Tencent Cloud EdgeOne
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Security Announcement
- Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Billing Items
- Basic Service Fees
- Value-added Service Fees
- Instructions for overdue and refunds
- Getting Started
- Domain Service&Origin Configuration
- Domain Service
- Hosting DNS Records
- Domain Connection
- Traffic Scheduling
- HTTPS Certificate
- HTTPS Configuration
- SSL/TLS Security Configuration
- Origin Configuration
- Load Balancing
- Related References
- Origin-pull configuration
- Related References
- Site Acceleration
- Access Control
- Cache Configuration
- EdgeOne Cache Rules
- Cache Configuration
- Clear and Preheat Cach
- File Optimization
- Network Optimization
- HTTP/3(QUIC)
- QUIC SDK
- Modifying Header
- Modify the response content
- Rule Engine
- Related References
- Request and Response Actions
- DDoS & Web Protection
- DDoS Protection
- Configuration of Exclusive DDoS protection Rules
- Related References
- Web Protection
- Rate Limiting
- Bot Management
- Related References
- Related References
- Image&Video Processing
- Edge Functions
- Runtime APIs
- Streams
- Images
- Sample Functions
- Best Practices
- L4 Proxy
- Obtaining Real Client IPs
- Obtaining Real Client IPs Through Protocol V1/V2
- Data Analysis&Log Service
- Log Service
- Real-time Logs
- Data Analysis
- Related References
- Legacy Console Relevant Documentation
- Security Analysis
- Alarm Service
- Version Management
- Site and Billing Management
- Site Management
- General Policy
- Terraform
- Practical Tutorial
- Automatic Warm-up/Cache Purge
- Resource Abuse/hotlinking Protection Practical
- HTTPS Related Practices
- Acceleration Optimization
- Scheduling Traffic
- Origin-pull Based On User IP/geolocation
- APK Dynamic Packaging
- Data Analysis and Alerting
- API Documentation
- Making API Requests
- Site APIs
- Acceleration Domain Management APIs
- Site Acceleration Configuration APIs
- Edge Function APIs
- Alias Domain APIs
- Security Configuration APIs
- Layer 4 Application Proxy APIs
- Content Management APIs
- Data Analysis APIs
- Log Service APIs
- Billing APIs
- Certificate APIs
- Load Balancing APIs
- Diagnostic Tool APIs
- Custom Response Page APIs
- DNS Record APIs
- Content Identifier APIs
- Old Version APIs
- Version Management APIs
- Common Guidelines
- FAQs
- Troubleshooting
- Tool Guide
- Speed Test Tools
- Diagnostic Tool
- Agreements
DocumentationTencent Cloud EdgeOneDomain Service&Origin ConfigurationHTTPS CertificateHTTPS ConfigurationEnabling HSTS
Enabling HSTS
Last updated: 2024-10-28 15:34:17
Overview
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a web security protocol promoted by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The protocol is used to instruct web browsers to access a site over the more secure HTTPS protocol. You can configure HSTS to improve the security and credibility of your website if you have any of the following needs: to prevent malicious attackers from stealing sensitive user information through man-in-the-middle attacks, to comply with data privacy protection regulations, or to enhance users' trust in your website.

When a client initiates a request to an EdgeOne node over HTTP, this HTTP request may still be intercepted or tampered even though forced HTTPS access is enabled.
To improve access security, HSTS can be used to force browsers to directly initiate HTTPS requests. When HSTS is enabled, EdgeOne adds the
Strict-Transport-Security header to HTTPS responses. The header tells browsers to send HTTPS requests in a specified period of time.Note:
1. The
Strict-Transport-Security header applies to only HTTPS requests. Therefore, we recommend that you configure forced HTTPS access before you enable HSTS. This ensures that a user's initial access request is made over HTTPS and the configuration takes effect.2. When the HSTS header is included in responses, browsers will alert users and intercept the access to the current site if a certificate security risk is detected. This further protects user data security.
Scenario 1: Enabling HSTS for All Domain Names
To enable HSTS for all domain names used to access the current site, refer to the following information.
Prerequisites
You have configured SSL certificates for all domain names used to access the current site as instructed in Certificate Configuration.
Directions
1. Log in to the EdgeOne console and click Site List in the left sidebar. In the site list, click the target Site.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global site configuration page. Then click HTTPS in the right sidebar.
3. On the HSTS configuration card, toggle on the Site-wide setting switch to configure HSTS.
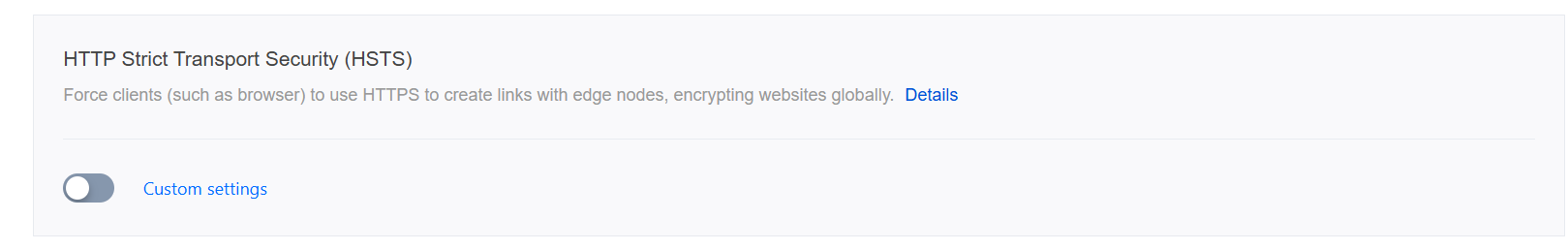
4. Configure the
Strict-Transport-Security header in the pop-up window.On/Off: Enable or disable HSTS.
Cache time: The value of the
max-age field, which can be set to an integer from 1 to 31536000.Contain subdomain name: When enabled, the
includeSubDomains instruction is contained.Preload: When enabled, the
preload instruction is contained.Scenario 2: Enabling HSTS for Specified Domain Names
To enable HSTS for specified domain names or differentiate the HSTS configuration for different domain names, refer to the following information.
Prerequisites
You have configured SSL certificates for the domain names for which you want to enable HSTS as instructed in Certificate Configuration.
Directions
1. Log in to the EdgeOne console and click Site List in the left sidebar. In the site list, click the target Site.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global site configuration page. Then click the Rule Engine tab.
3. On the rule engine management page, click Create rule and select Add blank rule.
4. On the page that appears, select HOST from Matching type and specify an operator and a value to match the requests of specified domain names.
5. From the Operation drop-down list, select HSTS. Then, configure the settings that appear.Then, click Switch.
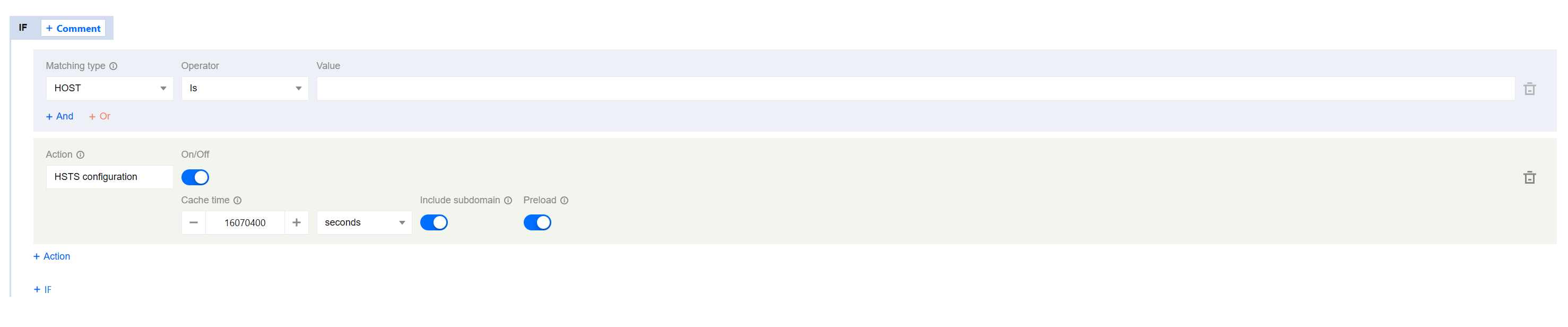
6. Click Save and publish.
More Information
The following table describes fields in the
Strict-Transport-Security header:Field | Description |
max-age=<expire-time> | The validity period of the HSTS header, measured in seconds. Within this period, browsers always send requests over HTTPS. |
includeSubDomains (optional) | Enable HSTS for the current domain name and all of its subdomain names. |
preload (optional) | Add the current domain name to the HSTS preload list of all major browsers. In this case, the browsers always send HTTPS requests to the domain name. Requirements: max-age is no less than 31536000 (one year).includeSubDomains is contained.preload is contained.You can view the HSTS preload list to check if the current domain name is in the browser's preload list. Major browsers regularly write the HSTS preload list into their version updates by hard coding. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No

