Tencent Cloud Observability Platform
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Application Performance Management
- Pay-as-you-go (Postpaid)
- Packages (Prepaid)
- Mobile App Performance Monitoring
- Real User Monitoring
- Cloud Automated Testing
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Pay-as-You-Go (Postpaid)
- Quick Start
- EventBridge
- Cloud Product Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- Microservice
- Networking
- TencentDB
- TencentDB for Redis Monitoring Metrics
- CPM
- CDN And EdgeOne
- Operation Guide
- Cloud Monitoring Overview
- Monitoring View
- CM Connection to Grafana
- Troubleshooting
- Application Performance Management
- Access Guide
- Accessing Go Application
- Accessing Java Application
- Accessing Python Application
- Accessing Node.js Application
- Accessing PHP Application
- Accessing .NET Application
- Operation Guide
- Resource Management
- Application Monitoring
- Application Diagnosis
- Database Call Monitoring
- Access Management
- Alarm Service
- System Configuration
- Associate Logs
- Inject TraceID Into Logs
- Practical Tutorial
- Parameter Information
- APM Data Protocol Standard
- Mobile App Performance Monitoring
- Access Guide
- Android Use Cases
- iOS Use Cases
- Tencent Cloud Real User Monitoring
- Operation Guide
- Application Management
- Access Management
- Resource Tag
- Connection Guide
- Web Use Cases
- Cloud Automated Testing
- Operation Guide
- Creating Test Task
- Testing Statistics
- Access Management
- References
- Testing Nodes
- FAQs
- Performance Testing Service
- Operation Guide
- Performance Testing in Script Mode
- Script Examples
- HTTP-based Performance Testing
- Performance Testing in JMeter Mode
- Project Management
- Scenario Management
- Advanced Configuration
- Export Stress Test Indicators
- Traffic Recording
- Performance Testing Report
- Access Control
- Alarm Management
- Tag Management
- Practice Tutorial
- JavaScript API List
- pts/http
- Response
- pts/dataset
- pts/grpc
- pts/jsonpath
- pts/redis
- pts/url
- URL
- pts/util
- pts/ws
- pts/socketio
- socketio
- pts/socket
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Product Introduction
- Access Guide
- EMR Integration
- Java Application Integration
- Exporter Integration
- Operation Guide
- Instance
- Recording Rule
- Alerting Rule
- Access Control
- TKE Metrics
- Practical Tutorial
- Terraform
- Grafana
- Operation Guide
- Instance
- Tencent Cloud Service Integration
- Plugin Management
- Dashboard
- Operation Guide
- Configuring Dashboard
- Monitoring Charts
- Creating Chart
- Use Cases of Different Chart Types
- Alarm Management
- Console Operation Guide
- Alarm Policy
- Configuring alert trigger conditions
- Alarm Notification
- Alarm Callback
- Alarm Receiving Channels and SMS Quota
- Dynamic Threshold Alarm
- Silencing Alarm
- EventBridge
- Product Introduction
- Practical Tutorial
- Migrating Event Alarm
- FAQs
- Related Agreements
- API Documentation
- Making API Requests
- Monitoring Data Query APIs
- Alarm APIs
- Notification Template APIs
- Legacy Alert APIs
- Prometheus Service APIs
- Grafana Service APIs
- Event Center APIs
- TencentCloud Managed Service for Prometheus APIs
- Monitoring APIs
DocumentationTencent Cloud Observability PlatformEventBridgePractical TutorialAutomatic Backup and Restart of Exceptional CVM Instance
Automatic Backup and Restart of Exceptional CVM Instance
Last updated: 2024-11-01 21:03:49
Automatic Backup and Restart of Exceptional CVM Instance
Last updated: 2024-11-01 21:03:49
Overview
A monitoring and alarming system is indispensable for a business production environment. Complete monitoring, prompt alarming, and automated alarm handling can help you quickly locate and fix problems to reduce possible economic losses.
Tencent Cloud EventBridge is a secure, stable, and efficient serverless event management platform. EventBridge in Event Center can receive real-time events and relevant data streams from your applications, SaaS services, and Tencent Cloud services. By integrating notification message and SCF, it can send alarm messages in real time and automatically handle alarms.
This document uses a server exception as an example to describe how to implement real-time alarm message push and automatic snapshot-based disk rollback with the aid of EventBridge and SCF after your CVM instances generate alarm events. In this way, you can quickly build an automated OPS architecture.
Architecture Design
The overall architecture is as shown below. When a CVM instance triggers an exception alarm, CVM will automatically generate an alarm event and actively push it to EventBridge. After the alarm is filtered by the alarm rules bound to EventBridge, the alarm message will be pushed to users promptly through the specified notification channels, and SCF will be triggered at the same time to call an API to quickly roll back the disk based on snapshot, so as to recover the business in time.
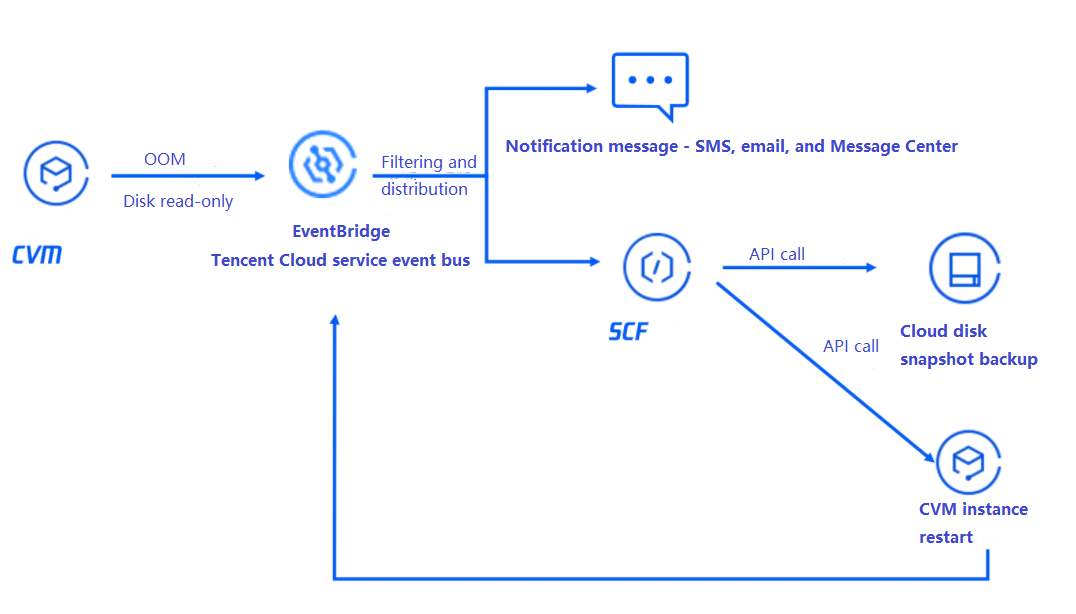

The basic process is as follows:An instance generates an alarm event > The event is filtered by the EventBridge rules > The event is delivered to notification message and SCF > SCF calls an API to back up the disk data and restart the instance > The alarm event is pushed to users after the restart.
Directions
Step 1. Create a function to implement the snapshot creation and restart logic
1. Log in to the SCF console.
2. Create a function as instructed in Creating Event-Triggered Function in Console.
3. Write the code logic of calling the API. Below is the sample code:
exports.main_handler = async (event, context) => {// Depends on tencentcloud-sdk-nodejs version 4.0.3 or higherconst tencentcloud = require("tencentcloud-sdk-nodejs");const CvmClient = tencentcloud.cvm.v20170312.Client;const CbsClient = tencentcloud.cbs.v20170312.Client;var secretId = process.env.secretId // Pass in `secretId` of your account to the environment variablevar secretKey = process.env.secretKey // Pass in `secretKey` of your account to the environment variablevar insID = event.subjectconst clientConfig1 = {credential: {secretId: secretId,secretKey: secretKey,},region: "ap-guangzhou",profile: {httpProfile: {endpoint: "cvm.tencentcloudapi.com",},},};const client1 = new CvmClient(clientConfig1);const params1 = {"InstanceIds": [${Replace it with the ID of the instance to be restarted}],"StopType": "SOFT"};client1.RebootInstances(params1).then((data) => {console.log(data);},(err) => {console.error("error", err);});const clientConfig2 = {credential: {secretId: secretId,secretKey: secretKey,},region: "ap-guangzhou",profile: {httpProfile: {endpoint: "cbs.tencentcloudapi.com",},},};const client2 = new CbsClient(clientConfig2);const params2 = {"DiskId": ${Replace it with the ID of the disk to be backed up}};client2.CreateSnapshot(params2).then((data) => {console.log(data);},(err) => {console.error("error", err);});};
Step 2. Create en event rule and filter alarm events
1. Log in to the EventBridge console.
2. Select Tencent Cloud service event bus > default in Event Bus.
3. In the details of the default event bus, click Manage Event Rules.
4. In Event Rule, click Create Event Rule to create rules to filter and convert events.
4.1 Taking the CVM disk is read-only event as an example, create rules as follows:
Rule 1: receive the disk read-only exception events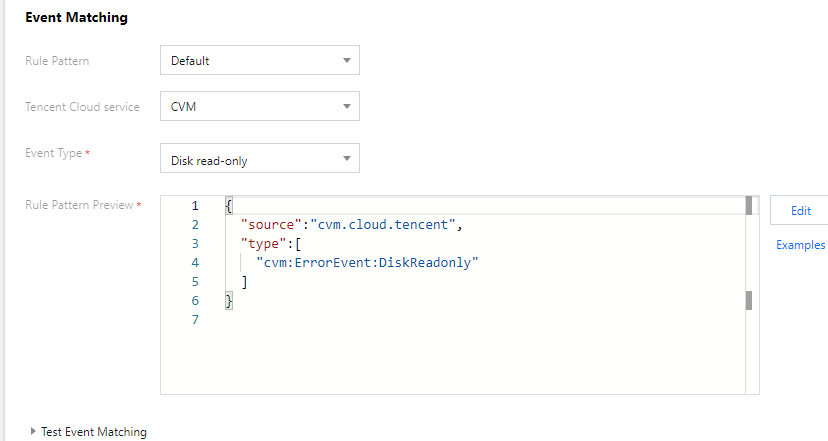

Rule 2: receive instance restart events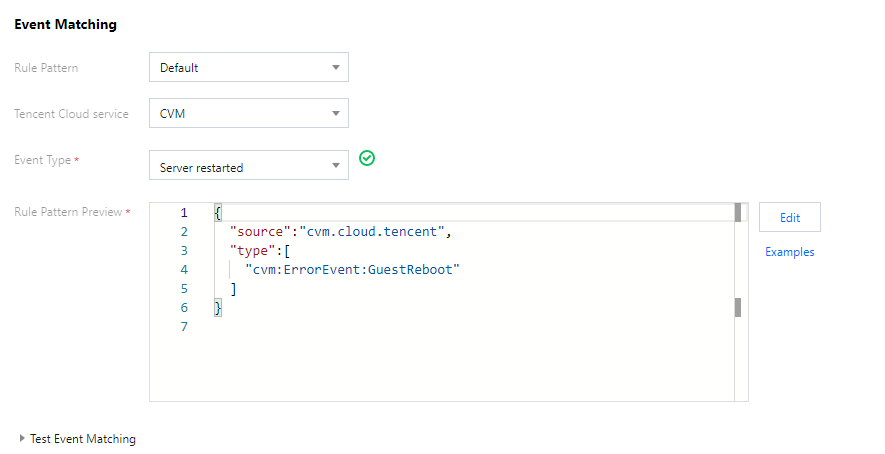

4.2 You can also customize the event rules based on your actual needs as follows:
Filter all CVM events in the Guangzhou region.
{"source":"cvm.cloud.tencent","region":"ap-guangzhou"}
Filter CVM events with the specified instance ID.
{"source":"cvm.cloud.tencent","subject":["ins-xxxxxx","ins-xxxxxx"]}
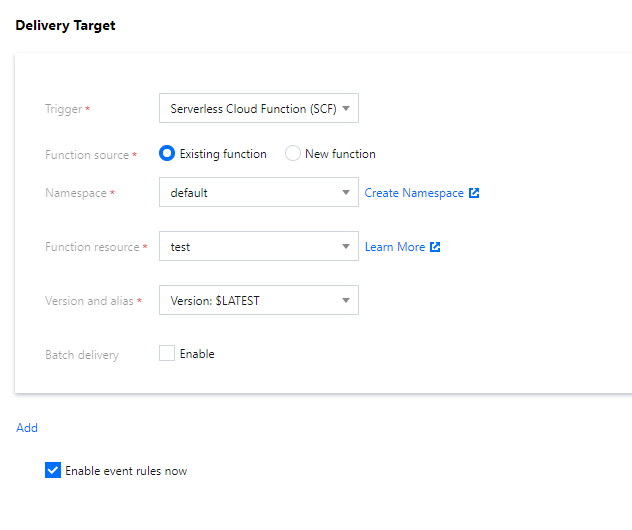
Step 3. Bind event targets and backend processing logic and set the push target
After creating rules, you can bind delivery targets to the rules as prompted. The above demo is used as an example here:
For rule 1, you need to bind two targets: notification message and SCF.
Select a method to receive alarm messages.
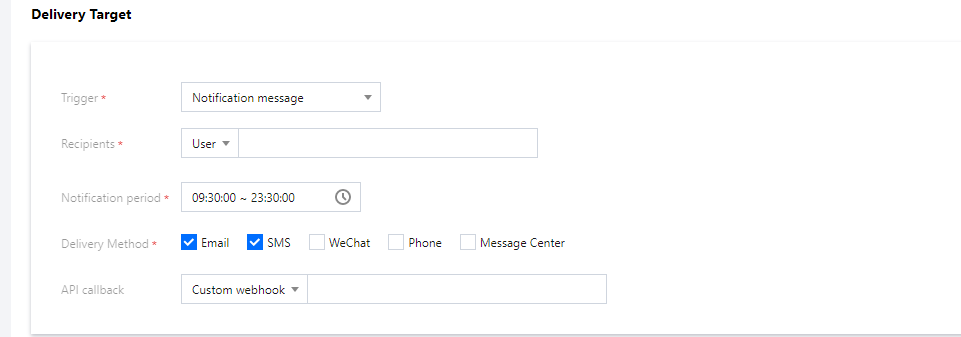

For rule 2, you only need to bind the notification message target.

Step 4. Send a simulated event to check whether the process works normally
At this point, you have built the automated alarm processing link. You can use a simulated alarm event to test whether the process can run normally:
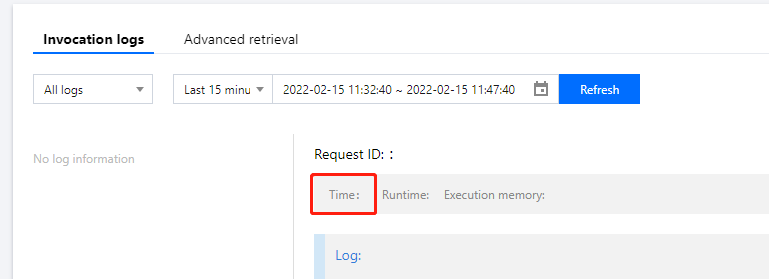
Successful function invocation:

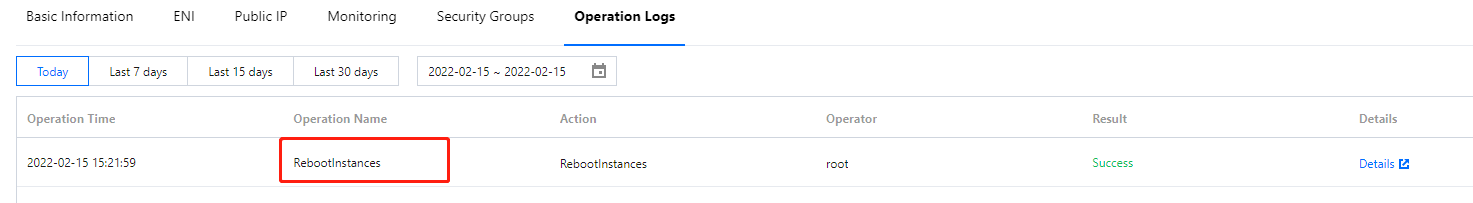
Instance restart:

Snapshot creation:
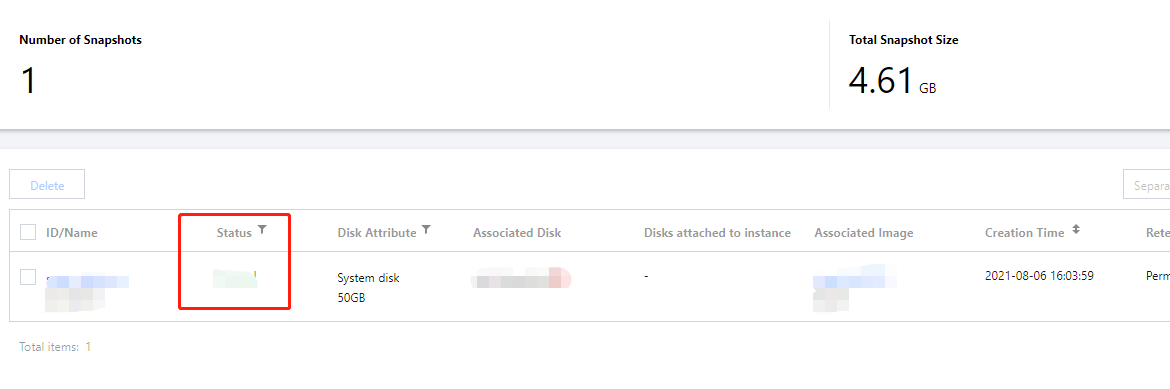

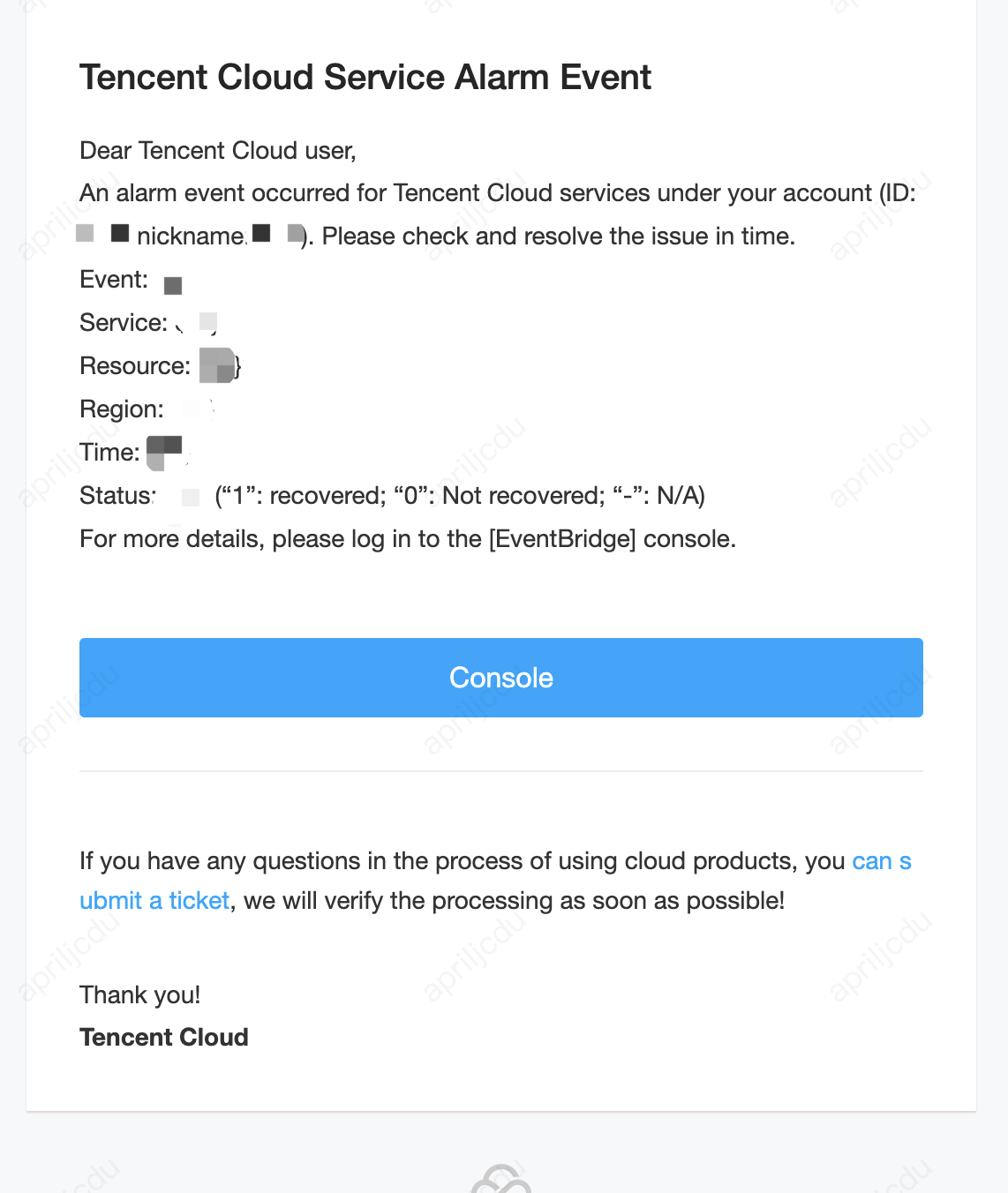
Alarm message receipt:

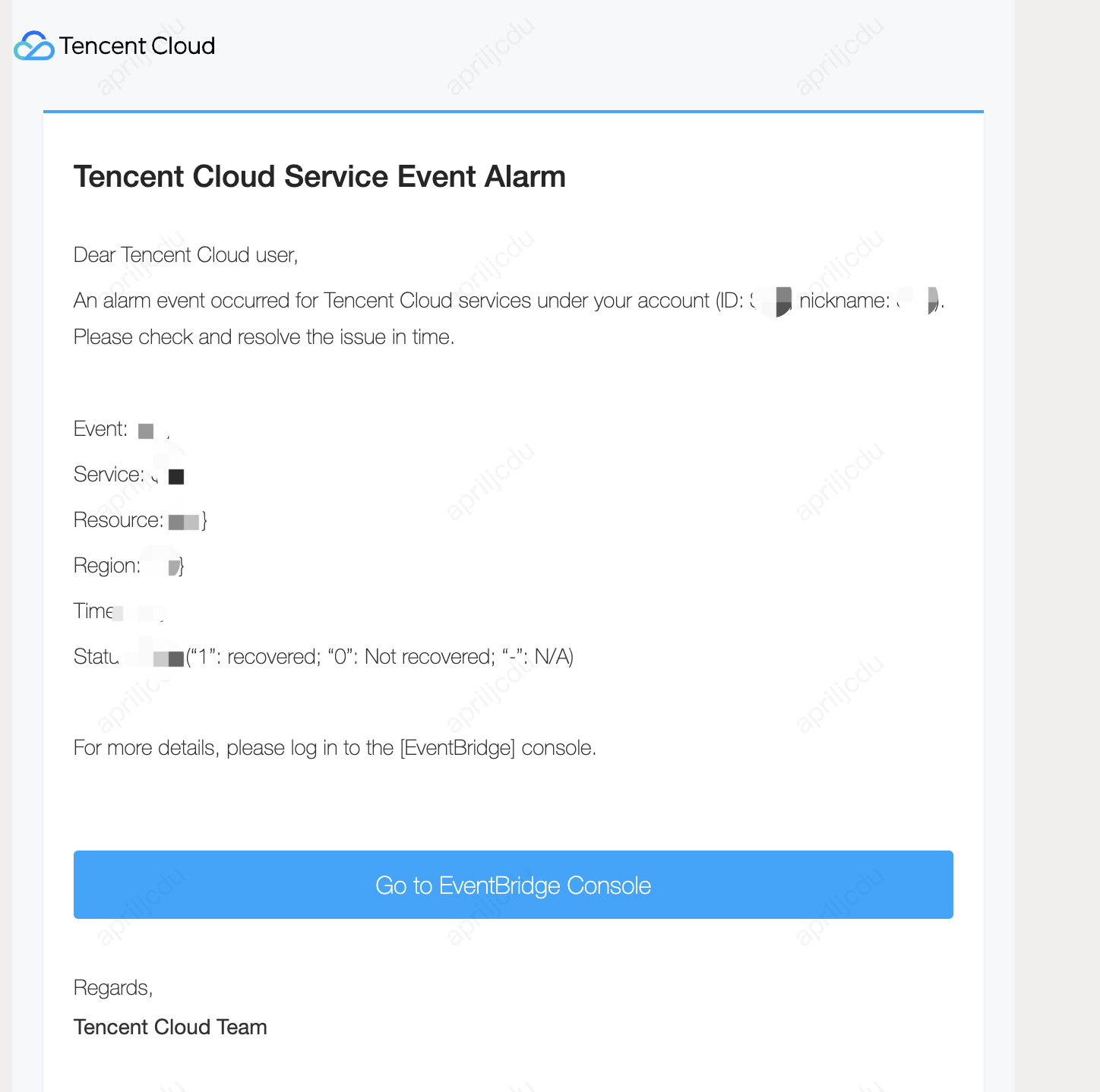
Restart email receipt:

Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No