如何防止视频流量和存储空间被盗用
最后更新时间:2021-05-21 11:16:34
UGC(用户生产内容)和 PGC(专业生产内容)是视频行业中常见的两类场景,可以由视频分享者自由上传和分享视频内容。
然而,第三方的视频平台,可能会冒充 App 的普通用户,上传自有视频,然后将视频的播放 URL 放在自己的平台上播放。这样,他们就能“寄生”于开发者的平台,享受“免费”的视频存储和加速播放。因为开发者的视频平台被当做了他人视频的温床,我们称之为“视频床”。
寄生者产生的所有存储和播放带宽流量上的费用,全部需要 App 开发者来承担,是一项严重的经济损失。
视频床问题产生的原因
UGC 和 PGC 平台的一般交互方式
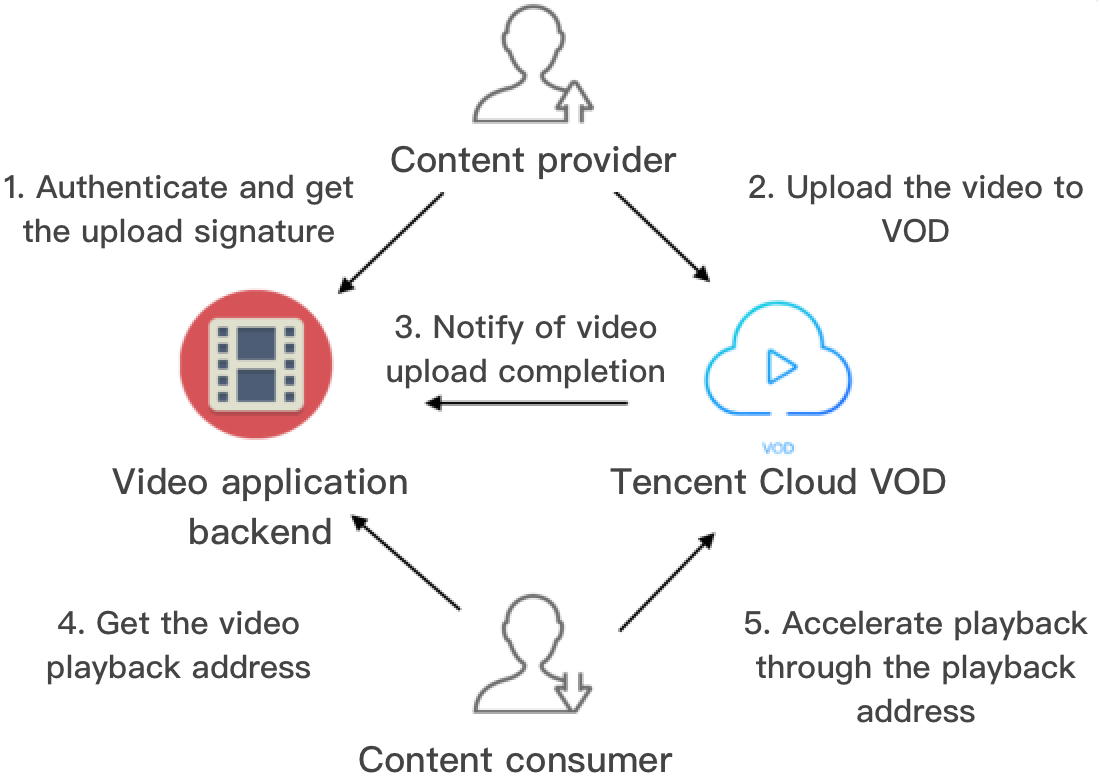

说明:
图中箭头方向是指网络请求方向。
1. App 后台对内容提供方进行鉴权,鉴权通过后派发视频上传签名。
2. 内容提供方执行上传,把分享的内容上传到云点播。
3. 云点播将成功上传的视频 fileId 及播放 URL 等相关信息通知到 App 后台。
4. 内容消费方向 App 后台请求视频的播放 URL。
5. 内容消费方通过播放 URL,从云点播加速播放视频。
恶意用户如何实现视频床
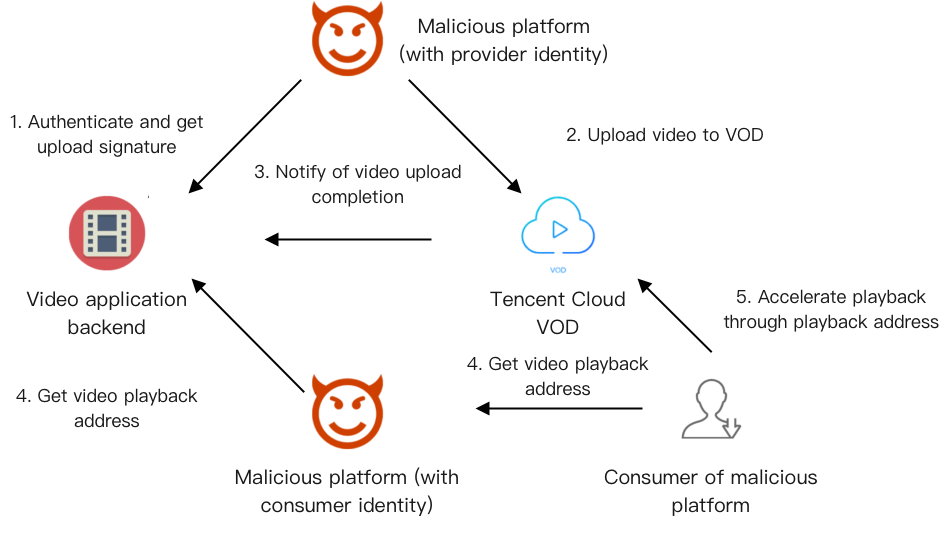

说明:
图中箭头方向是指网络请求方向。
恶意的第三方视频平台,会冒充开发者 App 平台的普通用户:
首先,以视频提供方的身份,将自有视频上传到云点播中(第1步和第2步)。
然后,再以消费者的身份,从 App 平台获取视频的播放地址(第4步)。
最后,恶意平台自己的用户,可以获取到这些播放地址(第4步),并通过云点播加速播放这些视频(第5步)。
导致问题的核心原因
恶意用户寻找猎物作为视频床的根本目的,是盗用他人的 CDN 带宽资源(附带也占用了存储资源)。恶意用户有机可乘的核心原因在于:
第4步:恶意平台能无限制地从 App 快速获取视频的播放 URL,存储并分发给自己的消费用户。
第5步:恶意平台的消费用户获取视频的播放 URL 后,能够无限制地加速播放视频。
视频床防范方案
面对视频床问题以上的核心原因,关键在于:
防止第4步中的无限制获取视频播放 URL。
防止第5步中的无限制加速播放视频。
下面,将分别介绍如何限制视频 URL 的播放和获取。
限制视频 URL 的播放
为了实现对视频播放 URL 的控制,开发者需要在控制台开启防盗链,并且在第4步中,App 后台需要按照 Key 防盗链生成规则(参考“视频播放地址最多可播放 IP 数”的 示例)生成防盗链,限制 URL 的有效时间和允许播放的 IP 数。
限制视频 URL 的获取
若仅限制视频的加速播放,视频床的防范是不完整的:在第4步中,恶意平台能对同一视频请求大量不同的防盗链 URL,然后为自己平台的用户分发各不相同的 URL,绕开 IP 播放数量的限制。
因此,App 后台需要识别第4步中的用户身份,对同一用户在指定时间内获取某一视频播放 URL 的次数进行频控,防止恶意用户短时间内获取视频的大量播放地址。
文档反馈

