Tencent Kubernetes Engine
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Release Notes
- Announcements
- Security Vulnerability Fix Description
- Release Notes
- Kubernetes Version Maintenance
- Runtime Version Maintenance Description
- Product Introduction
- Quick Start
- TKE General Cluster Guide
- Purchase a TKE General Cluster
- Permission Management
- Controlling TKE cluster-level permissions
- TKE Kubernetes Object-level Permission Control
- Cluster Management
- Images
- Worker node introduction
- Normal Node Management
- Native Node Management
- Purchasing Native Nodes
- Supernode management
- Purchasing a Super Node
- Registered Node Management
- Memory Compression Instructions
- GPU Share
- qGPU Online/Offline Hybrid Deployment
- Kubernetes Object Management
- Workload
- Configuration
- Auto Scaling
- Service Management
- Ingress Management
- CLB Type Ingress
- API Gateway Type Ingress
- Storage Management
- Use File to Store CFS
- Use Cloud Disk CBS
- Add-On Management
- CBS-CSI Description
- Network Management
- GlobalRouter Mode
- VPC-CNI Mode
- Static IP Address Mode Instructions
- Cilium-Overlay Mode
- OPS Center
- Audit Management
- Event Management
- Monitoring Management
- Log Management
- Using CRD to Configure Log Collection
- Backup Center
- TKE Serverless Cluster Guide
- Purchasing a TKE Serverless Cluster
- TKE Serverless Cluster Management
- Super Node Management
- Kubernetes Object Management
- OPS Center
- Log Collection
- Using a CRD to Configure Log Collection
- Audit Management
- Event Management
- TKE Registered Cluster Guide
- Registered Cluster Management
- Ops Guide
- TKE Insight
- TKE Scheduling
- Job Scheduling
- Native Node Dedicated Scheduler
- Cloud Native Service Guide
- Cloud Service for etcd
- Version Maintenance
- Cluster Troubleshooting
- Practical Tutorial
- Cluster
- Serverless Cluster
- Mastering Deep Learning in Serverless Cluster
- Scheduling
- Security
- Service Deployment
- Proper Use of Node Resources
- Network
- DNS
- Self-Built Nginx Ingress Practice Tutorial
- Logs
- Monitoring
- OPS
- DevOps
- Construction and Deployment of Jenkins Public Network Framework Appications based on TKE
- Auto Scaling
- KEDA
- Containerization
- Microservice
- Cost Management
- Hybrid Cloud
- Fault Handling
- Pod Status Exception and Handling
- Pod exception troubleshooter
- API Documentation
- Making API Requests
- Elastic Cluster APIs
- Resource Reserved Coupon APIs
- Cluster APIs
- Third-party Node APIs
- Network APIs
- Node APIs
- Node Pool APIs
- TKE Edge Cluster APIs
- Cloud Native Monitoring APIs
- Super Node APIs
- TKE API 2022-05-01
- Making API Requests
- Node Pool APIs
- FAQs
- TKE General Cluster
- TKE Serverless Cluster
- About OPS
- Service Agreement
- User Guide(Old)
Fine-Grained Network Scheduling
Last updated: 2024-12-24 15:47:21
The fine-grained scheduling capability of network provides a series of features to ensure the service quality of business networks, improving network performance in all aspects and flexibly limiting the use of network by a container.
Feature 1: Throttling of Inbound and Outbound Directions
Overview
Limit the inbound and outbound bandwidth of the container.
Operation Steps
1. Deploy QoS Agent.
2. Within the Add-on Management page in the cluster, locate the successfully deployed QoS Agent, and click Update Configuration on the right.
3. On the add-on configuration page for modifying QoS Agent, tick the Network QoS Enhancement.
4. Click Complete.
5. Deploy a business.
6. Deploy the PodQOS object associated with the business, and select the business to apply, as shown below:
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1kind: PodQOSmetadata:name: aspec:labelSelector:matchLabels:k8s-app: a # select the Label of the business that needs to lower the priorityresourceQOS:netIOQOS:netIOLimits:rxBps: 50 # rxBps represents the maximum inbound bandwidth, in Mbps. 0 means no limit. The maximum input value is a 13-digit integer.txBps: 50 # txBps represents the maximum outbound bandwidth, in Mbps. 0 means no limit. The maximum input value is a 13-digit integer.
Feature 2: Priority (Absolute Bandwidth Preemption)
Overview
Users can set different priorities for different containers and allocate bandwidth resources of network interfaces according to the priorities. An example of scheduling policy for inbound bandwidth with three priority levels is provided, which can be extended to more priority levels:
Containers with the highest priority (priority 0) are not subject to network QoS limitations and can use bandwidth resources freely.
When the total bandwidth used by all containers with the lower priorities (priorities 1 and 2) is less than rx_bps_max minus the bandwidth of the highest priority, and the bandwidth which can be used by each container can is not subject to limitations and can exceed rx_bps_min.
When the total bandwidth used by all containers with the lower priorities (priorities 1 and 2) exceeds rx_bps_max, the containers can use up to the difference between rx_bps_max and the total traffic of the containers with a higher priority. If the difference is less than rx_bps_min, then the containers with the lower priority are guaranteed to use the bandwidth of at least rx_bps_min.
The bandwidth of the container with the highest priority (priority 0) can exceed rx_bps_max/tx_bps_max, while the containers with lower priorities cannot exceed this parameter.
Scenarios
Scenario 1
When containers with higher priorities have lower bandwidth usage, an idle bandwidth will be allocated to the containers with low priorities.
When containers with higher priorities have higher bandwidth usage exceeding rx_bw_max, only the minimum guaranteed bandwidth will be allocated to the containers with low priorities.
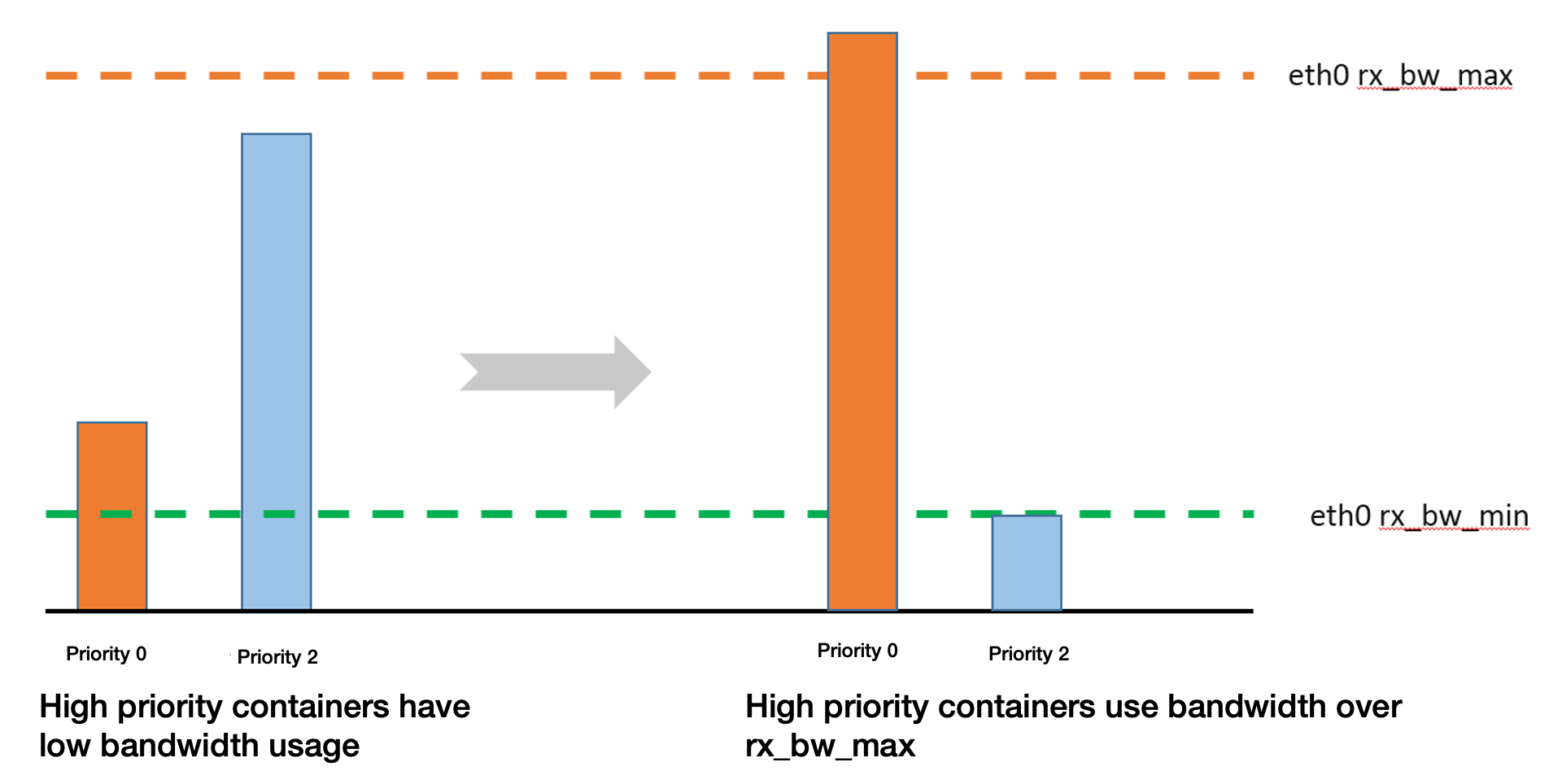
Scenario 2
When containers with higher priorities have lower bandwidth usage, an idle bandwidth will be allocated to the containers with low priorities.
When a container with medium priority is added, the bandwidth of the containers with relatively low priorities will be preempted.
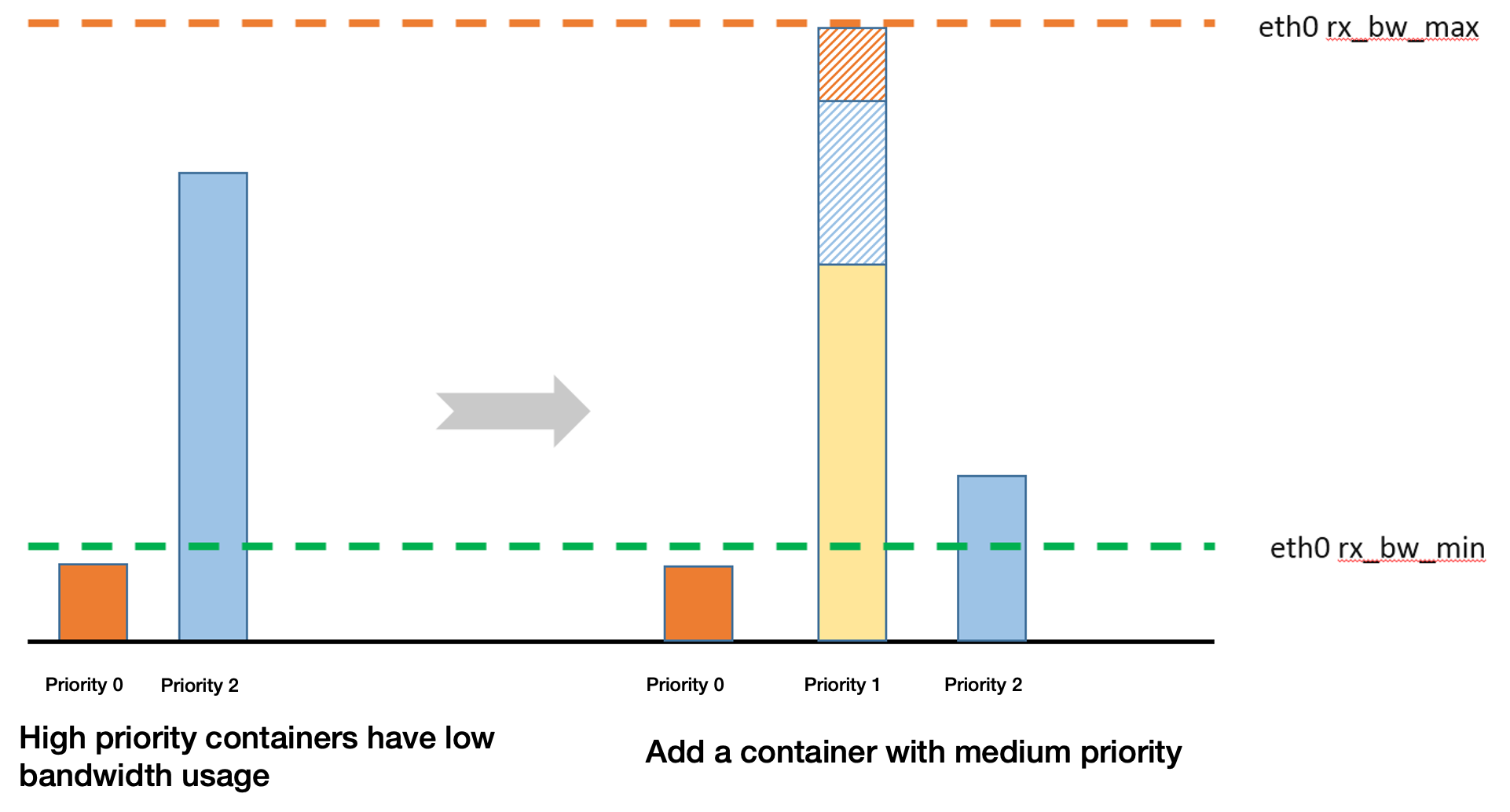
Scenario 3
When containers with higher priorities have lower bandwidth usage, an idle bandwidth will be allocated to the containers with low priorities.
When a container with medium priority is added, the bandwidth of the containers with relatively low priorities will be preempted. The maximum bandwidth which can be preempted shall subtract the bandwidth used by the containers with higher priorities and the minimum guaranteed bandwidth of the containers with lower priorities.
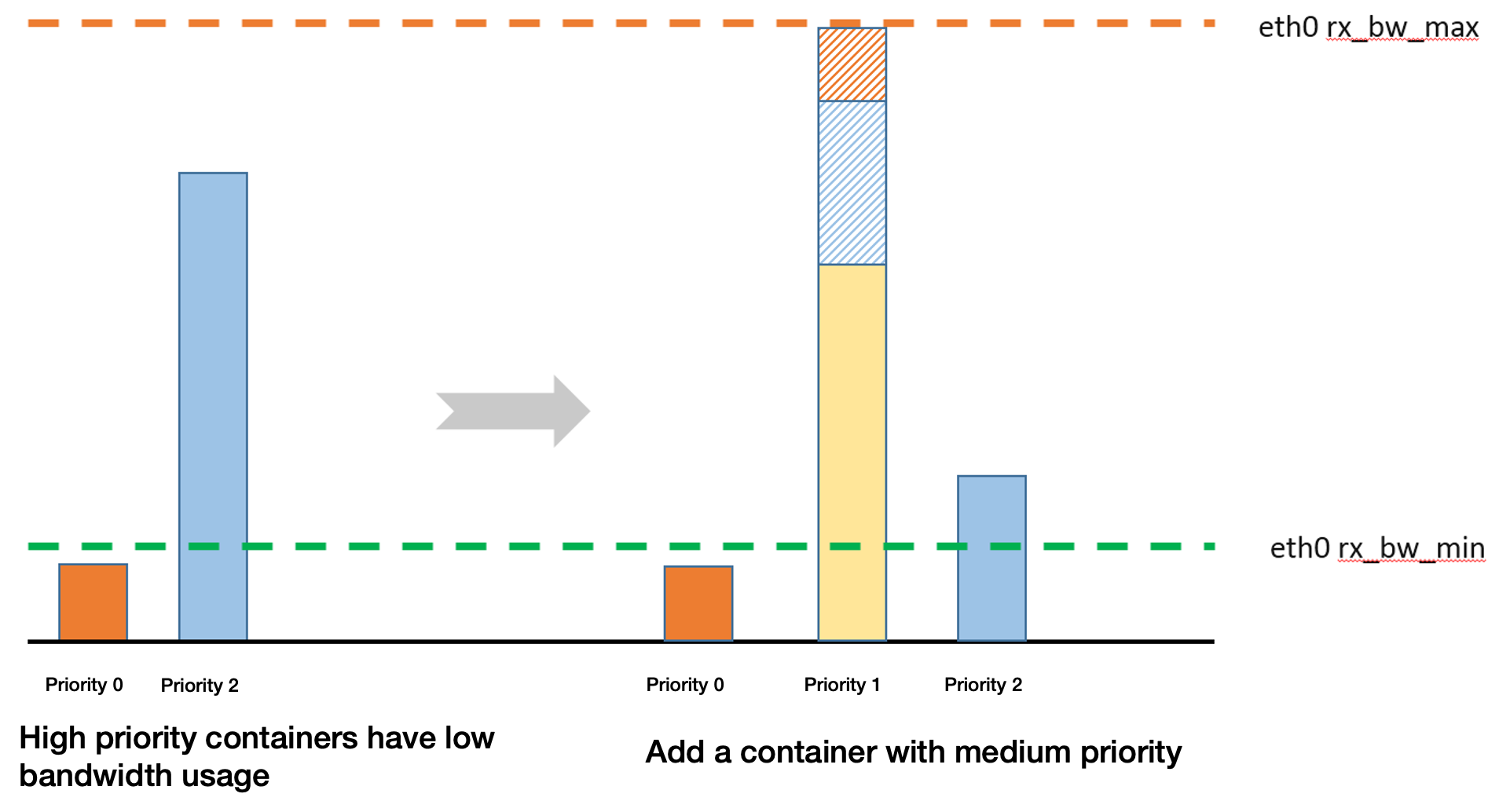
Operation Steps
1. Deploy QoS Agent.
2. Within the Add-on Management page in the cluster, locate the successfully deployed QoS Agent, and click Update Configuration on the right.
3. On the add-on configuration page for modifying QoS Agent, tick the Network QoS Enhancement.
4. Click Complete.
5. Deploy the business A.
6. Deploy the PodQOS object associated with the business, and select the business to apply, as shown below:
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1kind: PodQOSmetadata:name: aspec:labelSelector:matchLabels:k8s-app: a # select the Label of the businessresourceQOS:netIOQOS:netIOPriority: 6 # select the network priority of 0-7, a total of 8 levels
7. Deploy the business B.
8. Deploy the PodQOS object associated with the business, and select the business to apply, as shown below:
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1kind: PodQOSmetadata:name: bspec:labelSelector:matchLabels:k8s-app: b # select the Label of the businessresourceQOS:netIOQOS:netIOPriority: 7 # select the network priority of 0-7, a total of 8 levels
This feature needs to be used jointly with the node bandwidth limitation in NodeQOS, specifying rxBpsMin, rxBpsMax, txBpsMin and txBpsMax with NodeQOS.
rxBpsMin: The minimum guaranteed bandwidth in the inbound direction at the per-priority level. It is shared by the containers at this level. Currently, the minimum guaranteed bandwidth in the inbound direction is the same at different priority levels, except for priority 0.
txBpsMin: The minimum guaranteed bandwidth in the outbound direction at the per-priority level. It is shared by the containers at this level. Currently, the minimum guaranteed bandwidth in the outbound direction is the same at different priority levels, except for priority 0.
rxBpsMax: Maximum inbound bandwidth of the network interface.
txBpsMax: Maximum outbound bandwidth of the network interface.
Note:
Unit: Mbps.
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1kind: NodeQOSmetadata:name: totalspec:netLimits:rxBpsMin: 10rxBpsMax: 10240txBpsMin: 10txBpsMax: 10240
Feature 3: Port Allowlist
Overview
To prevent the containers with low priorities from starving, there are two mechanisms:
1. Minimum guaranteed bandwidth of per-priority: Shared by the containers with this priority.
2. Port allowlist mechanism: Users can add a local port or peer port from the container to the allowlist. The traffic of this port will not be throttled. It is generally used to protect control messages of specific protocols.
Operation Steps
1. Deploy QoS Agent.
2. Within the Add-on Management page in the cluster, locate the successfully deployed QoS Agent, and click Update Configuration on the right.
3. On the add-on configuration page for modifying QoS Agent, tick the Network QoS Enhancement.
4. Click Complete.
5. Deploy a business.
6. Deploy the PodQOS object associated with the business, and select the business to apply, as shown below:
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1kind: PodQOSmetadata:name: aspec:labelSelector:matchLabels:k8s-app: a # select the Label of the businessresourceQOS:netIOQOS:whitelistPorts: # The local port 5201 and the remote port 5205 representing the business a are set as allowlist ports and are not throttled. The default values for lports and rports are 0, with the value range of 0- to 13-digit integers.lports: 5201rports: 5205
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

