Cloud Streaming Services
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Announcements
- Product Introduction
- CSS Products
- Purchase Guide
- Basic Service Fee
- Value-Added Service Fee
- Live Video Broadcasting (LVB)
- Live Event Broadcasting (LEB)
- Live Video Caster
- General Cloud Director
- Console Guide
- Domain Management
- Adding Domain Names
- Push Domain Name Management
- Playback Domain Name Management
- HTTPS Configuration
- Feature Configuration
- Time Shifting
- Live Stream Moderation
- Live Subtitling
- Laboratory
- Monitoring
- Log Service
- Feature Guide
- Push and Playback
- WebRTC Protocol Push Stream
- Features
- Live Recording
- Practices in Typical Scenarios
- Live Streaming Security
- Global CSS Service
- Callback Notifications
- User Guides for Common Third-Party Tools
- SDK Guide
- 1. Stream Push
- API Documentation
- Making API Requests
- Monitoring Data Query APIs
- Billing Data Query APIs
- Live Transcoding APIs
- Delayed Playback Management APIs
- Domain Name Management APIs
- Watermark Management APIs
- Certificate Management APIs
- Live Stream Mix APIs
- Stream Pulling APIs
- Recording Management APIs
- Time Shifting APIs
- Live Callback APIs
- Screencapturing and Porn Detection APIs
- Authentication Management APIs
- Live Stream Management APIs
- Ops Guide
- Troubleshooting
- About Pushing
- Generating Push URLs
- PC Push
- Playing Method
- Web Player
- Web Player TcPlayer
- Web CSS Player 1.0
- Web VOD Player 1.0
- FAQs
Live Remuxing and Transcoding
Last updated: 2024-11-08 15:12:38
Live Remuxing
Live remuxing is the process of converting the original stream pushed from the live streaming site (commonly using the RTMP protocol) into different container formats in the cloud before pushing to viewers.
Supported Output Container Formats
RTMP
FLV
HLS
DASH
TS stream
Supported Output Types
Audio-only output: deletes video files and generates audio-only output. The container formats are as described above.
Video-only output: deletes audio files and generates video-only output. The container formats are as described above.
Supported Media Encryption Schemes
FairPlay
HLS remuxing supports the Apple FairPlay DRM solution.
Widevine
DASH remuxing supports the Google Widevine DRM solution.
Universal AES-128 encryption for HLS
HLS remuxing supports universal AES-128 encryption schemes.
Live Transcoding
Live transcoding (including both video transcoding and audio transcoding) is the process of transcoding the original stream pushed from the live streaming site to streams of different codecs, resolutions, and bitrates in the cloud before pushing to viewers. This helps meet the playback needs in different network environments and on different devices.
Typical Use Cases
An original video stream can be transcoded to streams of different definitions. Viewers can select video streams of different bitrates according to their network conditions to ensure smooth playback.
You can add a custom watermark to an original video stream for copyright and marketing purposes.
A video stream can be transcoded to a video codec with a higher compression ratio. For example, when there is a large number of viewers, you can convert an H.264 video stream to an H.265 stream which has a higher compression ratio, thus reducing bandwidth usage and costs.
An original video stream can be transcoded to different codecs suitable for playback on special devices. For example, if an H.264 video stream cannot be played back in real time due to issues in performance, you can transcode it to the .mpeg format for real-time decoding and playback.
Video Transcoding Parameters
Parameter Type | Description |
Video codec | Supported video codecs: H.264 H.265 AV1 |
Video profile | Supported video profiles: Baseline Main High |
Video encoding bitrate | Supported video output bitrate range: 101 Kbps - 8000 Kbps. The original bitrate will be the output bitrate if you specify an output bitrate higher than the original one. For example, if the specified output bitrate is 3,000 Kbps, yet the original bitrate of the input stream is only 2,000 Kbps, then the output bitrate will be 2,000 Kbps. |
Video encoding frame rate | Supported video output frame rate range: 1-60 fps. The original frame rate will be the output frame rate if you specify an output frame rate higher than the original one. For example, if the specified output frame rate is 30 fps, yet the original frame rate of the input stream is only 20 fps, then the output frame rate will be 20 fps. |
Video resolution | Supported width range: 0 - 3000. Supported height range: 0 - 3000. You can only specify the width and the height will be scaled proportionally. You can only specify the height and the width will be scaled proportionally. |
Video GOP length | Supported video GOP length range: 1-10s; recommended range: 2-4s. |
Video bitrate control method | Supported video bitrate control methods: Fixed bitrate (CBR) Dynamic bitrate (VBR) |
Video image rotation | The original video can be rotated clockwise by: 90 degrees 180 degrees 270 degrees |
Audio Transcoding Parameters
Parameter Type | Description |
Audio codec | Supported codecs: AAC-LC AAC-HE AAC-HE v2 |
Audio sample rate | Supported sample rates (48000 and 44100 are commonly used): 96000 64000 48000 44100 32000 24000 16000 12000 8000 |
Audio encoding bitrate | Supported bitrate range: 20-192 Kbps; commonly used bitrates include: 48 Kbps 64 Kbps 128 Kbps |
Sound channel | Supported sound channel modes: Mono Dual |
Common Preset Templates for Video Transcoding
Video Definition | Template Name | Video Resolution | Video Bitrate | Video Frame Rate | Video Codec |
Smooth | 550 | Image short side (proportionally scaled) x long side (540) | 500 Kbps | 23 | H.264 |
SD | 900 | Image short side (proportionally scaled) x long side (720) | 1000 Kbps | 25 | H.264 |
HD | 2000 | Image short side (proportionally scaled) x long side (1080) | 2000 Kbps | 25 | H.264 |
Top Speed Codec Transcoding
Based on years of experience in audio/video encoding, intelligent scenario recognition, dynamic encoding, three-level (CTU/line/frame) precise bitrate control model, and other technologies, the Top Speed Codec (TSC) transcoding feature provides higher-definition streaming at lower bitrates (50% less on average) for live streaming and video on-demand.
Use Cases
If the live push bitrate is high and the image is complex, you can use the intelligent dynamic encoding technology and precise bitrate control model to keep a high definition at a low bitrate, ensuring that the quality of the video image watched by the viewer is the same as the original quality.
Advantages
As users of various video platforms have an ever-increasing requirement for high video source definition and smooth watch experience, in the current live streaming industry, 1080p resolution and 3-10 Mbps bitrate have gradually become the mainstream configuration, and the bandwidth costs are taking a large part in the total video platform costs. In this case, the reduction of the video bitrate can effectively reduce the bandwidth costs.
Example:
Suppose you held a live session at 3 Mbps for 4 hours with 200 viewers. The codec is H.264 and TSC transcoding is not used. The peak bandwidth is 600 Mbps. The bandwidth cost for this live session is 600 x 0.2118 = 127.08 USD.
If TSC transcoding is used to reduce the bitrate, the incurred bandwidth fees will be around 127.08 x (100% - 30%) = 88.956 USD.
TSC transcoding fees: 0.0443 x 240 = 10.632 USD (published price without any discount applied).
Total fees: 88.956 + 10.632 = 99.588 USD.
Therefore, TSC transcoding can effectively reduce the platform bandwidth costs while delivering a better watch experience.
Key Parameters
The parameters of TSC transcoding are configured basically in the same way as standard live transcoding parameters. For more information, please see Video transcoding parameters.
Live Watermarking
You can use live watermarking to add a preset logo image to an original video stream for copyright and marketing purposes.
Watermark Parameters
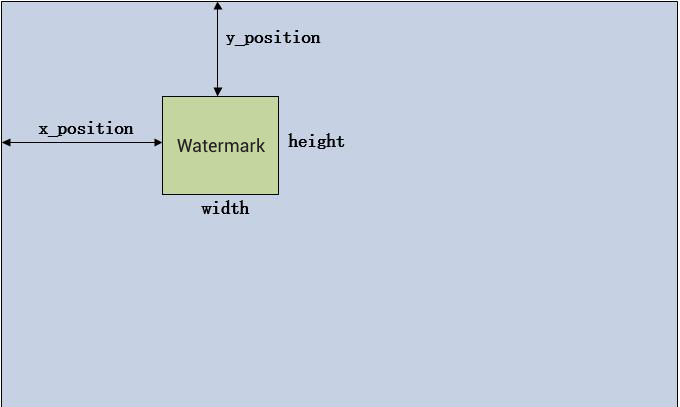
The main parameters of a watermark include watermark location and watermark size, which are determined by the
XPosition, YPosition, Width and Height parameters as detailed below:XPosition: X-axis offset, which indicates the percentage distance from the left edge of the watermark to the left edge of the video.
YPosition: Y-axis offset, which indicates the percentage distance from the top edge of the watermark to the top edge of the video.
Width: watermark width or its percentage of the live streaming video width.
Height: watermark height or its percentage of the live streaming video height.
Note:
If you enable multi-bitrate transcoding for a stream (i.e., one source stream is transcoded into streams of different resolutions) and want to add a watermark, you can set its percentage position on the X and Y axes in the CSS console or through the corresponding API, and the watermark position will be automatically determined by the system.
Example of Watermark Parameters
Suppose the resolution of the output image is 1920 x 1080, the watermark resolution is 320 x 240, XPosition = 5, YPosition = 5, and Width = 10 (unit: percent).
The absolute position and size of the watermark on the output video are as shown below:
XPosition_pixel = 1920 x 5% = 96YPosition_pixel = 1080 x 5% = 54Width_pixel = 1920 x 10% = 192Height_pixel = 192 x 240/320 = 144
The watermark is at 96 pixels away from the left edge of the output video image and 54 pixels away from the top edge of the image. The watermark size is 192 x 144.
How to Use
CSS Console
1. Go to Feature Configuration > Live Watermarking to add a watermark configuration template, set the watermark parameters, and generate the corresponding watermark template ID. For specific steps, please see Watermark Template Configuration.
2. Select Domain Management to add a domain name, and click Manage > Template Configuration to bind it with the watermark template. For more information, please see Watermark Configuration.
Calling APIs
1. Call the AddLiveWatermark API to add a watermark by setting the watermark name and other parameters.
2. Call the CreateLiveWatermarkRule API to create a watermark rule. Set
DomainName (push domain name) and WatermarkId (returned in step 1). Use the same AppName as the AppName in push and playback addresses, which is live by default.Note: Using the watermark feature will incur standard transcoding fees.
Configuring Transcoding Parameters
How to Use
You can set transcoding parameters via the CSS console or server APIs. Either way, you will mainly use watermark templates, transcoding templates, and transcoding rules for the configuration.
CSS Console
1. Go to Feature Configuration > Live Transcoding to add a transcoding configuration template. You can add a standard transcoding or TSC transcoding template.
2. Create the corresponding transcoding type and set transcoding parameters as needed. You can use the system's default parameters, and a corresponding transcoding template ID will be generated.
3. Select Domain Management to find the target pull domain name, and click Manage > Template Configuration to bind it with the transcoding template. For more information, please see Transcoding Configuration.
Calling APIs
1. Call the CreateLiveTranscodeTemplate API to set the transcoding type parameters.
2. Call the CreateLiveTranscodeRule API to set the
DomainName (pull domain name) and TemplateId (returned in step 1) parameters. Enter an empty string in AppName and StreamName as a wildcard for matching all streams under the domain name. You can also bind the transcoding template with different stream names to enable transcoding for these live streams.3. Each transcoding template has a unique transcoding template name which is used as the unique ID for playing back the output stream. You can place the transcoding template name after the stream ID in the playback address to pull the output stream corresponding to the transcoding template.
Note:
The transcoding rule is used to set whether to enable a specified transcoding template for a specified domain name or stream. A playback domain name can be used to pull a transcoding template only after the corresponding transcoding rule is created. If no transcoding rule has been created, a pull address spliced using the transcoding template name is invalid.
Example
**Playback address = Playback domain name + Playback path + Stream ID_transcoding template name + Authentication string**
For a push with stream ID of
1234_test, the original stream and watermarked streams of different bitrates can be played back via the following addresses:Original stream:
http://liveplay.tcloud.com/live/1234_test.flv?authentication stringStandard transcoding stream (watermarked):
http://liveplay.tcloud.com/live/1234_test_sd.flv?authentication stringTSC transcoding stream (watermarked):
http://liveplay.tcloud.com/live/1234_test_hd.flv?authentication stringNote:
To play back a watermarked stream, you need to bind the corresponding push domain name to the created watermark template.
Using APIs
1. Manage transcoding templates in the console:
You can query, add, modify, and delete transcoding templates in the console. For detailed operations, refer to Live Transcoding.
2. Manage transcoding templates through server APIs:
Feature Module | API |
Live Transcoding | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Live Watermarking | |
| |
| |
| |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

