- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Application Performance Management
- Mobile App Performance Monitoring
- Real User Monitoring
- Cloud Automated Testing
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Grafana
- EventBridge
- Quick Start
- Cloud Product Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- CVM
- TKE
- Microservice
- Networking
- CBS
- TencentDB
- TencentDB for SQL Server Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for Redis Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MongoDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for PostgreSQL Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL-C for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for TcaplusDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MariaDB Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics (Legacy)
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- SCF
- CKafka
- TDMQ
- CLB
- COS
- CFS
- CPM
- ECM
- CDN And EdgeOne
- Direct Connect
- GAAP
- CMQ
- Elasticsearch
- WAF
- CLS
- Data Analysis
- Operation Guide
- CVM Agents
- CM Connection to Grafana
- Troubleshooting
- Practical Tutorial
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- Application Performance Management
- Product Introduction
- Access Guide
- Operation Guide
- Practical Tutorial
- Parameter Information
- FAQs
- Mobile App Performance Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Real User Monitoring
- Product Introduction
- Operation Guide
- Connection Guide
- FAQs
- Cloud Automated Testing
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Product Introduction
- Access Guide
- Scrape Configuration Description
- Custom Monitoring
- EMR Integration
- Java Application Integration
- Go Application Integration
- Exporter Integration
- Elasticsearch Exporter Integration
- Kafka Exporter Integration
- MongoDB Exporter Integration
- PostgreSQL Exporter Integration
- NGINX Exporter Integration
- Redis Exporter Integration
- Aerospike Exporter Integration
- MySQL Exporter Integration
- SQL Server Exporter Integration
- Oracle DB Exporter Integration
- Consul Exporter Integration
- Memcached Exporter Integration
- Apache Exporter Integration
- Integration with Other Exporters
- CVM Node Exporter
- Health Check
- Cloud Monitoring
- Non-Tencent Cloud Host Monitoring
- Read Cloud-Hosted Prometheus Instance Data via Remote Read
- Agent Self-Service Access
- Pushgateway Integration
- Instructions for Installing Components in the TKE Cluster
- Security Group Open Description
- Operation Guide
- Practical Tutorial
- Terraform
- FAQs
- Grafana
- Dashboard
- Alarm Management
- Console Operation Guide
- Alarm Policy
- Alarm Notification
- Alarm Receiving Channels and SMS Quota
- Alarm Types and Channels
- Receiving Alarm Notification Through SMS
- Receiving Alarm Notification Through Email
- Receiving Alarm Notifications through a WeCom Group
- Receiving Alarm Notification by Using a Slack Group
- Using PagerDuty to Receive Alarm Notifications
- Receiving Alarm Notifications Through a DingTalk Group
- Dynamic Threshold Alarm
- Silencing Alarm
- Viewing Alarm Records
- Product Policy Type and Dimension Information
- Configuring Alarm by Tag
- Access Management
- Console Operation Guide
- EventBridge
- FAQs
- Documentation Guide
- Related Agreements
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Alarm APIs
- DescribeAlarmPolicies
- DescribeAlarmMetrics
- DescribeAlarmHistories
- CreateAlarmPolicy
- DeleteAlarmPolicy
- DescribeAlarmPolicy
- ModifyAlarmPolicyStatus
- SetDefaultAlarmPolicy
- BindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingAllPolicyObject
- ModifyAlarmPolicyCondition
- ModifyAlarmPolicyNotice
- ModifyAlarmPolicyTasks
- DescribeMonitorTypes
- DescribeAllNamespaces
- DescribeAlarmEvents
- DescribeBindingPolicyObjectList
- ModifyAlarmPolicyInfo
- DescribeConditionsTemplateList
- Notification Template APIs
- Monitoring Data Query APIs
- Legacy Alert APIs
- Prometheus Service APIs
- CreatePrometheusAgent
- CreatePrometheusMultiTenantInstancePostPayMode
- CreatePrometheusScrapeJob
- CreateRecordingRule
- CreateServiceDiscovery
- DeleteAlertRules
- DeleteExporterIntegration
- DeletePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DeleteRecordingRules
- DescribeAlertRules
- DescribeExporterIntegrations
- DescribePrometheusAgents
- DescribePrometheusInstanceUsage
- DescribePrometheusInstances
- DescribePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DescribeRecordingRules
- DescribeServiceDiscovery
- DestroyPrometheusInstance
- GetPrometheusAgentManagementCommand
- ModifyPrometheusInstanceAttributes
- TerminatePrometheusInstances
- UnbindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- UninstallGrafanaDashboard
- UpdateAlertRule
- UpdateAlertRuleState
- UpdateExporterIntegration
- UpdatePrometheusAgentStatus
- UpdatePrometheusScrapeJob
- UpdateRecordingRule
- UpgradeGrafanaDashboard
- DescribePrometheusZones
- CreateAlertRule
- CreateExporterIntegration
- BindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- Grafana Service APIs
- UpgradeGrafanaInstance
- UpdateSSOAccount
- UpdateGrafanaWhiteList
- UpdateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- UpdateGrafanaIntegration
- UpdateGrafanaEnvironments
- UpdateGrafanaConfig
- UpdateDNSConfig
- UninstallGrafanaPlugins
- ResumeGrafanaInstance
- ModifyGrafanaInstance
- InstallPlugins
- EnableSSOCamCheck
- EnableGrafanaSSO
- EnableGrafanaInternet
- DescribeSSOAccount
- DescribeInstalledPlugins
- DescribeGrafanaWhiteList
- DescribeGrafanaNotificationChannels
- DescribeGrafanaIntegrations
- DescribeGrafanaInstances
- DescribeGrafanaEnvironments
- DescribeGrafanaConfig
- DescribeDNSConfig
- DeleteSSOAccount
- DeleteGrafanaNotificationChannel
- DeleteGrafanaIntegration
- DeleteGrafanaInstance
- CreateSSOAccount
- CreateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- CreateGrafanaIntegration
- CreateGrafanaInstance
- CleanGrafanaInstance
- DescribeGrafanaChannels
- Event Center APIs
- TencentCloud Managed Service for Prometheus APIs
- CreatePrometheusAlertPolicy
- CreatePrometheusGlobalNotification
- CreatePrometheusTemp
- DeletePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DeletePrometheusClusterAgent
- DeletePrometheusTemp
- DeletePrometheusTempSync
- DescribeClusterAgentCreatingProgress
- DescribePrometheusAgentInstances
- DescribePrometheusGlobalNotification
- DescribePrometheusInstanceDetail
- DescribePrometheusInstanceInitStatus
- DescribePrometheusTargetsTMP
- DescribePrometheusTempSync
- ModifyPrometheusAgentExternalLabels
- ModifyPrometheusAlertPolicy
- ModifyPrometheusGlobalNotification
- ModifyPrometheusTemp
- RunPrometheusInstance
- SyncPrometheusTemp
- CreatePrometheusClusterAgent
- DescribePrometheusClusterAgents
- DescribePrometheusGlobalConfig
- DescribePrometheusRecordRules
- DescribePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DescribePrometheusInstancesOverview
- DescribePrometheusTemp
- Monitoring APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- Glossary
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Application Performance Management
- Mobile App Performance Monitoring
- Real User Monitoring
- Cloud Automated Testing
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Grafana
- EventBridge
- Quick Start
- Cloud Product Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- CVM
- TKE
- Microservice
- Networking
- CBS
- TencentDB
- TencentDB for SQL Server Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for Redis Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MongoDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for PostgreSQL Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL-C for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for TcaplusDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MariaDB Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics (Legacy)
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- SCF
- CKafka
- TDMQ
- CLB
- COS
- CFS
- CPM
- ECM
- CDN And EdgeOne
- Direct Connect
- GAAP
- CMQ
- Elasticsearch
- WAF
- CLS
- Data Analysis
- Operation Guide
- CVM Agents
- CM Connection to Grafana
- Troubleshooting
- Practical Tutorial
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- Application Performance Management
- Product Introduction
- Access Guide
- Operation Guide
- Practical Tutorial
- Parameter Information
- FAQs
- Mobile App Performance Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Real User Monitoring
- Product Introduction
- Operation Guide
- Connection Guide
- FAQs
- Cloud Automated Testing
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Product Introduction
- Access Guide
- Scrape Configuration Description
- Custom Monitoring
- EMR Integration
- Java Application Integration
- Go Application Integration
- Exporter Integration
- Elasticsearch Exporter Integration
- Kafka Exporter Integration
- MongoDB Exporter Integration
- PostgreSQL Exporter Integration
- NGINX Exporter Integration
- Redis Exporter Integration
- Aerospike Exporter Integration
- MySQL Exporter Integration
- SQL Server Exporter Integration
- Oracle DB Exporter Integration
- Consul Exporter Integration
- Memcached Exporter Integration
- Apache Exporter Integration
- Integration with Other Exporters
- CVM Node Exporter
- Health Check
- Cloud Monitoring
- Non-Tencent Cloud Host Monitoring
- Read Cloud-Hosted Prometheus Instance Data via Remote Read
- Agent Self-Service Access
- Pushgateway Integration
- Instructions for Installing Components in the TKE Cluster
- Security Group Open Description
- Operation Guide
- Practical Tutorial
- Terraform
- FAQs
- Grafana
- Dashboard
- Alarm Management
- Console Operation Guide
- Alarm Policy
- Alarm Notification
- Alarm Receiving Channels and SMS Quota
- Alarm Types and Channels
- Receiving Alarm Notification Through SMS
- Receiving Alarm Notification Through Email
- Receiving Alarm Notifications through a WeCom Group
- Receiving Alarm Notification by Using a Slack Group
- Using PagerDuty to Receive Alarm Notifications
- Receiving Alarm Notifications Through a DingTalk Group
- Dynamic Threshold Alarm
- Silencing Alarm
- Viewing Alarm Records
- Product Policy Type and Dimension Information
- Configuring Alarm by Tag
- Access Management
- Console Operation Guide
- EventBridge
- FAQs
- Documentation Guide
- Related Agreements
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Alarm APIs
- DescribeAlarmPolicies
- DescribeAlarmMetrics
- DescribeAlarmHistories
- CreateAlarmPolicy
- DeleteAlarmPolicy
- DescribeAlarmPolicy
- ModifyAlarmPolicyStatus
- SetDefaultAlarmPolicy
- BindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingAllPolicyObject
- ModifyAlarmPolicyCondition
- ModifyAlarmPolicyNotice
- ModifyAlarmPolicyTasks
- DescribeMonitorTypes
- DescribeAllNamespaces
- DescribeAlarmEvents
- DescribeBindingPolicyObjectList
- ModifyAlarmPolicyInfo
- DescribeConditionsTemplateList
- Notification Template APIs
- Monitoring Data Query APIs
- Legacy Alert APIs
- Prometheus Service APIs
- CreatePrometheusAgent
- CreatePrometheusMultiTenantInstancePostPayMode
- CreatePrometheusScrapeJob
- CreateRecordingRule
- CreateServiceDiscovery
- DeleteAlertRules
- DeleteExporterIntegration
- DeletePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DeleteRecordingRules
- DescribeAlertRules
- DescribeExporterIntegrations
- DescribePrometheusAgents
- DescribePrometheusInstanceUsage
- DescribePrometheusInstances
- DescribePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DescribeRecordingRules
- DescribeServiceDiscovery
- DestroyPrometheusInstance
- GetPrometheusAgentManagementCommand
- ModifyPrometheusInstanceAttributes
- TerminatePrometheusInstances
- UnbindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- UninstallGrafanaDashboard
- UpdateAlertRule
- UpdateAlertRuleState
- UpdateExporterIntegration
- UpdatePrometheusAgentStatus
- UpdatePrometheusScrapeJob
- UpdateRecordingRule
- UpgradeGrafanaDashboard
- DescribePrometheusZones
- CreateAlertRule
- CreateExporterIntegration
- BindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- Grafana Service APIs
- UpgradeGrafanaInstance
- UpdateSSOAccount
- UpdateGrafanaWhiteList
- UpdateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- UpdateGrafanaIntegration
- UpdateGrafanaEnvironments
- UpdateGrafanaConfig
- UpdateDNSConfig
- UninstallGrafanaPlugins
- ResumeGrafanaInstance
- ModifyGrafanaInstance
- InstallPlugins
- EnableSSOCamCheck
- EnableGrafanaSSO
- EnableGrafanaInternet
- DescribeSSOAccount
- DescribeInstalledPlugins
- DescribeGrafanaWhiteList
- DescribeGrafanaNotificationChannels
- DescribeGrafanaIntegrations
- DescribeGrafanaInstances
- DescribeGrafanaEnvironments
- DescribeGrafanaConfig
- DescribeDNSConfig
- DeleteSSOAccount
- DeleteGrafanaNotificationChannel
- DeleteGrafanaIntegration
- DeleteGrafanaInstance
- CreateSSOAccount
- CreateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- CreateGrafanaIntegration
- CreateGrafanaInstance
- CleanGrafanaInstance
- DescribeGrafanaChannels
- Event Center APIs
- TencentCloud Managed Service for Prometheus APIs
- CreatePrometheusAlertPolicy
- CreatePrometheusGlobalNotification
- CreatePrometheusTemp
- DeletePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DeletePrometheusClusterAgent
- DeletePrometheusTemp
- DeletePrometheusTempSync
- DescribeClusterAgentCreatingProgress
- DescribePrometheusAgentInstances
- DescribePrometheusGlobalNotification
- DescribePrometheusInstanceDetail
- DescribePrometheusInstanceInitStatus
- DescribePrometheusTargetsTMP
- DescribePrometheusTempSync
- ModifyPrometheusAgentExternalLabels
- ModifyPrometheusAlertPolicy
- ModifyPrometheusGlobalNotification
- ModifyPrometheusTemp
- RunPrometheusInstance
- SyncPrometheusTemp
- CreatePrometheusClusterAgent
- DescribePrometheusClusterAgents
- DescribePrometheusGlobalConfig
- DescribePrometheusRecordRules
- DescribePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DescribePrometheusInstancesOverview
- DescribePrometheusTemp
- Monitoring APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- Glossary
Configuring Data Conversion
Last updated: 2024-11-01 20:59:36
Overview
In addition to basic event filtering, EventBridge provides simple data processing capabilities. After you pass in data and configuration items to EventBridge, EventBridge formats the data and distributes the structured data obtained after processing to downstream targets, creating a bridge between data sources and data processing systems.
Directions
Creating a rule
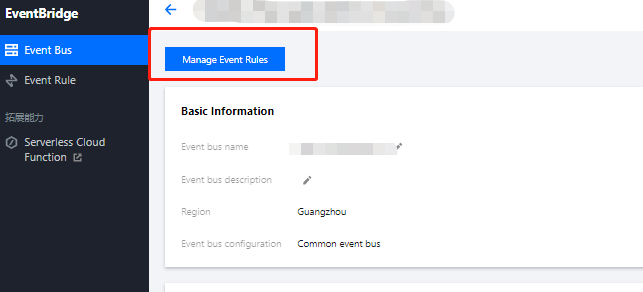
1. Log in to the EventBridge console and select a specified event bus.
2. On the event bus details page, click Manage Event Rules and configure a new rule as shown below:

3. Go to the Event Rule page and click Create Event Rule.
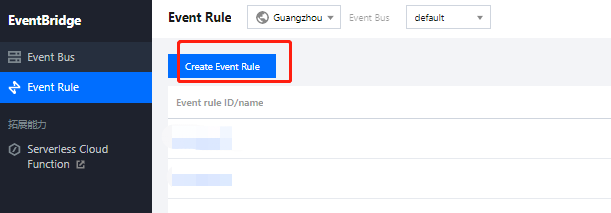

4. Enter the basic task information as instructed and select Enable data conversion.
5. Click Next and set the data conversion rule.
Rule pattern: Select Template data or Custom.
Parsing mode: Select JSON.
6. After selecting a parsing mode, click OK to start data parsing.
7. After data parsing is completed, set the filtering rule and data processing mode.
Note:
Currently, the output format is JSON.
Filter: Only data that meets the configured filter rule is output. The filter supports the following matching modes: Prefix match, Suffix match, Inclusion match (contains), Exclusion match (except), Data matching, and IP matching.
Data processing: Valid values of
TYPE are Default, Preset, Mapping, Custom.TYPE = Default:
VALUE is mapped based on the parsing result and cannot be modified.TYPE = Preset: You can select a system preset value for
VALUE. Currently, DATE (timestamp) is supported.TYPE = Mapping: You can select an existing key. The final output value of
VALUE is mapped by the specified key.TYPE = Custom: You can enter a custom value for
VALUE.8. Click Test to check the test result.
9. Click Next to complete data target binding.
Editing a rule
On the Event Rule Details page, click Edit in the upper-right corner of the Data conversion module to modify a data processing rule. You can also add or delete a data processing rule on the page.
Filter rule description
The filter allows you to configure filtering rules such as field sizes to filter data. Only data that meets the specified rules will be retained.
Notes
Filter matching is exact matching down to the character and case-sensitive. During matching, no standardized operations will be performed on strings.
Values to be matched must be in JSON format, which include strings and numeric values enclosed in quotation marks as well as keywords not enclosed in quotation marks (
true, false, and null).Prefix match
You can perform key value matching by comparing a specified prefix with the prefix in data.
For example, for data
{"password":"topicname"}, you can specify top as the prefix of the password value so that {"password":"topicname"} can be normally matched.Suffix match
You can perform key value matching by comparing a specified suffix with the suffix in data.
For example, for data
{"password":"topicname"}, you can specify name as the suffix of the password value so that {"password":"topicname"} can be normally matched.Inclusion match
You can specify a field to be included in data as a match condition.
For example, for data
{"password":"topicname"}, you can specify na to be included in the password value so that {"password":"topicname"} can be normally matched.Exclusion match
You can specify a field to be excluded from data as a match condition.
For example, for data
{"password":"topicname"}, you can specify topicname to be excluded from the password value so that {"password":"topicname"} cannot be normally matched.Numeric match
You can specify the value or value range of a certain field as a match condition.
For example, for data
{ "numeric": 10}, you can specify the value of numeric to be less than 15 (<15) as a match condition so that { "numeric": 10} can be normally matched.The following are examples of value match rules:
Greater than 10: Enter `>10`
Greater than or equal to 10: Enter `>=10`
Greater than or equal to 10, and less than or equal to 20: Enter `>=10&<=20`
Greater than or equal to 10, or less than or equal to 5: Enter `>=10|<=5`
IP match
You can specify an IP in CIDR notation as a match condition. For example, you can enter
1.2.3.4/24 to match IPs whose leading 24 bits start with "1.2.3.".
 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?