Cloud Object Storage
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Billing Method
- Billable Items
- Metadata Acceleration Fees
- Data Processing Fees
- Getting Started
- Console Guide
- Bucket Management
- Domain Name Management
- Object Management
- Folder Management
- Monitoring Reports
- Data Processing
- Image Processing
- File Processing
- Media Processing
- Function Service
- Content Moderation
- Automatic Moderation
- Historical data moderation
- Data Processing Workflow
- User Tools
- COSBrowser
- COSCLI (Beta)
- Common Commands
- Online Auxiliary Tools
- Practical Tutorial
- Access Control and Permission Management
- Performance Optimization
- Data Migration
- Data Disaster Recovery and Backup
- Domain Name Management Practice
- Image Processing
- Audio/Video Practices
- Direct Data Upload
- Content Moderation
- Data Verification
- Big Data Practice
- Using COS in the Third-party Applications
- Developer Guide
- Creating Request
- Object
- Uploading Object
- Downloading Object
- Copying Objects
- Deleting Objects
- Data Management
- Lifecycle Management
- Data Disaster Recovery
- Versioning
- Using Versioning
- Cross-Bucket Replication
- Data Security
- Cloud Access Management
- Access Permission Configuration Description
- Access Control Overview
- Access Control Methods
- Access Policy Language
- Using CDN to Accelerate Access
- Batch Operation
- Performing Batch Operation
- Global Acceleration
- Data Workflow
- Data Lake Storage
- Cloud Native Datalake Storage
- Metadata Accelerator
- Big Data Security
- GooseFS
- Key Features
- Deployment Guide
- OPS Guide
- Logging Guide
- Data Processing
- Image Processing
- Media Processing
- Troubleshooting
- Resource Access Error
- API Documentation
- Service APIs
- Bucket APIs
- Basic Operations
- Access Control List (acl)
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (cors)
- Bucket Policy (policy)
- Hotlink Protection (referer)
- Static Website (website)
- Intelligent Tiering
- Bucket inventory(inventory)
- Cross-Bucket Replication(replication)
- Log Management(logging)
- Global Acceleration (Accelerate)
- Bucket Encryption (encryption)
- Custom Domain Name (Domain)
- Origin-Pull (Origin)
- Object APIs
- Basic Operations
- Access Control List (acl)
- Multipart Upload
- Batch Operation APIs
- Data Processing APIs
- Image Processing
- Basic Image Processing
- AI-Based Content Recognition
- Queue APIs
- Service Configuration
- Media Processing
- Media Screenshot API
- Media Information API
- Private M3U8 API
- File Processing
- File Transcoding
- Async Processing Job APIs
- Async Processing Queue APIs
- File Processing
- Hash Calculation
- File Decompression
- Multi-File Zipping
- Job and Workflow
- Workflow APIs
- Workflow Instance
- Job APIs
- Media Processing
- Canceling Media Processing Job
- Querying Media Processing Job
- Media Processing Job Callback
- Image Processing
- Submit Image Processing Job
- Canceling Image Processing Job
- Querying Image Processing Job
- Multi-Job Processing
- Submitting Multiple Jobs
- AI-Based Content Recognition
- Submitting Content Recognition Job
- Querying Content Recognition Job
- Content Recognition Job Callback
- Sync Media Processing
- Media Screenshot API
- Template APIs
- Media Processing
- Creating Media Processing Template
- Deleting Media Processing Template
- Querying Media Processing Template
- Updating Media Processing Template
- AI-Based Content Recognition
- Creating AI-Based Content Recognition Template
- Querying AI-Based Content Recognition Template
- Updating AI-Based Content Recognition Template
- Batch Job APIs
- Callback Content
- Appendix
- Content Moderation APIs
- Image Moderation
- Video Moderation
- Audio Moderation
- Text Moderation
- Submitting Virus Detection Job
- SDK Documentation
- Android SDK
- Object Operations
- Remote Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Access Management
- Data Verification
- Image Processing
- C SDK
- Object Operations
- Data Management
- Cloud Access Management
- Content Moderation
- Data Verification
- C++ SDK
- Cross-Region Disaster Recovery
- Data Management
- Cloud Access Management
- Data Verification
- Content Moderation
- .NET(C#) SDK
- Bucket Operations
- Object Operations
- Cross-Region Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Access Management
- Image Processing
- SDK for Flutter
- Object Operations
- Go SDK
- Bucket Operations
- Object Operations
- Cross-Region Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Access Management
- Data Verification
- File Processing
- Image Processing
- iOS SDK
- Object Operations
- Cross-region Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Access Management
- Image Processing
- Content Recognition
- Speech Recognition
- Java SDK
- Object Operations
- Cross-Region Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Access Management
- File Processing
- Media Processing
- AI-Based Content Recognition
- JavaScript SDK
- Object Operations
- File Processing
- Remote disaster-tolerant
- Data Management
- Cloud Access Management
- Data Verification
- Image Processing
- Node.js SDK
- Object Operations
- Remote disaster-tolerant
- Cloud Access Management
- Data Verification
- Image Processing
- PHP SDK
- Object Operations
- Bucket Operations
- Remote disaster-tolerant
- Cloud Access Management
- Image Processing
- Media Processing
- Document Processing
- File Processing
- Job APIs
- Template APIs
- Python SDK
- Object Operations
- Server-Side Encryption
- Cross-Region Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Access Management
- Content Recognition
- React Native SDK
- Object Operations
- Mini Program SDK
- Object Operations
- Remote disaster-tolerant
- Cloud Access Management
- Data Verification
- Content Moderation
- Image Processing
- FAQs
- Bucket Configuration
- Domain Names and CDN
- Object Operations
- Data Processing
- Related Agreements
- Appendices
- Historical version
DocumentationCloud Object StorageData Lake StorageGooseFSData SecurityConnecting GooseFS to Kerberos Authentication
Connecting GooseFS to Kerberos Authentication
Last updated: 2024-03-25 16:04:01
Overview
Kerberos is a unified authentication service widely used in the big data ecosystem. GooseFS, as the storage acceleration service for big data and data lake scenarios, allows you to connect cluster nodes and user access requests to Kerberos. This document describes how to configure GooseFS connection to Kerberos and how to use a Hadoop Delegation Token for authentication.
Connecting GooseFS to the Kerberos Authentication Architecture
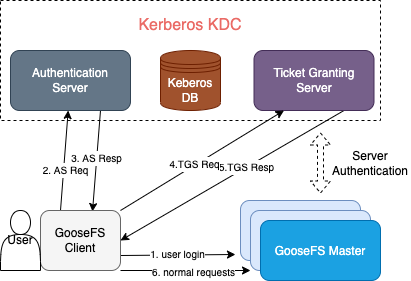
Strengths of Kerberos Authentication for GooseFS
The authentication architecture and process are basically the same as those of HDFS connection to Kerberos. Applications for which the Kerberos authentication process is enabled in HDFS can be migrated to GooseFS easily.
The Hadoop Delegation Token authentication mechanism is supported, so GooseFS is well compatible with Hadoop-based application jobs.
Configuring GooseFS connection to Kerberos
Prerequisites
GooseFS 1.3.0 or later.
Make sure that the Kerberos KDC service exists in your environment and GooseFS and the application client can access its port normally.
Creating the GooseFS identity information in Kerberos KDC
First, create Kerberos identities for the GooseFS cluster server and client in Kerberos KDC before configuring the connection. Here,
kadmin.local is used on the Kerberos KDC server for creation:Note:
You need to run the
kadmin.local tool with the root/sudo privileges.$ sudo kadmin.local
If the command is executed successfully, you will enter the interactive shell environment of kadmin:
Authenticating as principal root/admin@GOOSEFS.COM with password.kadmin.local:
Here,
kadmin.local indicates the command prompt of the interactive execution environment.Creating GooseFS server/client identities
The following takes a simple test cluster and its use case as an example to describe how to configure Kerberos:
1. Cluster environment description:
A one-master-dual-worker standalone architecture is used:
Master (JobMaster): 172.16.0.1
Worker 1 (JobWorker1): 172.16.0.2
Worker 2 (JobWorker2): 172.16.0.3
Client: 172.16.0.4
2. Create the server and client identities in
kadmin.local:kadmin.local: addprinc -randkey goosefs/172.16.0.1@GOOSEFS.COMkadmin.local: addprinc -randkey client/172.16.0.4@GOOSEFS.COM
Note:
Here,
-randkey is used as no matter whether you log in to GooseFS on the server or client, a .keytab file instead of a plaintext password will be used for authentication. If the identity information needs to be used for login with a password, you can remove this field.3. Generate and export the
.keytab file for each identity:kadmin.local: xst -k goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab goosefs/172.16.0.1@GOOSEFS.COMkadmin.local: xst -k client_172_16_0_4.keytab client/172.16.0.4@GOOSEFS.COM
Configuring Kerberos authentication for GooseFS server/client access
1. Distribute the
.keytab files exported above to the corresponding servers. Here, we recommend you use the path ${GOOSEFS_HOME}/conf/.$ scp goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab <username>@172.16.0.1:${GOOSEFS_HOME}/conf/$ scp goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab <username>@172.16.0.2:${GOOSEFS_HOME}/conf/$ scp goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab <username>@172.16.0.3:${GOOSEFS_HOME}/conf/$ scp client_172_16_0_4.keytab <username>@172.16.0.4:${HOME}/.goosefs/
2. On the corresponding server, change the user/user group to which the server principal keytab file belongs to the user/user group used during GooseFS server startup, so as to grant GooseFS the required read permission during startup.
$ chown <GooseFS_USER>:<GOOSEFS_USERGROUP> goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab$ # Modify the Unix access permission bit$ chmod 0440 goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab
3. Change the user/user group to which the client keytab file belongs to the client account initiating GooseFS requests, so as to guarantee that the client has the required permission to read the file.
$ chown <client_user>:<client_usergroup> client_172_16_0_4.keytab$ # Modify the Unix access permission bit$ chmod 0440 client_172_16_0_4.keytab
GooseFS configuration on the server and client
1.
goosefs-site.properties on the master/worker server:# Security properties# Kerberos propertiesgoosefs.security.authorization.permission.enabled=truegoosefs.security.authentication.type=KERBEROSgoosefs.security.kerberos.unified.instance.name=172.16.0.1goosefs.security.kerberos.server.principal=goosefs/172.16.0.1@GOOSEFS.COMgoosefs.security.kerberos.server.keytab.file=${GOOSEFS_HOME}/conf/goosefs_172_16_0_1.keytab
After configuring authentication on the GooseFS server, restart the entire cluster for the configuration to take effect.
2.
goosefs-site.properties on the client:# Security properties# Kerberos propertiesgoosefs.security.authorization.permission.enabled=truegoosefs.security.authentication.type=KERBEROSgoosefs.security.kerberos.unified.instance.name=172.16.0.1goosefs.security.kerberos.server.principal=goosefs/172.16.0.1@GOOSEFS.COMgoosefs.security.kerberos.client.principal=client/172.16.0.4@GOOSEFS.COMgoosefs.security.kerberos.client.keytab.file=${GOOSEFS_HOME}/conf/client_172_16_0_4.keytab
Note:
You need to specify the server principal on the client, as in the Kerberos authentication system, KDC needs to know the service accessed by the client currently, and GooseFS uses the server principal to identify the service requested by the client currently.
At this point, GooseFS has been connected to the basic authentication service of Kerberos, and all requests initiated by the client will be authenticated by Kerberos subsequently.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

