Cloud Virtual Machine
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Image
- Public Image
- TencentOS Server
- Network and Security
- OPS and Monitoring
- Purchase Guide
- Purchasing Instances
- Purchasing Cloud Disks
- Purchasing Reserved Instances
- Purchasing Public Network Bandwidth
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Convenience Features
- Instances
- Creating Instances
- Logging In to Linux Instances
- Logging in to Windows instance
- Adjusting Configuration
- View Instance Details
- Managing Instance IPs
- Terminating/Returning Instances
- Reserved Instances
- Images
- Importing Images
- CentOS Linux Operations
- Migrating Servers
- Online Migration
- Migration Operation Guide
- Maintenance Tasks
- Networking
- Security
- Security Groups
- Managing Security Groups
- Managing Security Group Rules
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Practical Tutorial
- Building an Environment
- Setting up LNMP
- Setting up LAMP manually
- Setting up Java Web
- Setting up Node.js
- Manual Setup of WIPM Environment
- Building a Website
- Discuz! Forum
- Building an Application
- Setting Up FTP Site
- NTP Service
- Building a Visual GUI
- Uploading Local Files to CVM
- High-throughput Network Performance Test
- Operations Guide
- Initializing Data Disks
- Environment Configurations
- Installing Software
- Work with Operating Systems
- Troubleshooting
- Instance-Related Failures
- Windows Instance Login Failures
- Linux Instance Login Failures
- Linux CVM Memory Issues
- API Documentation
- Region APIs
- Instance APIs
- Cloud Hosting Cluster APIs
- Image APIs
- Instance Launch Template APIs
- Making API Requests
- Placement Group APIs
- Key APIs
- Security Group APIs
- Network APIs
- FAQs
- Billing
- Instance
- Storage
- Images
- OPS & Monitoring
- Related Agreement
Changing Kernel of a Linux Instance Manually
Last updated: 2024-01-06 17:43:10
Overview
Bottleneck Bandwidth and Round-trip propagation time (BBR) is a TCP congestion control algorithm developed by Google in 2016. It helps significantly improve the throughput and the TCP connection latency of Linux servers. However, enabling BBR requires a Linux kernel version of 4.10 or later. If you use an earlier version, you need to upgrade your kernel.
This document describes how to manually change the kernel and enable BBR in a Linux CVM instance on CentOS 7.5 as an example.
Directions
Updating the kernel package
1. Run the following command to check the current kernel version.
uname -r
2. Run the following command to update the software package.
yum update -y
3. Run the following command to import the public key of ELRepo.
rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
4. Run the following command to install the yum repository of ELRepo.
yum install https://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-4.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
Installing a new kernel
1. Run the following command to check the supported kernel package in the ELRepo repository.
yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="elrepo-kernel" list available
2. Run the following command to install the latest mainline stable kernel.
yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-ml
Modifying the grub configuration
1. Run the following command to open the
/etc/default/grub file.vim /etc/default/grub
2. Press i to switch to the edit mode and change 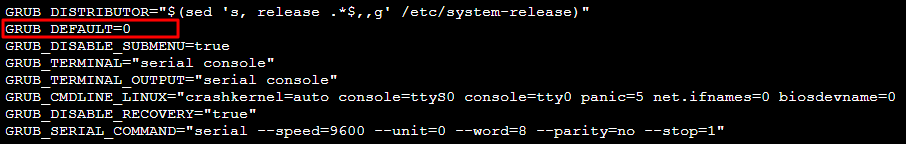
GRUB_DEFAULT=saved to GRUB_DEFAULT=0.

3. Click Esc and enter :wq to save and close the file.
4. Run the following command to generate the kernel configuration again.
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
5. Run the following command to restart the server.
reboot
6. Run the following command to check whether the modification is successful.
uname -r
Deleting unnecessary kernels
1. Run the following command to view all kernels.
rpm -qa | grep kernel
2. Run the following command to delete the older kernel.
yum remove kernel-old_kernel_version
For example:
yum remove kernel-3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64
Enabling BBR
1. Run the following command to edit the
/etc/sysctl.conf file.vim /etc/sysctl.conf
2. Press i to switch to the edit mode and enter the following:
net.core.default_qdisc=fqnet.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control=bbr
3. Click Esc and enter :wq to save and close the file.
4. Run the following command to load the kernel parameter settings to the
/etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.sysctl -p
5. Run the following commands to verify whether BBR has been successfully enabled.
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control# The following appears if the configuration succeeds:# net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbr
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control# The following appears if the configuration succeeds:# net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control = reno cubic bbr
6. Run the following commend to check whether the kernel module is loaded.
lsmod | grep bbr
If the following information is returned, BBR has been successfully enabled.


Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

