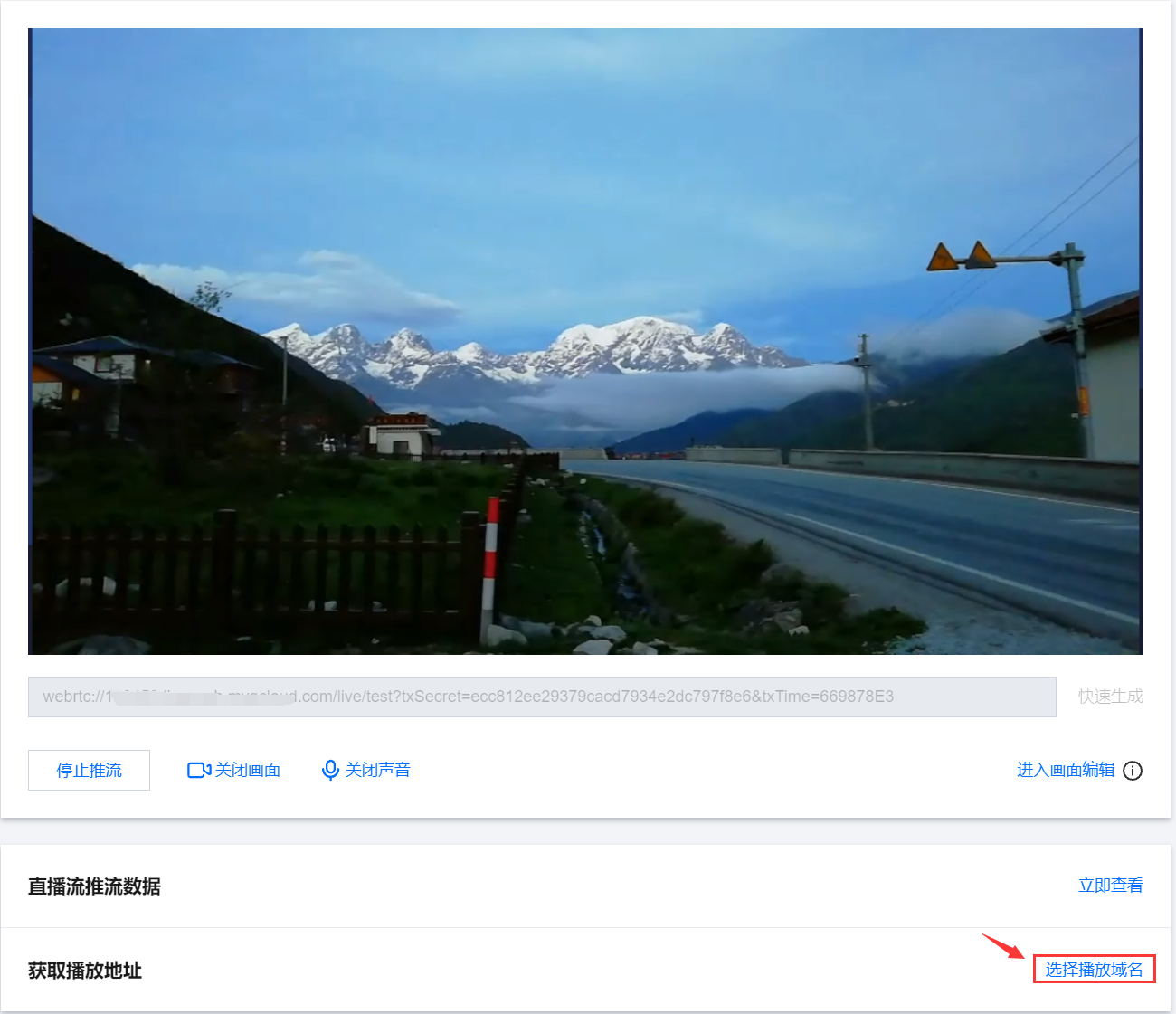
web 推流的音频编码方式为 opus 编码,推荐使用快直播 WebRTC 地址进行播放。若使用标准直播的播放地址(RTMP/FLV/HLS),系统会自动转换为 aac 编码才能正常播放,从而会产生音频转码费用,详见计费文档。 5. 推流预览。在确定采集方式和配置以及推流配置后,开启预览,即可在右侧看到推流预览。
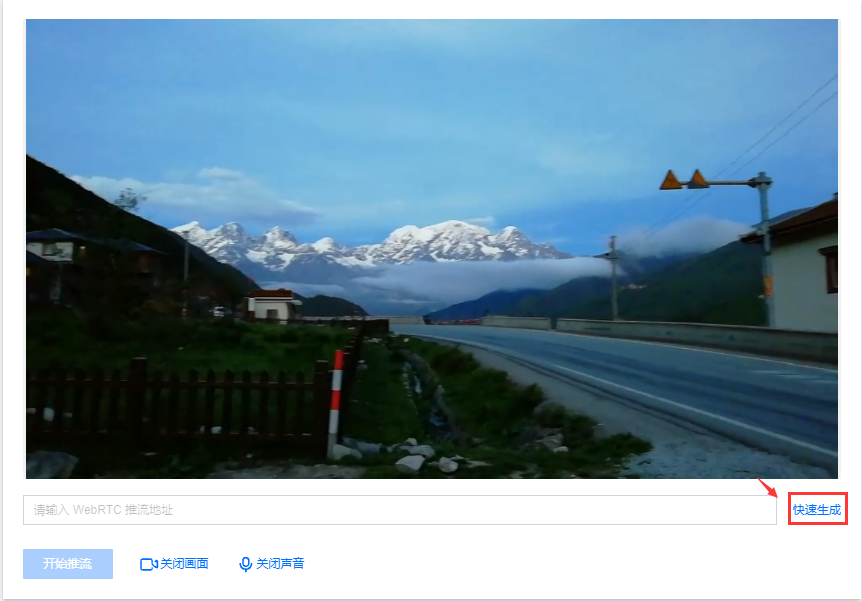
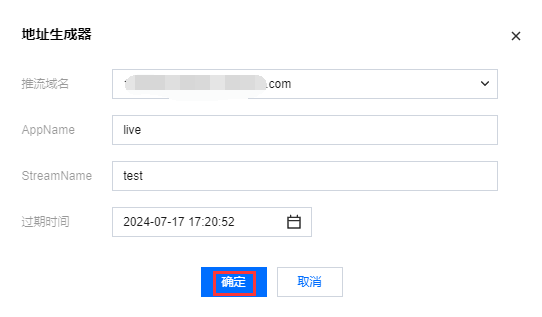
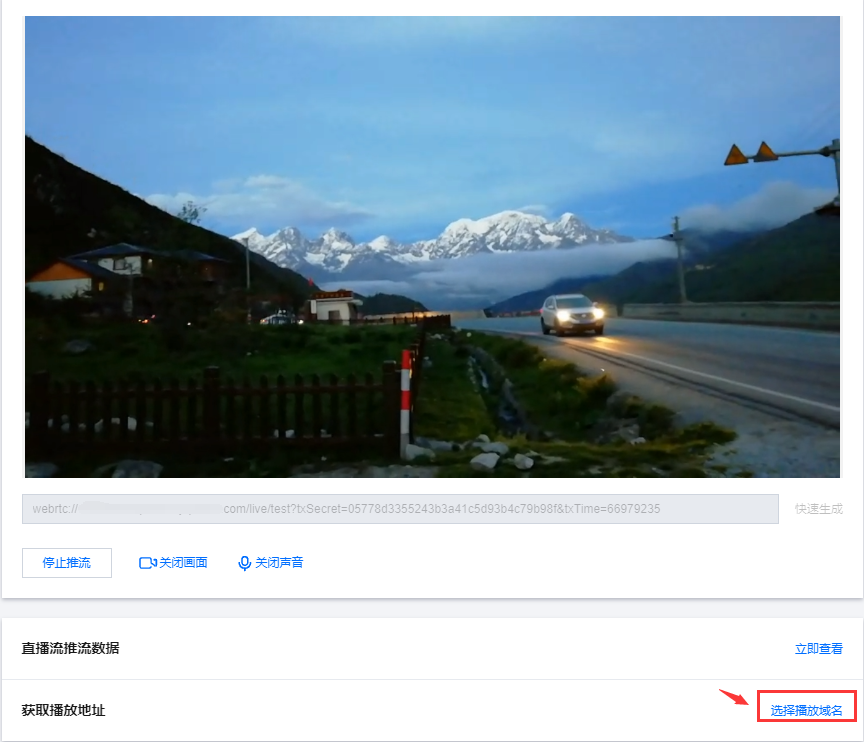
6. 输入 WebRTC 推流地址或单击快速生成。在弹窗中配置以下信息:
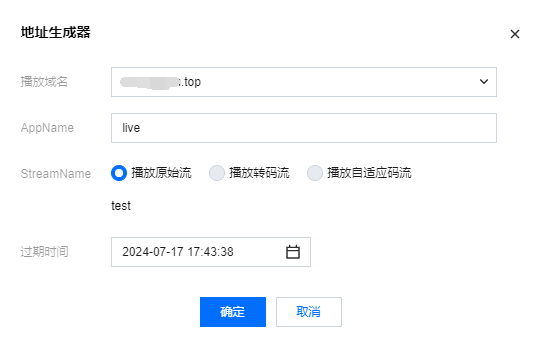
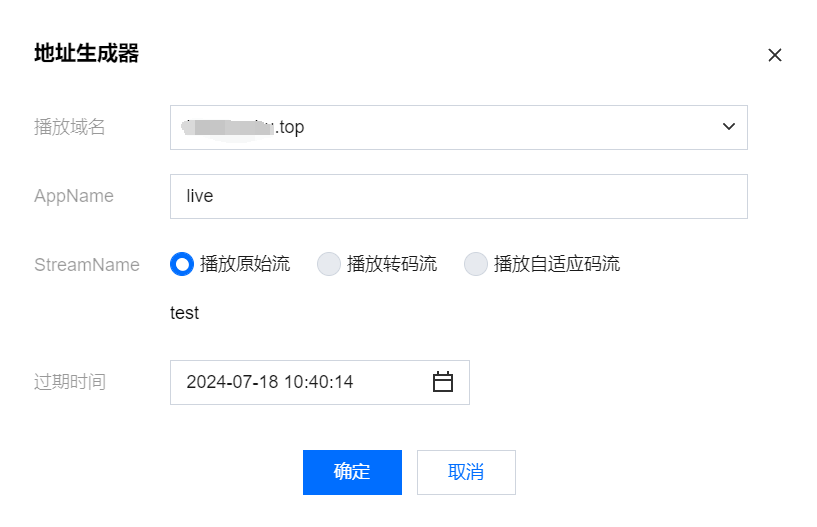
6.1 选择您的推流域名。
6.2 编辑 AppName,用于区分同一个域名下多个 App 的地址路径,默认值为 live。
6.3 填写自定义的流名称 StreamName,例如:test。
6.4 选择过期时间,例如:2024-07-17 17:20:52。
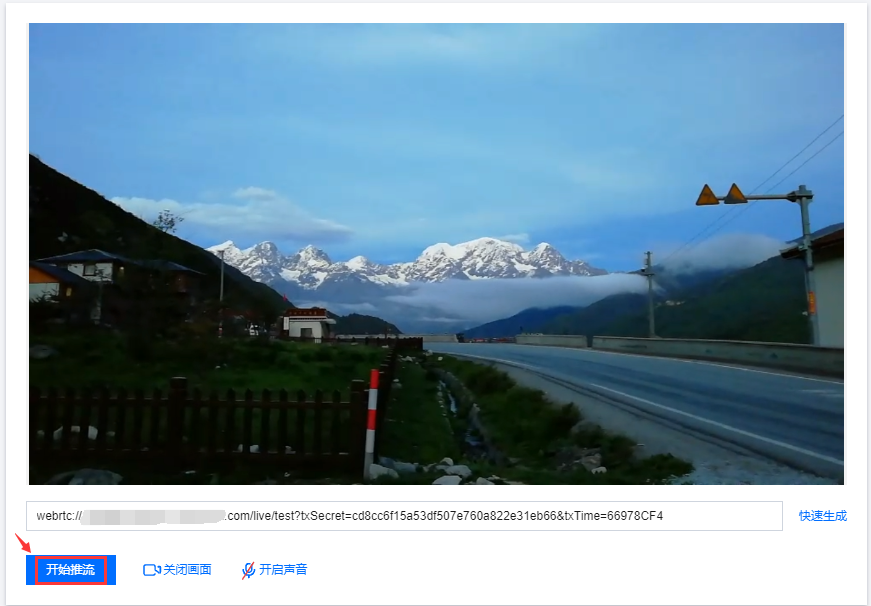
6.5 单击确定,快速自动生成 WebRTC 推流地址填入地址栏。
7. 单击开始推流,即可开始推流。
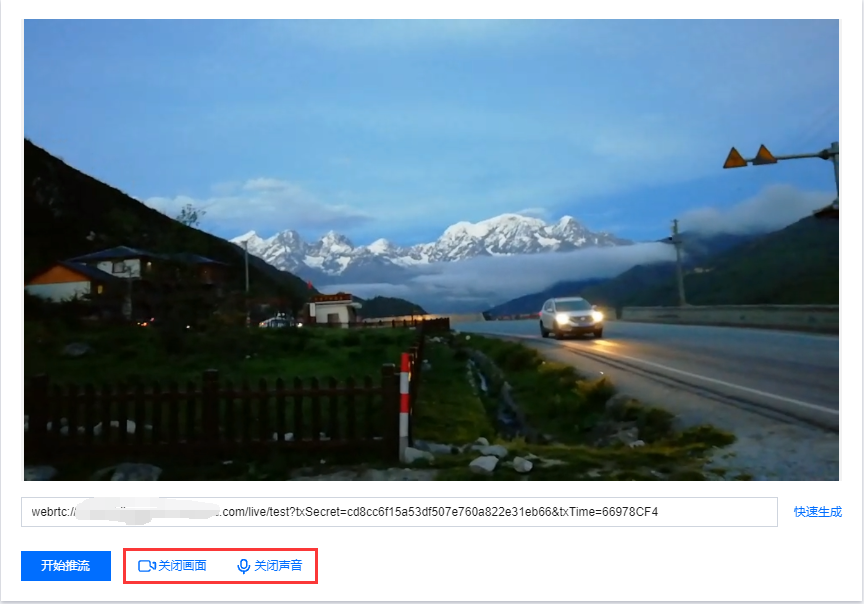
7.1 您可单击和按钮来关闭/开启画面和声音,单击关闭画面或声音系统依旧正常采集,但是无法预览,推流可以正常发起但是没有画面和声音。 说明:
推流成功后,采集预览的状态不支持变更,而且推流可能会产生对应的带宽/流量或其他增值服务费用。
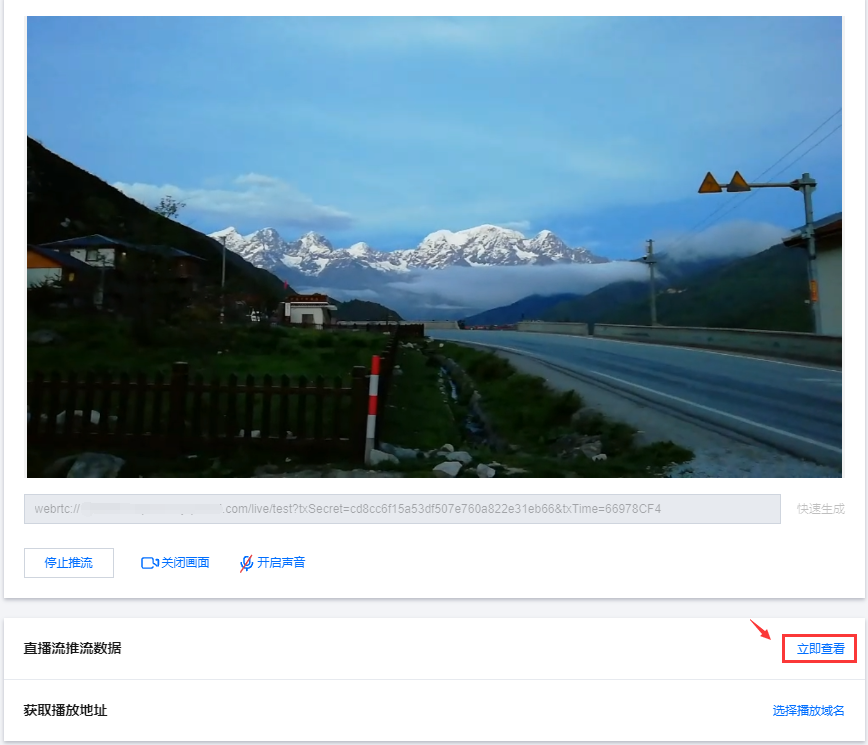
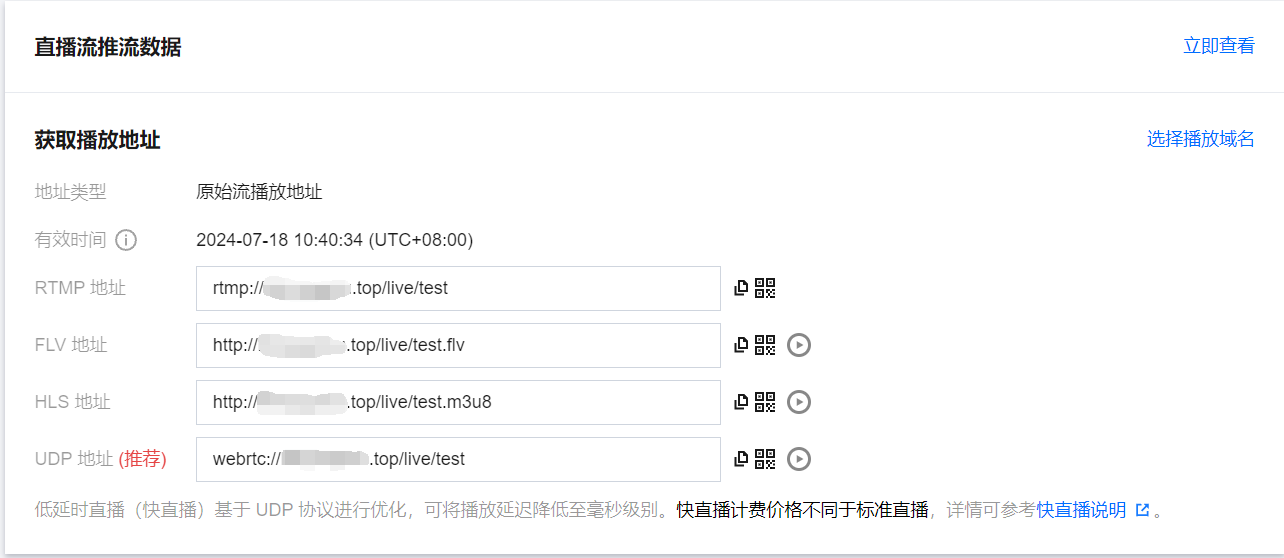
8. 推流成功后您可在下方单击立即查看,快速跳转至查看直播流推流相关数据。非当前账号推流地址无法获取推流数据和播放地址,您可以通过当前账号下的推流域名生成推流地址,或者使用拉流转推功能,将直播流同时转推到当前账号下。
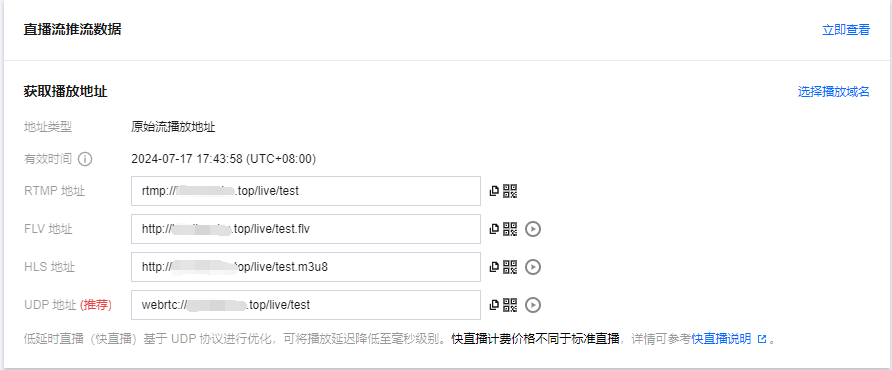
9. 若您在域名管理中已添加播放域名,即可在下方选择播放域名快速生成的播放地址。若您需生成有转码或自适应转码配置的播放地址,需先将播放域名绑定转码模板或自适应转码模板,才可生成播放转码流或自适应转码流。
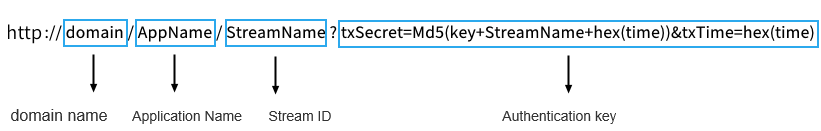
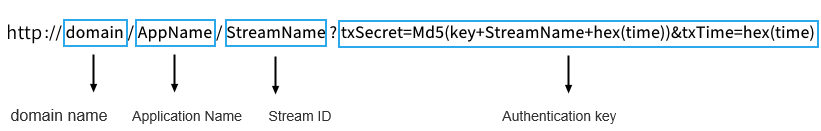
其中,播放地址由以下4部分组成:
支持 RTMP、FLV 、HLS 和 UDP 协议,可以单击播放地址后的二维码,通过 TCToolkit App 扫码查看播放地址: 注意:
当选择的播放域名已开启 HTTPS 配置时,生成的 FLV 和 HLS 地址会默认带上 HTTPS。
多路混流
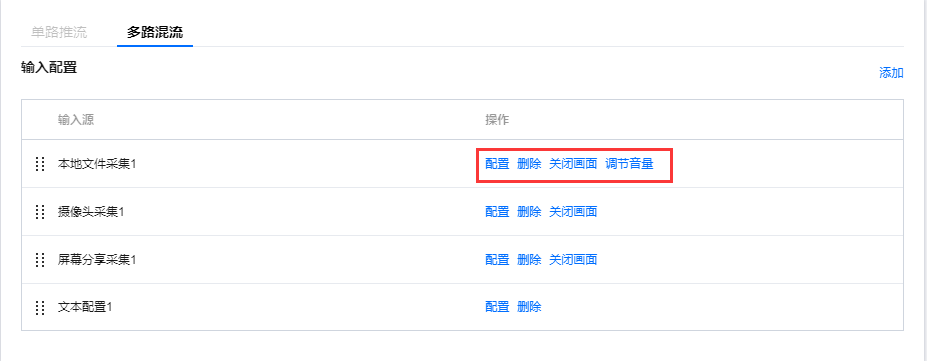
输入配置
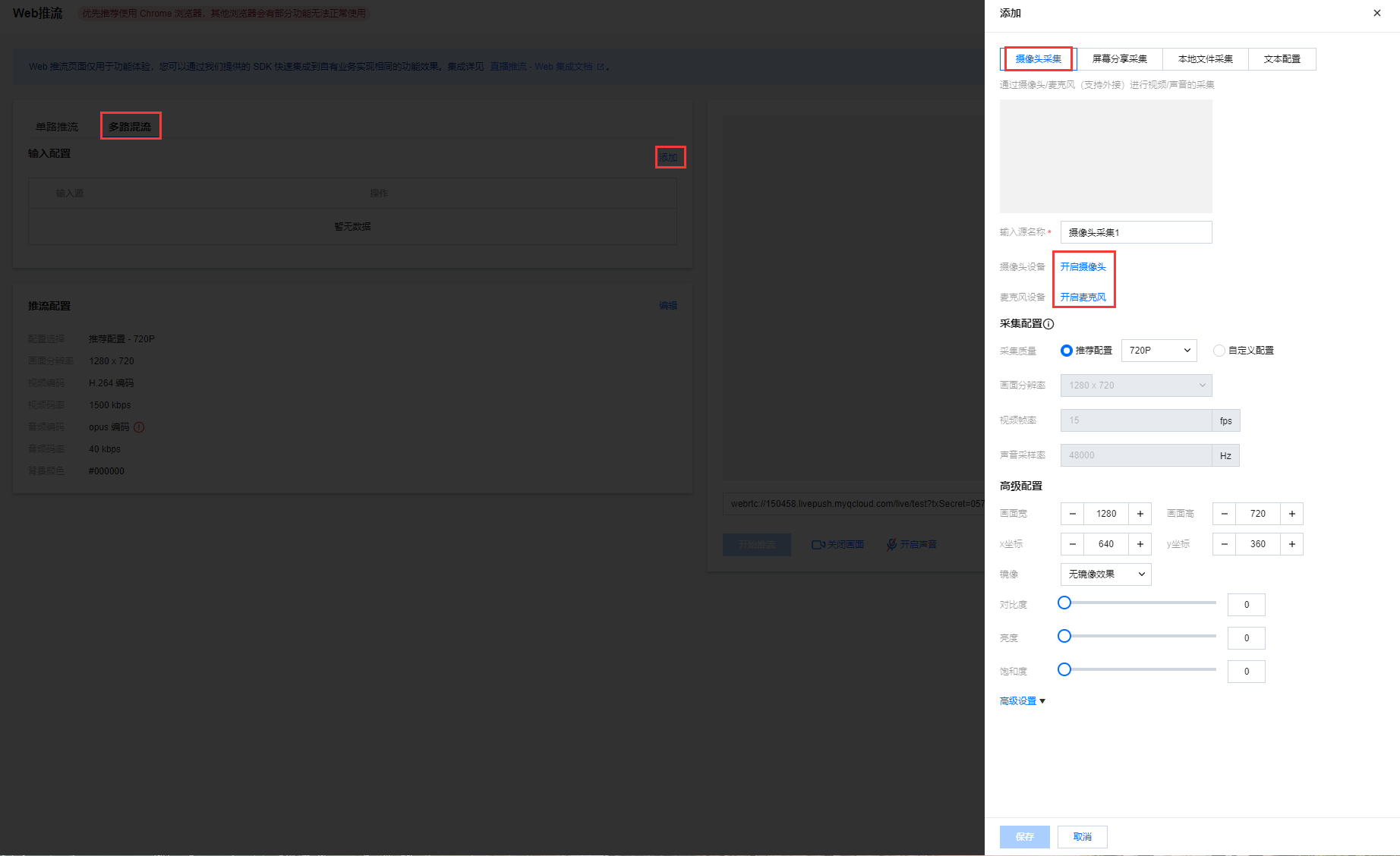
1. 登录云直播控制台,选择 Web推流,单击多路混流。 2. 在输入配置中单击添加。 选择采集方式。您可选择摄像头采集、屏幕分享采集和本地文件采集三种采集方式,并且可添加文本配置进行多路混流直播。最多可添加10个输入源。
摄像头采集是通过摄像头/麦克风(支持外接)进行视频/声音的采集。单击开启摄像头/ 开启麦克风,首次开启需授予浏览器使用摄像头和麦克风权限。
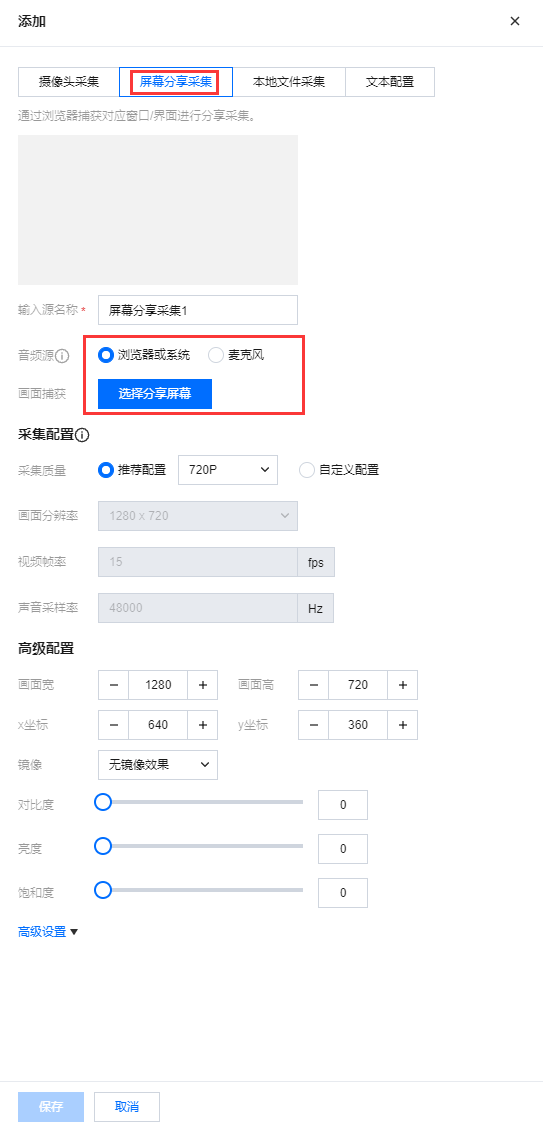
屏幕分享采集是通过浏览器捕获对应窗口/界面进行分享采集。单击选择屏幕分享 选择分享的内容,可为整个屏幕/某个窗口/浏览器标签页。需选择分享屏幕后才可进行保存。
屏幕分享采集支持选择音频源,目前只有 Chrome 74+ 和 Edge 79+ 支持采集声音,在 Windows 系统可以采集整个系统的声音,在 Linux 和 Mac 上面只能采集标签页的声音。
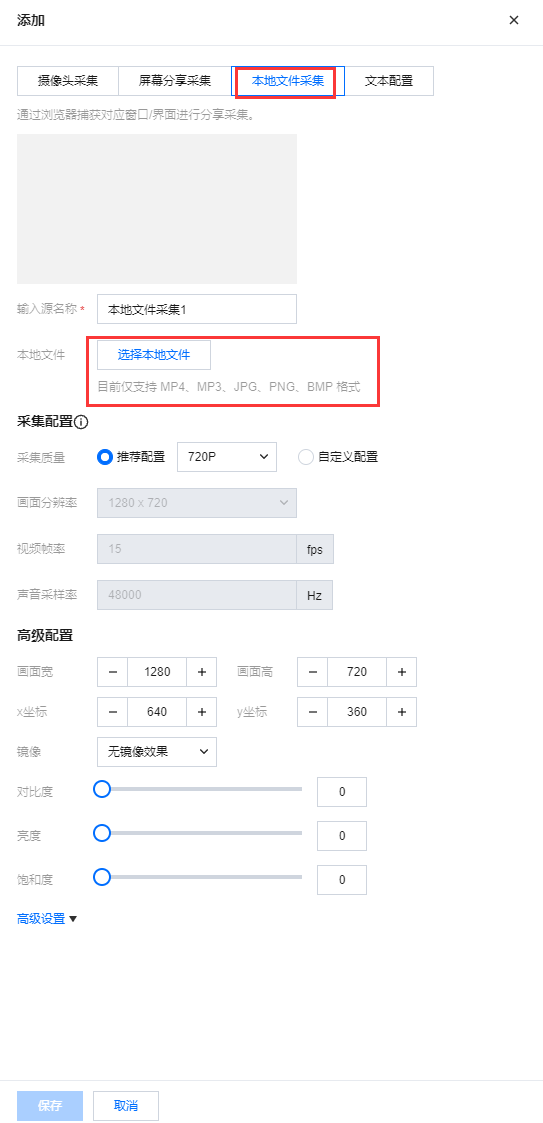
本地文件采集是通过指定本地文件进行画面采集,再通过 Web 推流工具推送到云直播。单击选择本地文件 选择需要推流的内容,目前支持选择 MP4、MP3、JPG、PNG和BMP 格式文件。单击开启预览才可进行保存。
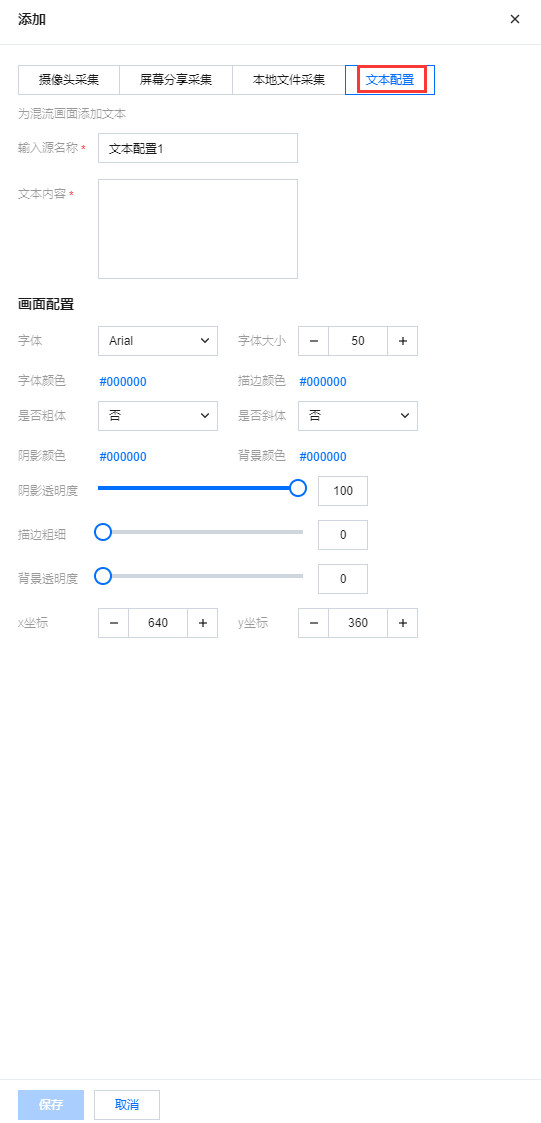
文本配置为混流画面添加文本,再通过 Web 推流工具推送到云直播。在文本内容中输入文本。
可在画面配置中对字体、颜色、阴影、透明度、粗细、文本坐标等进行配置。文本坐标默认是页面中间。
3. 可对摄像头采集、屏幕分享采集、本地文件采集设置采集配置,默认为推荐配置(不同分辨率有不同推荐配置),采集过程中不支持切换或修改配置,需在关闭预览的情况下进行修改。
4. 可对摄像头采集、屏幕分享采集、本地文件采集设置高级配置,可对画面、坐标、镜像、对比度、亮度和饱和度进行调整。
5. 单击保存,该输入源添加进配置中。
修改配置
1. 在输入配置中,可对已配置的输入源进行操作。
2. 选择您需要修改配置的输入源,单击配置,右侧弹窗展示该输入源的配置信息,可重新修改配置信息。采集过程中不支持切换或修改配置,需在关闭预览的情况下进行修改。
3. 输入源之间可以通过拖动输入源左侧按钮上下调节其展示层级。
4. 单击删除可删除该输入源。
5. 单击关闭画面,则关闭该输入源的预览,但是在画面编辑中可以选中画面进行编辑。
6. 有音频输入的输入源可进行调节音量,单击调节音量,拖动音量条,单击确定即可。
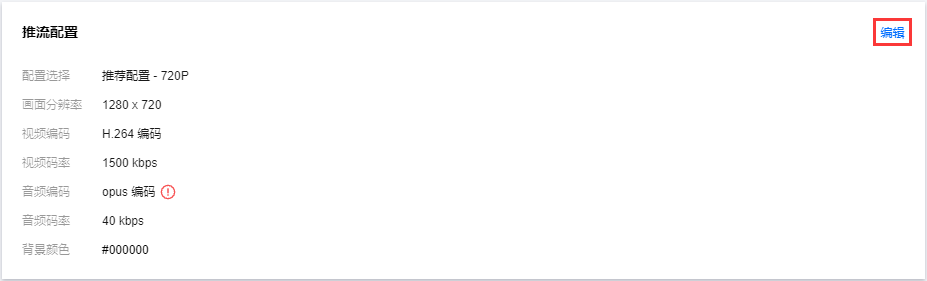
推流配置
推流配置。设置推流配置,默认为推荐配置(不同分辨率有不同视频码率的推荐配置,音频码率不支持修改),可在右上角单击编辑进入自定义编辑配置,可自定义修改视频码率和音频码率。
说明:
web 推流的音频编码方式为 opus 编码,推荐使用快直播 WebRTC 地址进行播放。若使用标准直播的播放地址(RTMP/FLV/HLS),系统会自动转换为 aac 编码才能正常播放,从而会产生音频转码费用,详情请参见 计费文档。 画面编辑
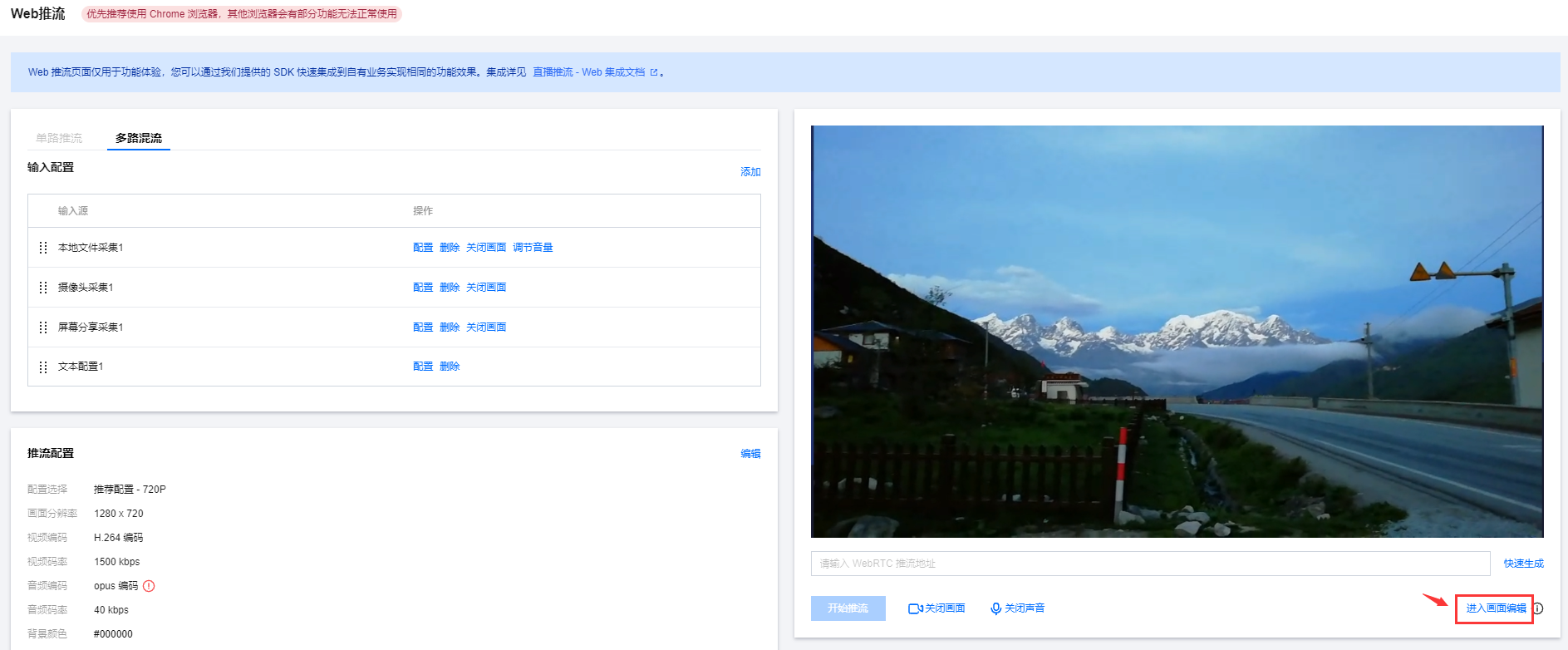
1. 在确定输入配置以及推流配置后,可在右侧预览框中看到预览画面,并且可对画面进行画面编辑。
2. 单击进入画面编辑,选中预览框中需要调整的画面,可对画面进行拖动与缩放大小。
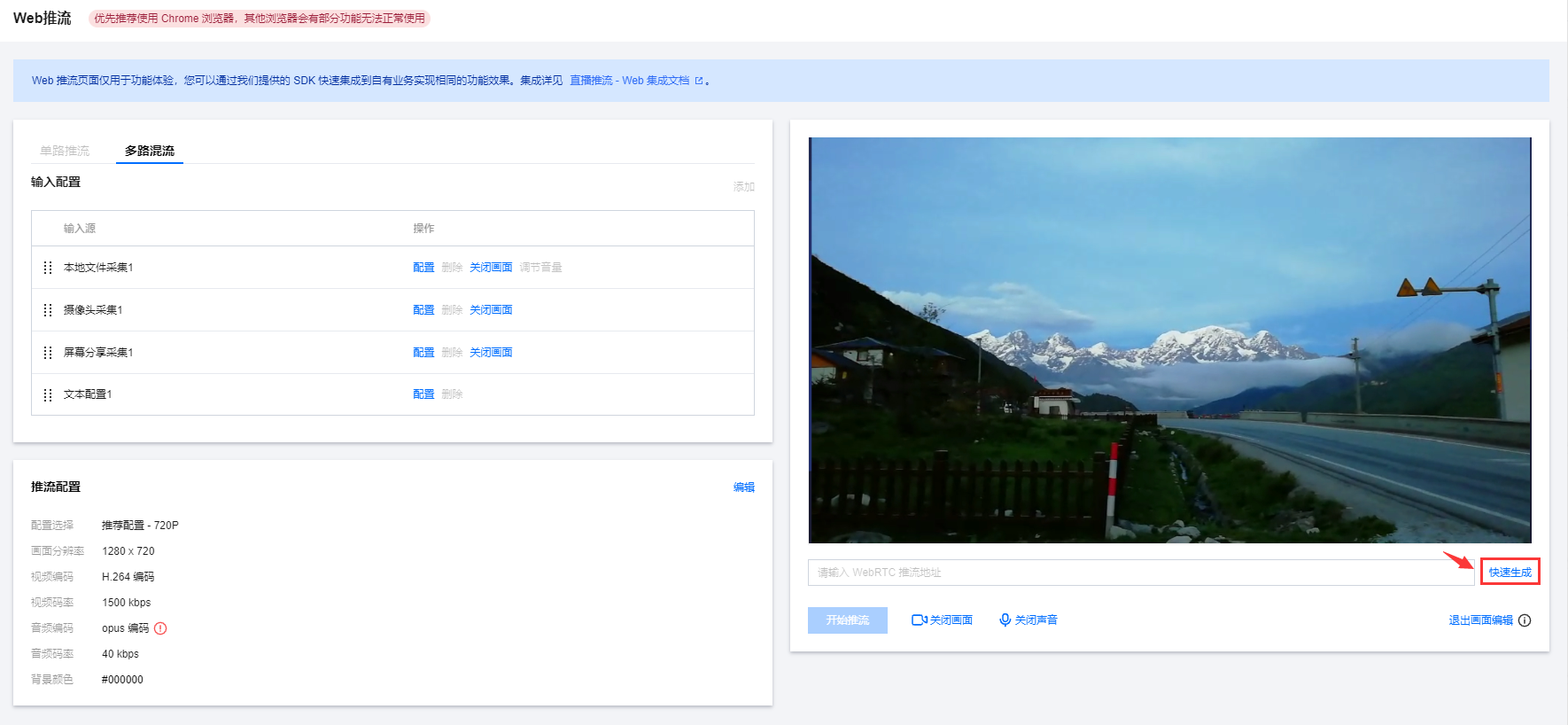
3. 调整完成后单击退出画面编辑,若是处于推流中,保存后将按新画面布局继续推流。
说明:
进入画面编辑可以在预览框中调整画面布局,退出画面编辑可在预览框中查看推流的预览画面,编辑页面不影响实时推流,退出编辑才会保存配置。
推流地址
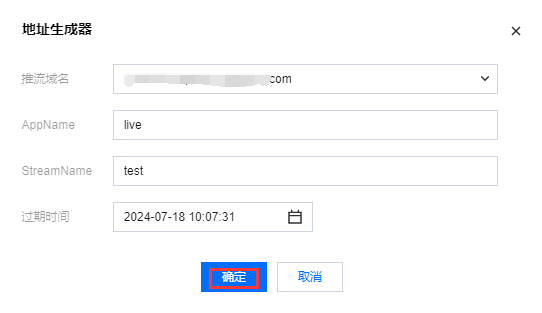
1. 在预览框下输入 WebRTC 推流地址或单击快速生成,在弹窗中配置以下信息:
1.1 选择您的推流域名。
1.2 编辑 AppName,用于区分同一个域名下多个 App 的地址路径,默认值为 live。
1.3 填写自定义的流名称 StreamName,例如:test。
1.4 选择过期时间,例如:2024-07-18 10:07:31。
1.5 单击确定,快速自动生成 WebRTC 推流地址填入地址栏。
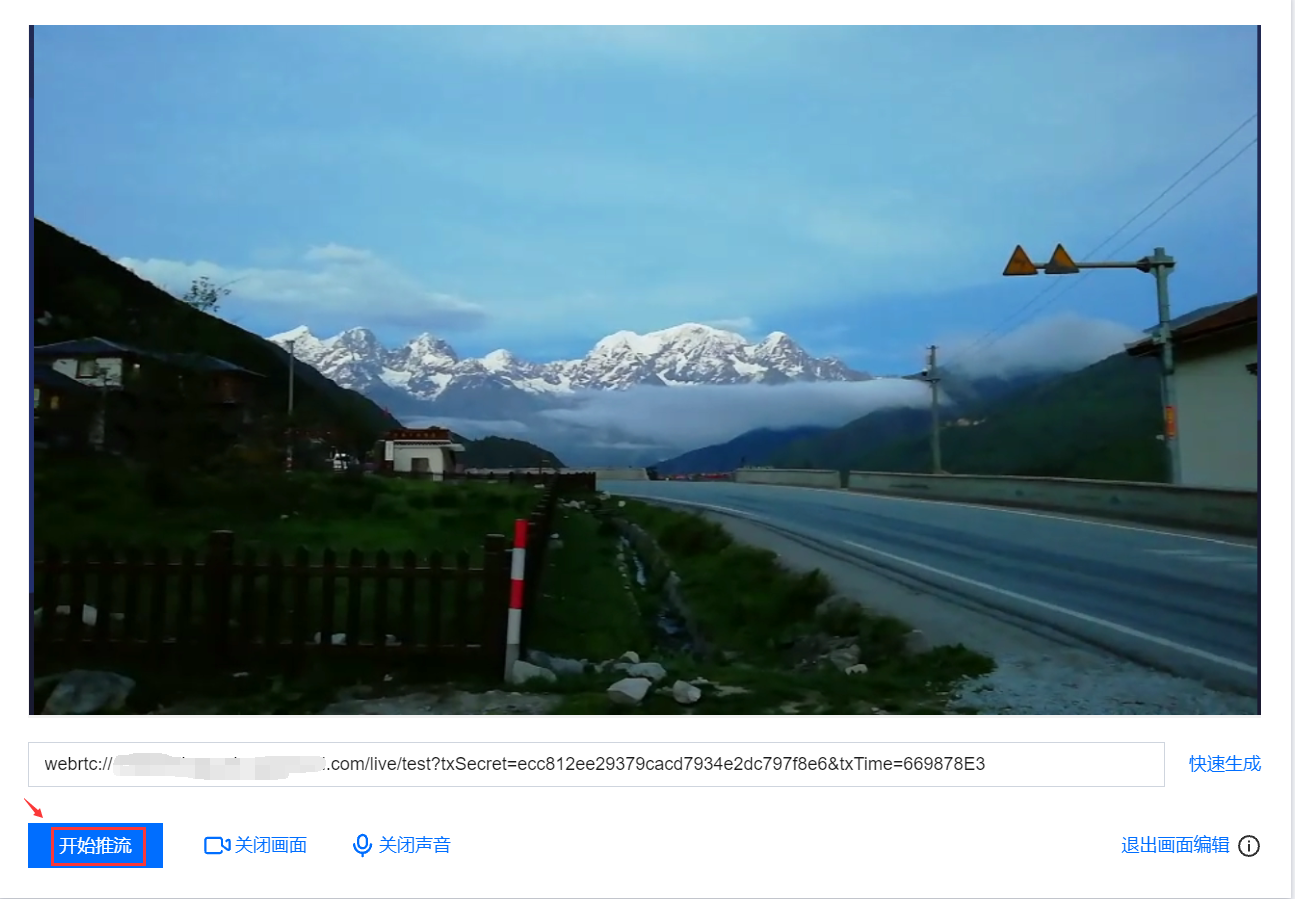
开始推流
1. 单击 开始推流,即可开始推流。
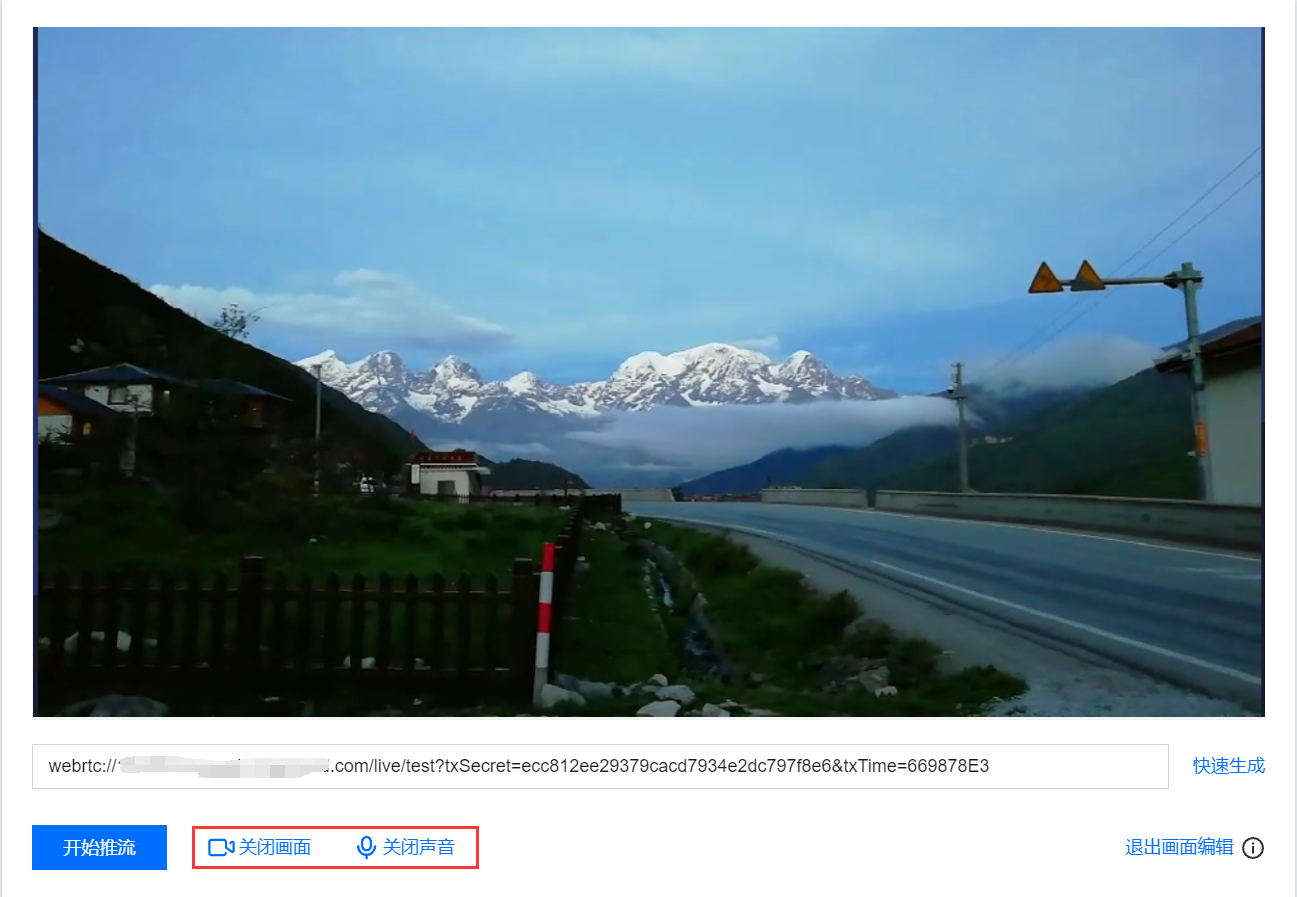
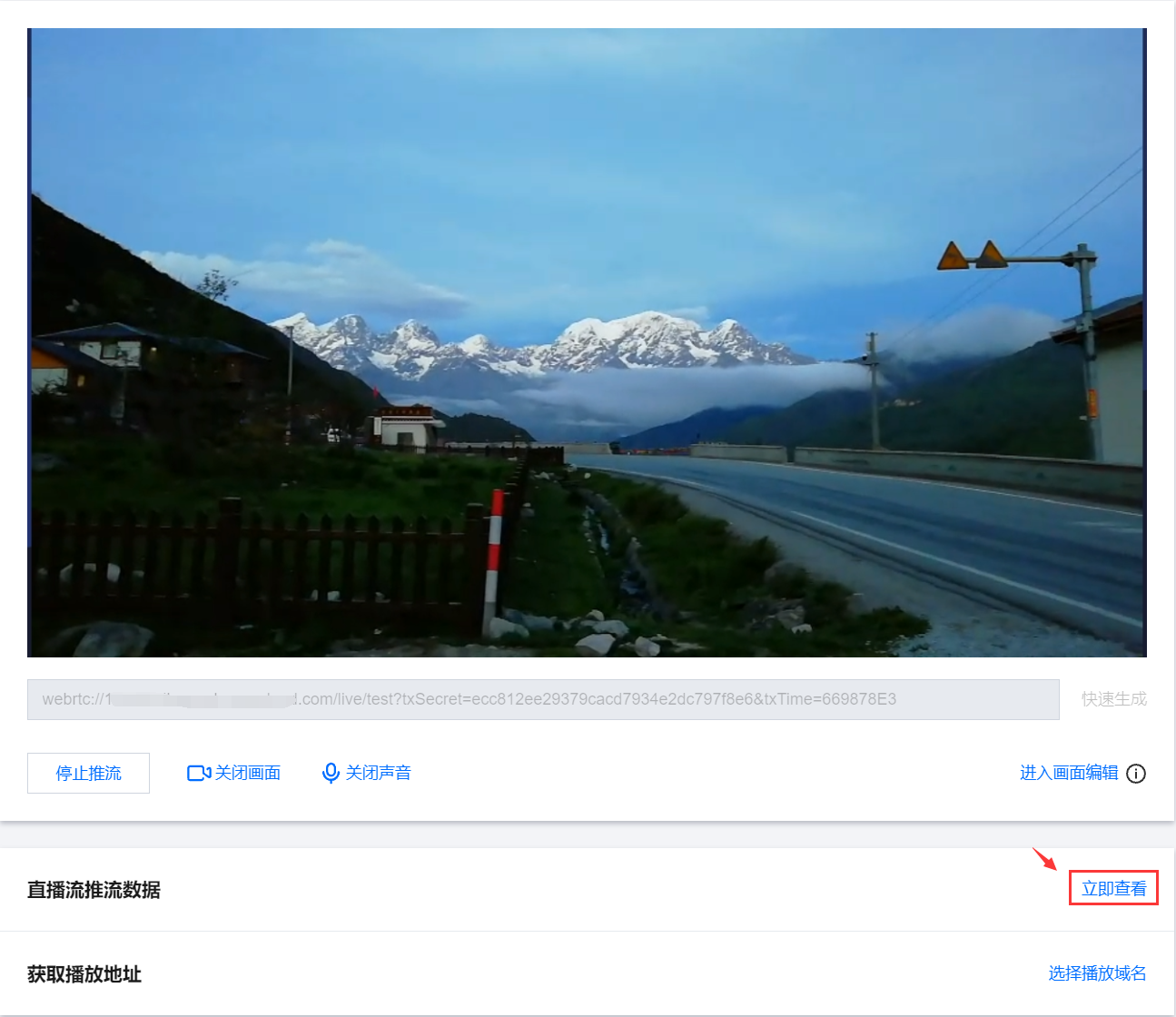
1.1 您可单击和 按钮来关闭/开启画面和声音,单击关闭画面或声音系统依旧正常采集,但是无法预览,推流可以正常发起但是没有画面和声音。 1.2 推流成功后您可在下方单击立即查看,快速跳转至查看直播流推流相关数据。非当前账号推流地址无法获取推流数据和播放地址,您可以通过当前账号下的推流域名生成推流地址,或者使用拉流转推功能,将直播流同时转推到当前账号下。
1.3 若您在域名管理中已添加播放域名,即可在下方选择播放域名快速生成的播放地址。若您需生成有转码或自适应转码配置的播放地址,需先将播放域名绑定转码模板或自适应转码模板,才可生成播放转码流或自适应转码流。
其中,播放地址由以下4部分组成:
支持 RTMP、FLV 、 HLS 和 UDP 协议,可以单击播放地址后的二维码,通过 TCToolkit App 扫码查看播放地址: 注意:
当选择的播放域名已开启 HTTPS 配置时,生成的 FLV 和 HLS 地址会默认带上 HTTPS。